How to Calculate Electricity Charges – Electric Bill Calculator + Solved Examples
Calculating electricity bills and tariffs is generally straightforward for electrical engineering students, electricians and professionals. However, it can be confusing for non-technical individuals and layman persons who are trying to understand the charges mentioned in the electric bill from their electricity service providers.
Below is a simple example and step-by-step calculation of a electrical utility bill. By following this tutorial, you will be able to calculate your power bill with ease. Additionally, we’ve included a handy electrical energy and electricity bill calculator to simplify the process of estimating your power consumption and costs.

Example:
Suppose a consumer uses a 1000-watt load for 1 hour per day over the course of one month. Calculate the total electricity bill if the per-unit rate is 9 (in $, £, €, INR, Rs, DHR, Riyal, etc.). [Assume 1 month = 30 days].
Solution:
1 Unit = 1kWh.
Therefore, the total kWh = 1000 Watts × 24 Hrs. × 30 Days = 720000 … Watts / hour.
We want to convert it into electric units, where 1 Unit = 1kWh.
Hence, the total consumed units by user: = 720000 / 1000 … (k = kilo =1000).
Total Consumed Units = 720 kWh.
As the cost of per unit electricity is 9.
Therefore, the total cost of electricity bill = 720 units × 9 = 6480. (In $, £, €, ¥, INR “₹”, Rs, Peso, AED “Dirham”, SAR “Riyal” etc. or any other currency).
Note: If the unit cost of electricity is in cents or pennies (¢), pence or peso (p), etc., simply divide the overall cost by 100 to get the amount in USD ($), Pounds (£), or any other currency, etc.
That’s it. You have Done :)
Where is the Confusion?
A common question arises: why do we multiply the total consumed watts by 24, even though the daily usage is already specified? It’s important to clarify that the given rate is not a daily rate, but rather a per-unit electricity cost, where 1 unit = 1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) (also known as 1 B.T.U (Board of Trade Unit) in some regions).
For example, if you turn on a 1000-watt (1 kW) bulb for 1 hour, you consume 1 kWh, which equals 1 unit of electricity. If the rate per unit is 16.66¢, then the electricity cost for operating that bulb for one hour would be 16.66¢. So, 1000 watts × 1 hour = 1 kWh = 1 unit, and the bill would be calculated accordingly.
If the same light bulb remains ON for 24 hours, and the electricity rate is 16.66¢/kWh, the service provider will charge you ≈ $4.
Good to know: 1 Board of Trade Unit = 1 B.O.T Unit = 1kWh = 1000Wh = 36 x105 … Joule or Watt-seconds = 3.6 MJ
Electricity Bill Calculator
Electric Utility Bill Calculation
Calculation of Electric Energy Consumption
The following formula is used for electrical energy consumption.
E = P × t … (Wh)
E = P × t ÷ 1000 … (kWh)
Consumed Energy = Energy Used in Watts × Time in Hours
Where:
- E = Electrical Energy (Consumed in kWh)
- P = Power in Watts
- t = Time in hours per day
Wh (Watt-hour) is a small unit, so we divide the consumed energy on 1000 to get the value of energy in kWh instead of Wh.
- Example: Consumed energy = 2kW × 5 Hours = 10kWh
Related Post: Electric Energy Cost Calculator – Cost of Energy Calculation
Calculation of Cost of Electricity and Bill Estimation
The following formula can be used as electric bill estimator per hour in dollars or other local currency.
Cost of electricity per hour = Consumed Energy in kWh x Cost of 1 Unit electricity
Cost Per Hour = kWh x Unit Price
E = P × t … (Wh)
E = P x t ÷ 1000 … (kWh)
Energy Cost = Energy Used in kWh × Time in Hours
- Example: Cost Per Hour = 5kWh × .50 Cents per unit = $2.5
Related Post: Energy and Power Consumption Calculator – kWh Calculator
Power Consumption of Typical Home Appliances in Watts
The following table shows the estimated value of wattage rating (in Watts) for different and common household devices, appliances and equipment.
| Electrical Appliance | Power Wattage in Watts “W” |
| Fan | 80 |
| LED Light Bulb | 25 |
| AC – Air Conditioner | 900 |
| Refrigerator | 250 |
| Electric Heater | 2000 |
| Water Heater | 4000 |
| Hair Dryer | 1500 |
| Clothes Dryer | 3000 |
| Clothes Iron | 1400 |
| Dishwasher | 1300 |
| Electric Kettle | 1700 |
| Toaster Oven | 1100 |
| Microwave Oven | 1000 |
| Desktop Computer | 150 |
| Laptop Computer | 100 |
| TV – Television | 120 |
| Stereo Receiver | 300 |
| Vacuum Cleaner | 1200 |
| Washing Machine | 1500 |
| Coffee Machine | 1000 |
| Blender | 500 |
| Water Pump | 800 |
| Sewing Machine | 100 |
| Thankless Water Heater | 15000 |
Isn’t it easy to calculate your electricity bill?
If you face any difficulties with your calculations or need additional information related to your specific electricity usage (whether for home, residential, or commercial purposes) feel free to ask in the comment section below. We’re here to help!
Related Posts:
- Breaker Calculator in Amps – How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation?
- How to Determine the Number of Lamps in the final Sub Circuit?
- How to Convert Capacitor Farads into kVAR & Vice Versa?
- How to Find the value of SMD Resistors?
- How to find the value of Burnt Resistor?
- How to Check a Capacitor with Digital Multimeter and Analog AVO Meter?
- How To Wire Single Phase energy meter?
- Wire & Cable Size Calculator in AWG
- Electrical Wire & Cable Size Calculator (Copper & Aluminum)
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
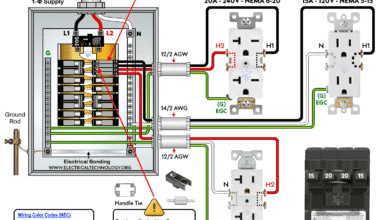 How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits
How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits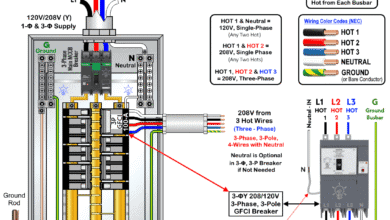 How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel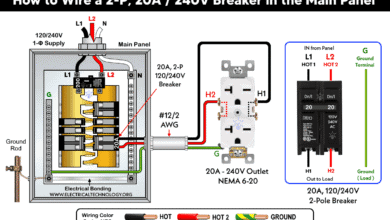 How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel