What is Electricity? Types, Sources & Generation of Electricity
Electricity – Sources, Generation, Transmission, Measurement, Parameters & Types of Electricity
The phenomenon associated with the presence and the flow of charge is called electricity. It is a source of energy used for powering our electrical machines and equipment. In this era of modern technology, almost everything has been automatized with some sort of tech inside it powered by electricity such as kids toys, various alarms, product manufacturing machines in industries and equipment used in hospitals etc.
What is Electricity & Charge?
The atom which is the basic building block of any material contains sub atomic particles. The three basic sub atomic particles are neutron, proton and electron. The neutron and proton exists in the central nucleus of the atom while the electron revolves around it in fixed orbits. The neutron as its name suggests is neutral i.e. it does not contain any charge. While, the proton and electron contains equal amount of charge but with opposite polarities.
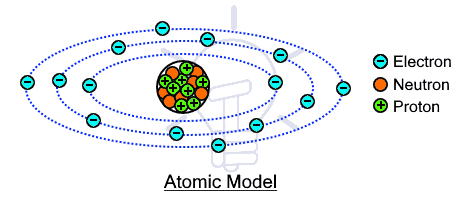
In a normal state, the total charge on an atom is zero because the number of electron & protons are equal & their equal amount of charges cancels each other. The protons are tightly bounded to the nucleus so they cannot move while the electrons that exist in the outer orbit called valence electrons are somewhat loosely bounded. They can be exited with enough energy to leave the orbit & flow out of the atom.
When the valence electrons are excited they release from the orbit thus leaving positive charge on the atom behind (since the negative charged electron is removed). Some elements such as metals contain loosely connected electrons called free electrons that require very low energy to move freely and the movement of such charges is called electricity.
- Related Post: Difference Between Electric Current and Electric Charge
Flow of Charge
As we have established before, the flow of charges is called electricity. But the charge could be positive or negative. We have discussed that the positive charge protons are tightly bounded to the nucleus so it never moves while the electrons can freely moves when enough energy is provided. Therefore we can say that electricity is the flow of electrons (the similarity between their names also gave it away).
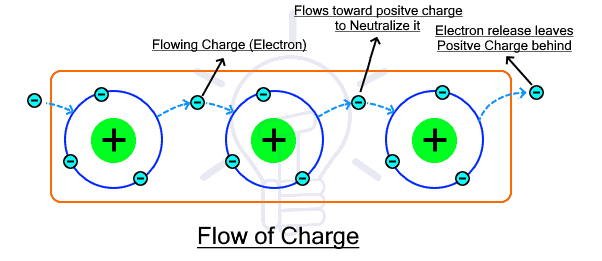
Suppose several atoms are placed in a line, if enough energy is provided, the electron leaves the last atom leaving positive charge behind. The electron from the adjacent atoms jumps & neutralizes the positive charge, leaving positive charge behind. So on until the last atom. It shows that during electricity, the both charges (i.e. positive & negative) flow. These two types of charge flow introduces two types of electricity.
Conventional Current: In earlier days, when electricity was discovered. The scientist believed that the electricity flows from high potential (Positive) to low potential (negative) i.e. it is the product of positive charge carriers. But they didn’t know about the two types of charges at the moment. They just guessed it, & proposed the fundamental electrical laws, rules & other equation based on it. There was a 50/50 chance, & they messed up.

Therefore, according to electron current, electricity is the flow of electron which is technically correct. But there were various laws, rules published using the direction of conventional current for devices such as diode etc.
The fact is that it does not matter which direction the current is flowing, as long as it is consistent, it does not make any difference. Therefore the conventional current is maintained as the standard direction of current flow.
Electrostatic Force
According to coulomb’s law there is an electrostatic force between two charges where the opposite charges attract & same charges repel each other. The force is inversely proportional to the distance between them.
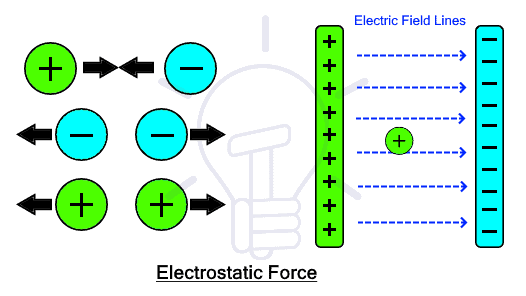
If we use a test positive charge & place it between two charged plates i.e. positively charged & negatively charged. There is an electric field existing between these two plates. The direction of this e-field is conventionally from positive charge towards negative charge. The test charge will experience a force of repulsion from positively charged plate & a force of attraction from negatively charged plate because of coulomb’s law. Therefore we can say that a positive charge moves from higher potential (positive charged plate) to lower potential (negative charge plate) in an electric field.
This idea is used in electricity where an electric potential is applied between two ends of a conductor & the current (which is charge) flows from the higher potential towards the lower potential.
Types of Electricity
There are two types of electricity i.e. static electricity & Current electricity. The static electricity is the accumulation of charge due to rubbing two objects together while the current electricity is the flow of electrical charges.
Static Electricity
The static electricity is the charge imbalance in an object or the charge buildup on the surface of the object. The charge builds up on the surface of the object which is then discharge through any electrical conductor or sometimes ionizes the isolator & discharge causing sparks. You may have experience that in a lightning storm.
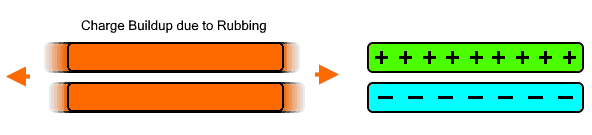
When the charged object come close to any other neutral object, it rearranges its positive & negative charges in such a way to generate a force of attraction between them. For example, a negative charged object will push away the positive charge & pulls in the negative charge on the surface of the neutral object. You may have done or heard about such experiment, rubbing balloon against your hairs.

The static electricity is formed inside the clouds. When its particles rub against each other it becomes oppositely charged & it separates. The charge ionizes the air between it & immediately discharges the electrons in the form of a visible sparks commonly known as lightening & thunder. Another example is balloon rubbing against our hair. The hair release electrons & the balloon gain electrons producing opposite charges. The balloon starts lifting your hair due to force of attraction between the charges when it comes near it.
Current Electricity
The current electricity is the flow of charge. We usually refer to this type of electricity when we are talking about electricity. Unlike static electricity which is due to stationary charges, the current electricity is due to the movement of the charges inside a conductor.
When an electric potential (from a battery) is applied to a piece of conductor, the electrons in the conductor are excited and moves through it. We usually use copper wire as a conductor that contains free electrons. The current electricity is measured using the rate of the flow of charges known as amperes. We normally consume this type of electricity in our homes, industries & the article down below explains everything about it.
Electrical Circuit
An electrical circuit is a complete loop of a conductor that provides a path for the flow of charge or current. It is very essential that the circuit should contain only conductors & there should be no insulators in it otherwise the electricity would not flow.
The electrical circuit can be a simple loop of conductor or having a combination of conductor & other components to do any useful work. Therefore we can classify circuits into two categories.
Short Circuit
When a simple loop of conductor is used as an electrical circuit & is power by connecting a power source to it, it is known as short circuit. The conductor directly connects both terminals of the power source & since conductors have negligible resistance, there is a huge amount of current flow through the power source.

However, we can use a short circuit in controlled manner to perform spot welding & solders etc. Also using a very low voltage signal (using multimeter), we can test the continuity of a conductor. It determines any breakage in the conductor while inside its plastic insulation.
Useful Circuit
It is made of multiple electrical & electronic components connected together using conductors to form a loop & perform any useful function.
A simple electrical circuit would be lighting a bulb. A bulb connected by a conductor with a power source forms an electrical circuit. Powering on the source will allow the current flow & turns on the bulb to illuminate its surrounding. The same process occurs is powering fans, heater.
Every electrical gadget or device has electrical circuit in them. Our homes appliances are connected using these simple electrical circuits. However, there are other circuits used for sound amplification (in loud speaker), charging phones, controlling machines & other more complex & logical circuits such as the one inside your smart phone & computer that can even compute complex mathematical equations. They all work on electricity.
Basic Parameters of Electricity
The electricity has three basic parameters i.e. the Volt, Ampere & Ohm. These electrical parameters are related to each other & expressed using Ohm’s Law.
V= IR
Volts = Ampere-Ohm
Where
- V = Voltage
- I = Current
- R = Resistance
Volt (Voltage or EMF)
The voltage or EMF (Electromotive force) is the pressure behind the electrons in an electrical circuit that causes it to move through it. The volt is a unit of voltage or EMF.
A one volt is the amount of voltage responsible for pushing one ampere of current through a circuit having resistance of one Ohm.
Ampere (Current)
The current is the flow of electrons in an electrical circuit. The electrons flow under the influence of the voltage between them. Ampere is the amount of electrons flowing in a unit time.
One ampere is the amount of current flowing in a circuit having resistance of one ohm when one volt of voltage is applied to it.
Ohm (Resistance)
The resistance in an electrical circuit is the property of any material to oppose the flow of current. The Ohm is the unit of resistance & it is denoted by Ω.
An electrical circuit is said to have a resistance of one ohm when a voltage of one volt moves one ampere of current through it.
Electrical Power & Measurement of Electricity
The Electrical power is the electrical energy transferred per unit time. In an electrical circuit, It is equal to the product of voltage & current.
Electrical Power = Voltage x Current
P = VI
Substituting I & V using Ohm’s law we also get;
P = I2R
P = V2/R
It is SI unit is Watt named after famous Scottish inventor James Watt who invented steam engine. The electrical power is also measured in Horse Power HP which is equal to 746 Watts.
We pay our bills based on the electrical energy we consume. The unit of energy is joule but the SI unit used for measurement of electrical energy is kWh (Kilo-Watt-Hour). One kWh is equal to 3600 kilo joules of energy. This is the standard unit used for billing of electrical energy around the world.
Generation of Electricity
The Electricity can be generated using any of the following methods;
Generator
The Electrical Generators are devices that convert kinetic energy into electrical energy. It is the most commonly used method for generation of electricity around the world.
The generators contain turbines that rotate using kinetic energy of any other source such as water in dam, steam, wind etc. Upon rotation of the turbine, the magnetic field & conductors interacts with each other & generates electricity.
The generators can be designed to generate alternating current (AC) or direct current (DC) depending on its design & requirement. We mostly use AC generators in our power plants due to its easier voltage conversion & transmission benefits.
This method is used in huge power generation plants that supply electricity to the whole cities in ranges of Megawatts of power.
Electrochemistry
Electrochemistry deals with relation between chemicals & electricity. In such method, the chemical energy inside chemicals is converted into electrical energy. The chemical reaction release electrons which can flow out through a metal electrode.
Metal electrodes are place inside a chemical called electrolyte. The chemicals react with the electrodes & exchange electrons that flow out through the electrodes into the electrical circuit thus generating electricity. This process can be reversed to store the same electrical charge inside the chemical.
Such method of electricity generation is used in batteries. Batteries can be of two types i.e. primary battery and secondary battery. The primary batteries are not rechargeable & it can’t be used once it’s fully discharged. It is also known as disposable batteries. While the secondary batteries are rechargeable & offer hundreds to thousands of recharging cycles. They are mostly used for backup power supply & in portable device such as smartphone & laptop etc.
The batteries are a portable source of DC electricity that powers every portable devices. The rechargeable batteries such as Li-ion is mostly used in cellphone & laptops while lead-acid batteries are used in vehicles & as a secondary power source in case of power failure.
Photovoltaic Effect
The conversion of light energy into electrical energy is called photovoltaic effect. In this process, the material generates electricity when it is exposed to light. A solar panel works on the same phenomenon using the sun as the source of light energy & converts it into electricity.
The solar panels contain small photovoltaic cells. Each photovoltaic cell is made of semiconductor material. The photon (light particle) hits & knocks off electrons from it that flows out through the circuit. These electrons flow in a single direction which is why solar panels generate DC electricity.
The DC supply can be easily converted into AC using Power inverter. We use multiple solar panels in remotes areas to generate electricity. It is also used as secondary power source in day-light for houses & businesses.
Sources of Electricity
Energy can neither be created nor destroyed; it can be changed from one form to another. According to law of conservation of energy we can converts any form of energy into electrical energy & energy exist in various forms. We use different energy sources to generate electricity based on the three electricity generation methods discussed above.
