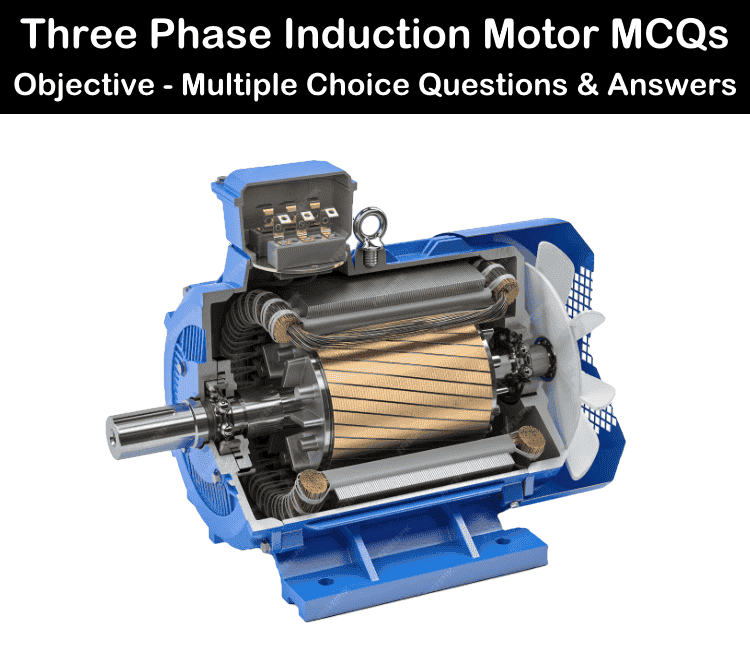
3-Phase Induction Motors – Objective Multiple Choice Questions with Explanatory Answers
1. The induction motor is also known as ________.
- Asynchronous motor
- Synchronous motor
- DC motor
- Servo motor
Explanation: Rotor never reaches synchronous speed.
Show Explanatory Answer
2. If the frequency of 3-phase supply to the stator of 3-phase induction motor is increased, then synchronous speed is ________?
- Increased
- Decreased
- Remain unchanged
- None of the above
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: As we know that; f = (NSP) / 120
It is clear that f ∝ NS i.e., frequency (f) is directly proportional to the Synchronous speed (NS).
In more clear words, when frequency increases, Speed also increases.
3. The rotating magnetic field in a three-phase induction motor is produced by ________.
- Rotor current
- Stator current
- Exciter
- Permanent magnets
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: The 3-phase AC supply to stator windings produces a rotating magnetic field that induces current in the rotor.
4. The speed of a three-phase induction motor depends on ________.
- Rotor resistance
- Stator voltage
- Supply frequency and number of poles
- Rotor reactance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Synchronous speed
NS = 120f / P
5. Slip in an induction motor is defined as ________.
- Difference between rotor and stator current
- Ratio of rotor speed to synchronous speed
- Difference between synchronous and rotor speed divided by synchronous speed
- Ratio of stator to rotor voltage
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Slip = s = (NS − Nr) / NS
6. At synchronous speed, the slip of an induction motor is ________.
- 0
- 1
- Between 0 and 1
- Infinity
Explanation: At synchronous speed, Nr = 0, hence s = 1
Show Explanatory Answer
7. At no-load, the slip of an induction motor is typically ________.
- 0.1 to 0.5
- 0.001 to 0.03
- 0.2 to 0.4
- 1
Explanation: At light load, slip is very small but non-zero.
Show Explanatory Answer
8. The rotor frequency in an induction motor is given by ________.
- Supply frequency
- Slip × Supply frequency
- Rotor speed / Supply frequency
- Constant always
Explanation: Rotor frequency = fr = s⋅f
Show Explanatory Answer
9. If slip is zero, the rotor induced EMF is ________.
- Maximum
- Zero
- Equal to supply voltage
- Infinite
Explanation: Induced EMF depends on relative speed; if slip = 0, no relative motion exists.
Show Explanatory Answer
10. The torque produced in an induction motor is proportional to ________.
- Slip
- Square of slip
- Frequency
- Synchronous speed
Explanation: At small slips, torque T ∝ s
Show Explanatory Answer
11. Maximum torque of an induction motor occurs when ________.
- Slip = 0
- Rotor resistance = Rotor reactance
- Rotor resistance = Stator resistance
- Slip = 1
Explanation: From torque equation, maximum torque when R2 = sX2.
