Why Can’t AC Be Stored in Batteries Like DC?
Batteries are electrochemical devices that store energy in the form of direct current (DC). In DC, the polarity of the terminals remains constant i.e. one terminal is always positive (+) and the other is always negative (−). This matches how a battery naturally works e.g. storing and delivering energy in a fixed direction.
Right to the question, we cannot store AC in batteries because AC continuously changes its polarity i.e. 50 times per second at 50 Hz, or 60 times per second at 60 Hz. This means the battery terminals would need to alternate between positive (+) and negative (−) at the same frequency. However, a battery cannot switch its polarity back and forth at such high speeds, which is why AC cannot be stored directly in batteries.
Furthermore, if a battery is connected directly to an AC supply, it would charge during the positive half cycle and discharge during the negative half cycle. Since the positive half cycle cancels out the negative half cycle, the average voltage or current over one complete cycle becomes zero. Therefore, there is no possibility of storing AC in a battery.
To store AC, it must first be converted into DC using a rectifier (like in chargers and power supplies), and then the battery can store the converted DC energy.
- Related Post: Why Can’t a 12V Car Battery Electrocute You?
Good to Know: Average Voltage x Average Current ≠ Average Power.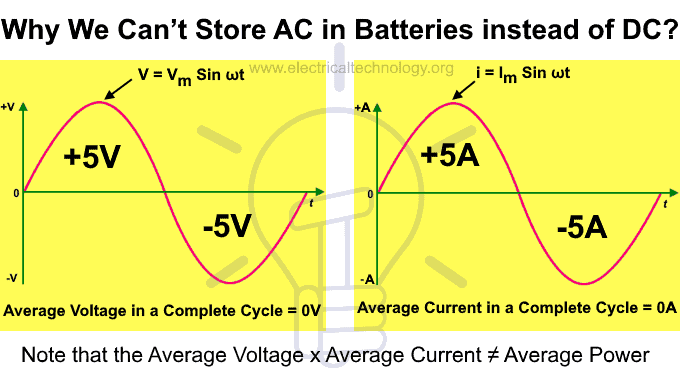
Related Posts:
- Why is a Battery Rated in Ah (Ampere hour), Not in VA?
- What Happens if a Battery is Connected to the AC Supply?
- What Happens to the Battery with Reverse Polarity Wiring Connection
- What Happens When an AC Line Touches a DC Line?
- Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
- AC or DC – Which One is More Dangerous And Why ?
- Why Do Electronic Circuits Use DC Current instead of AC?
- Is It Dangerous to Carry a Battery in an Elevator?
- How to Calculate the Right Size Battery?
 Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle?
Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle? Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V?
Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V? Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors?
Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors? Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage?
Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage? How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?
How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings? Why is AC Commonly Used in Households Instead of DC?
Why is AC Commonly Used in Households Instead of DC?