Following are some of the source of energy that can be used to generate electricity.
Natural Gas
The natural gas also called fossil gas is a combustible gas naturally available below earth surface. It is highly combustible gas. It is used to convert water into steam or the hot gases released during its combustions. The highly pressurized steam or gas is directed toward the turbine to rotate it & generate electricity.
Petroleum
The petroleum is also fuel just like natural gas. It is used to heat up water to generate steam. The steam is then used to rotate turbines of the generator to generate electricity.
Hydro Power
The kinetic energy of flowing water can also be used to turn turbines. The water is usually collected in a dam (an artificial barrier) used to elevate the water level. The water is release in a narrow pipe where turbine blades are installed. The water spins the blade of turbine connected to a generator to generate electricity. This electricity generated from water flow is called hydro power.
Nuclear Power
In nuclear power, nuclear fission process is used to generate electricity by using steam to rotate turbines. The nuclear fission is a process of splitting of nucleus of radioactive atoms such as uranium or plutonium.
In a nuclear reactor, the nucleus of uranium atom is bombarded with neutron which splits the nucleus releasing heat energy & neutrons. The neutrons strike other uranium atoms causing a chain reaction & a lot of heat energy. In controlled conditions, this heat energy can be utilized to heat up water to generate steam which is used to rotate turbine.
Geothermal Power
Geothermal power means the heat energy inside the earth. The temperature increase as we go down below the earth surface. We can utilize this heat energy to spin steam turbines.
About 2 miles deep wells are drilled on the surface of earth. The high temperature boils the water inside which is pumped out. As soon as it reaches the surface, it turns into steam due to the pressure drop. Huge turbines are installed in its path which utilizes its kinetic energy to rotate.
Solar Power
The sun is a natural source of light energy which can be converted into electricity using photovoltaic effect. Solar plants use hundreds to thousands of solar panel to generate electricity using the solar radiation.
Wind Power
The wind turbines are used to converts the wind kinetic energy into electricity. Huge wind farms that contains multiple wind turbines are installed offshore & on shores (in high windy areas) are used to supply electricity using the wind energy.
Biomass
Biomass is organic waste that comes from plants & animals such as animal wastes, agriculture waste, wood wastes & municipal solid waste etc. It contains energy stored inside which can be released in the form of heat during combustion.
Biomass energy is renewable energy & it is used as a fuel to run steam turbines to generate electricity.
Transmission of Electricity
Huge power generation plants are installed in remote areas to utilize some of the power sources given above. This generated power is transmitted over a long distances to the load centers (urban areas) like cities. Sometimes, the power is even transmitted between cities to meet the load demand. For more details, read the previous post about Electric Power System – Generation, Transmission & Distribution of Electricity.
The voltage level of the electricity must be very high in order to reduce the losses in the transmission line. Therefore, we either use HVAC (High voltage Alternating Current) or HVDC (High Voltage Direct Current) to transmit power over long distances.
- Related Post: Advantages of HVDC over HVAC Power Transmission
The AC voltage level can be easily converted from low to high & vice versa using transformer. The generators at the power plant generate AC whose voltage is increased using transformer. The Transformers are also used at the receiving end to step-down (decrease) the voltage level for domestic or commercial use. Transformers are cheap which can be used to tap the power lines at any point & decrease its voltage economically for use.
On the other hand, HVDC is a direct current whose voltage can be increased or decreased only using complex converters. These converters are very expensive. However, the DC voltage in a very high range (known as HVDC) has very low line losses, which is why; it is used for power transmission over very long distance. Since the HVDC converters are very expensive, we cannot use it at any point to tap power from HVDC line. it is only used for power transmission between two points over very long distance over 600 km.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Current and Voltage
- Which One Kills? Current or Voltage and Why? Amps vs Volts
- Why Do Electronic Circuits Use DC Current instead of AC?
- AC or DC – Which One is More Dangerous And Why ?
- Difference between AC and DC Transmission System
- Difference between AC and DC Resistance
- Flexible AC Transmission System – Types of FACTS Controllers & Devices








Thank you.