Show Explanatory Answer
12. Which part of a squirrel cage induction motor resembles a “rotating transformer”?
- Stator
- Rotor
- Shaft
- Bearings
Explanation: Rotor bars act as secondary of a transformer.
Show Explanatory Answer
13. The starting current of a squirrel cage induction motor is ________.
- 1 to 2 times full-load current
- 5 to 7 times full-load current
- Equal to full-load current
- Zero
Explanation: No back EMF at standstill; hence high inrush current.
Show Explanatory Answer
14. In slip ring induction motors, external resistance is added to ________.
- Stator winding
- Rotor winding
- Shaft
- Air gap
Explanation: Improves starting torque and reduces starting current.
Show Explanatory Answer
15. The power transferred across the air gap is called ________.
- Input power
- Rotor copper loss
- Air-gap power
- Mechanical power
Explanation: Power crossing the air gap is called air-gap power.
Show Explanatory Answer
16. Mechanical power developed in rotor = ________.
- Air-gap power – Rotor copper loss
- Air-gap power + Stator copper loss
- Rotor copper loss only
- None
Explanation: Pm = Pg − Pcu.
Show Explanatory Answer
17. If supply frequency increases, synchronous speed ________.
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains constant
- Becomes zero
Explanation: Ns ∝ f.
Show Explanatory Answer
18. Which of the following is NOT a starting method for squirrel cage induction motors?
- Direct-on-line (DOL)
- Star-delta starter
- Rotor resistance starter
- Autotransformer starter
Explanation: Rotor resistance starter is used for slip-ring motors.
Show Explanatory Answer
19. The efficiency of a three-phase induction motor is generally ________.
- 40–50%
- 60–70%
- 85–95%
- 99%
Explanation: Good efficiency, typically above 85%.
Show Explanatory Answer
20. The relation between rotor copper loss and slip is ________.
- Rotor copper loss = s × Rotor input
- Rotor copper loss = (1 – s) × Rotor input
- Rotor copper loss = s × Mechanical power
- None
Explanation: Pcu = sp⋅g
Show Explanatory Answer
21. At full load, slip is usually ________.
- 0–1%
- 2–6%
- 10–15%
- 50%
Explanation: For normal induction motors, slip is 2–6% at full load.
Show Explanatory Answer
22. The torque-speed characteristic of an induction motor is ________.
- Linear
- Parabolic
- Non-linear
- Constant
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Torque vs. speed curve is non-linear with maximum torque at a certain slip.
23. If rotor resistance is increased, the maximum torque ________.
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains same
- Becomes infinite
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Maximum torque is independent of rotor resistance, but slip at which it occurs changes.
24.The no-load current of an induction motor is about ________.
- 1–2% of full-load current
- 5–10% of full-load current
- 25–40% of full-load current
- 50–60% of full-load current
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Magnetizing current is large compared to transformers, typically 25–40%.
25. Which losses are present in the rotor at standstill?
- Only copper losses
- Only core losses
- Copper + core losses
- Mechanical losses
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: At standstill, rotor frequency = supply frequency → high core + copper losses.
26. The starting torque of a squirrel cage induction motor is usually ________.
- High
- Low
- Zero
- Infinite
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Rotor resistance is low; hence poor starting torque.
27. The crawling phenomenon in induction motor occurs due to ________.
- Rotor resistance
- Harmonics in supply
- Improper rotor design
- Supply voltage unbalance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: 7th harmonics create torque dips causing crawling at about 1/7th speed.
28. Cogging in induction motor is ________.
- Running at high speed
- Running at synchronous speed
- Failure to start due to magnetic locking
- Sudden stalling
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Cogging is magnetic locking between stator and rotor teeth at standstill.
29. Which rotor has better starting torque?
- Squirrel cage
- Slip ring
- Permanent magnet rotor
- Salient pole rotor
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Resistance can be added externally to improve starting torque.
