Why is a Single-Phase Motor Not Self-Starting?
Necessity of Capacitors in 1-Phase Motors
A capacitor is required for a single-phase motor to provide the necessary phase shift to start the motor and to improve its running efficiency. In a 1-phase motor, the starting torque is essential to overcome the initial inertia and bring the motor to its operating speed.
Capacitors are used in single-phase motors to create a phase difference between the currents in the start and run windings. This phase difference creates a rotating magnetic field, which is necessary for starting torque and running the motor. That’s why a capacitor is necessary for a 1-phase motor.
Additionally, capacitors help overcome voltage fluctuations in the power supply and improve the power factor of the motor, which means it uses electrical power more efficiently. This is particularly important in applications where power efficiency is crucial, such as in industrial or commercial settings.
- Related Post: Why is the Synchronous Motor Not Self Starting?
Why is a Single-Phase Motor Not Self-Starting?
A single-phase motor is not self-starting because it lacks a rotating magnetic field during startup. In a three-phase induction motor, the three phases create a rotating magnetic field that causes the rotor to turn. However, in a single-phase induction motor, there is only one phase, so there is no rotating magnetic field to start the rotor turning.
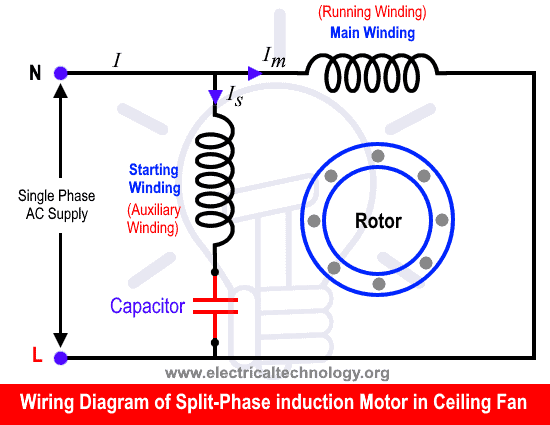
To overcome this limitation, 1-Φ motors use methods to create a rotating magnetic field during startup. One common method is to use and connect a capacitor in series with the starting winding to create a phase shift, which effectively creates a second phase. This additional phase shift creates a rotating magnetic field and produces the starting torque, allowing the motor to start and run.
- Related Post: What is the Role of Capacitor in a Ceiling Fan?
What happens if there is no Capacitor in a 1-Φ Motor?
A capacitor start motor will not run without a rated capacitor connected in series with the starting winding because the capacitor is needed to create the necessary phase shift to start the motor. The capacitor plays a crucial role in single-phase motors by creating a phase shift in the current, which is necessary for starting and running the motor.
If there is no capacitor in a 1-Φ motor, it will not be able to start or run efficiently. For example, if a ceiling fan 1-phase motor without a capacitor is connected to a single-phase supply (120V, 230V, or 240V), both the starting and running windings are connected in parallel to the power supply. Therefore, there will be only one revolving flux and two rotating torques in clockwise and counterclockwise directions. Both torques will cancel each other after a half cycle (according to the double field revolving theory), resulting in a zero resultant rotating magnetic field, and the motor will not start to rotate.
Without a capacitor, the motor will lack the necessary phase shift to create a rotating magnetic field. As a result, the motor will either not start at all or will start slowly and with reduced torque. This can cause the motor to overheat and eventually fail.
- Related Post: How to Replace a Ceiling Fan Capacitor – 3 Ways
Why Do We Need a Capacitor to Run a 1-Phase Motors?
Single-phase motors are widely used in various applications due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. These electric motors are commonly found in household appliances, pumps, ceiling fans, and many other devices. One critical component that plays a crucial role in the operation of single-phase motors is the capacitor. In this article, we will explore the reasons why a capacitor is required for a 1-Φ motor to function effectively.
We need to install a capacitor in a single-phase motor due to the essential role of capacitors in 1-phase motors, as follows:
Starting Torque:
One of the primary reasons a capacitor is required in a single-phase motor is to improve the starting torque. Unlike three-phase motors that have a rotating magnetic field, 1-phase motors rely on the creation of a secondary magnetic field to start rotating. The capacitor helps create this secondary field, which significantly enhances the starting torque of the motor.
Phase Shift:
Another crucial function of the capacitor in a single-phase motor is to create a phase shift between the start and run windings. This phase shift is essential for generating a rotating magnetic field within the motor, allowing it to start and run smoothly. Without the capacitor, the motor may experience difficulties starting or may not start at all.
Improved Efficiency:
Capacitors help improve the efficiency of single-phase motors by reducing power factor losses. By correcting the phase angle between the current and voltage, capacitors ensure that the motor operates at its optimal efficiency, thereby reducing energy consumption and lowering operating costs.
Motor Size and Cost:
Capacitors enable single-phase motors to be smaller and more cost-effective compared to their three-phase counterparts. The use of capacitors allows manufacturers to design compact and affordable motors suitable for a wide range of applications.
Reduced Starting Current:
Capacitors help reduce the starting current drawn by 1-phase motors. This is particularly important in applications where a high starting current could lead to voltage drops or other electrical issues. By limiting the starting current, capacitors help protect the motor and the electrical system.
Good to Know:
When a capacitor is connected in series with the starting winding of a single-phase motor, the following occurs:
- The current leads by 45° from the voltage (or the voltage lags 45 degrees behind the current) in the starting winding due to inductance.
- The current lags 45° behind the voltage (or the voltage leads by 45 degrees from the current) in the running winding due to capacitance.
Related Posts:
- What is the Role of Capacitor in AC and DC Circuit?
- Why Do We Need to Install a Starter with a Motor?
- Why Do DC Motors Have Higher Starting Torque than AC Motors?
- How to Run a Three-Phase Induction Motor on a Single-Phase Power Supply?
- Why is a Motor Rated in kW instead of kVA?
- Why Does A Capacitor Block DC But Pass AC?
- What Happens if We Connect a Polar Capacitor the Wrong Way?

 Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle?
Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle? Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V?
Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V? Difference Between Rated Current and Nominal Current
Difference Between Rated Current and Nominal Current Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors?
Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors? Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage?
Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage? How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?
How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?