30. The torque under blocked rotor test is proportional to ________.
- Supply voltage
- Square of supply voltage
- Slip
- Resistance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Torque T ∝ V2 at standstill.
31. Rotor copper loss is maximum when slip is ________.
- 0
- 0.5
- 1
- Between 0 – 1
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: At standstill, all air-gap power is lost in rotor resistance.
32. Which of the following is not a part of induction motor losses?
- Stator copper loss
- Rotor copper loss
- Stray losses
- Commutation losses
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Induction motors don’t have commutators.
33. The frequency of rotor current at standstill is ________.
- Zero
- Equal to supply frequency
- Half of supply frequency
- Twice supply frequency
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: At standstill, slip = 1 → fr = f.
34. When the motor is running close to synchronous speed, rotor frequency is: ________.
- Zero
- High
- Very low
- Equal to stator frequency
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Slip is very small near synchronous speed → rotor frequency also small.
35. Double cage induction motor is designed to improve ________.
- Speed regulation
- Efficiency
- Starting torque
- Power factor
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Outer cage provides high resistance → improved starting torque.
36. Which starting method gives the lowest starting current for squirrel cage motors?
- DOL starter
- Star-delta starter
- Autotransformer starter
- None
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: It reduces supply voltage, lowering starting current.
37. Slip at maximum torque is directly proportional to ________.
- Stator resistance
- Rotor resistance
- Synchronous speed
- Stator leakage reactance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: smax = (R2 / X2).
38. For constant torque load, the motor draws ________.
- Same current at all speeds
- More current at lower speeds
- More current at higher speeds
- Zero current
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: To maintain torque, current must increase as speed drops.
39. The induction motor operates in braking region when ________.
- Slip is positive and < 1
- Slip > 1
- Slip is negative
- Slip = 0
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Negative slip → regenerative braking.
40. The rotor bars of a squirrel cage motor are usually made of ________.
- Copper or aluminum
- Brass
- Steel
- Silver
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Copper or aluminum is used for conductivity and cost effectiveness.
41. The stator winding of a 3-phase induction motor is similar to ________.
- Armature of DC machine
- Primary of transformer
- Rotor winding
- Exciter
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Stator acts like primary of a transformer.
42. Which factor mainly decides synchronous speed?
- Supply voltage
- Frequency and poles
- Stator current
- Rotor resistance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: NS = 120f / P.
43. If supply frequency is halved, the synchronous speed will ________.
- Remain constant
- Be halved
- Double
- Zero
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Speed directly proportional to frequency.
44. The main reason for using laminated cores in stator is ________.
- Reduce copper losses
- Reduce eddy current losses
- Reduce hysteresis losses
- Increase efficiency
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Laminations increase resistance to eddy currents.
45. The type of bearing mostly used in induction motors is ________.
- Thrust bearing
- Ball/roller bearing
- Magnetic bearing
- Hydrostatic bearing
Explanation: Ball or roller bearings are standard.
Show Explanatory Answer
46. Induction motor torque decreases if ________.
- Supply voltage decreases
- Supply voltage increases
- Frequency decreases
- Poles increase
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: T ∝ V2.
47. The induced emf in the rotor is due to ________.
- Direct supply
- Relative speed between rotor and RMF
- External excitation
- Residual magnetism
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Rotor emf is induced by relative motion with RMF.
48. If number of poles increases, synchronous speed ________.
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains constant
- Becomes zero
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: NS ∝ 1/P
49. The main advantage of squirrel cage motor is ________.
- High starting torque
- Simple and rugged construction
- Variable speed operation
- Easy to add external resistance
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: It is maintenance-free, robust, and cheap.
50. The ratio of starting torque to full load torque is highest in ________.
- Squirrel cage motor
- Slip ring motor
- Double cage motor
- Star-delta starting
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: Outer cage provides high resistance at start → better torque.
51. Which of the following applications use slip-ring induction motors?
- Ceiling fans
- Pumps
- Cranes and hoists
- Mixers
Show Explanatory Answer
Explanation: They need high starting torque, which slip-ring motors provide.
 Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle?
Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle? Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V?
Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V? Difference Between Rated Current and Nominal Current
Difference Between Rated Current and Nominal Current Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors?
Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors? Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage?
Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage? How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?
How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?