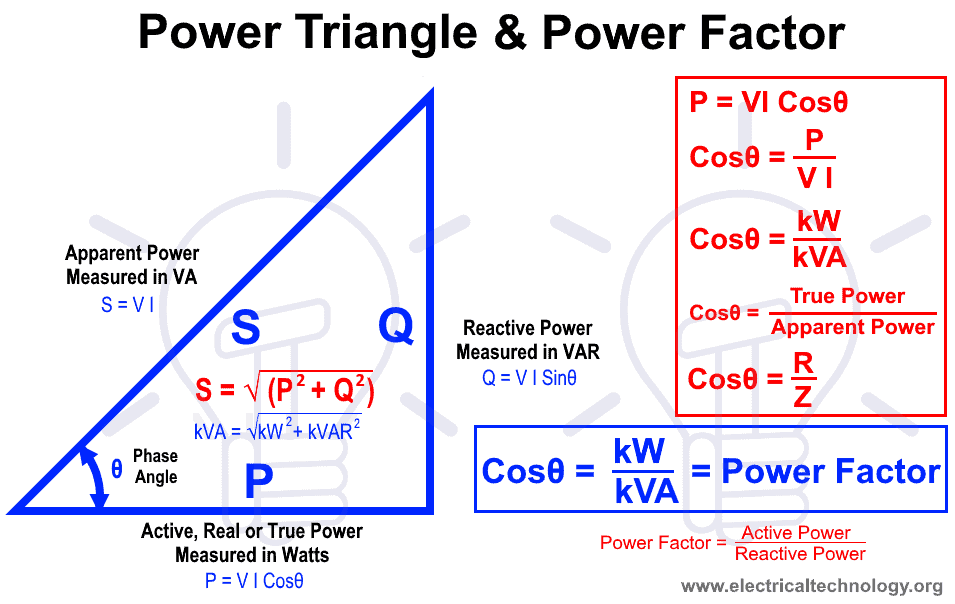
Power Factor Definitions and Formulas
In electrical engineering, power factor is only and only related to AC circuits i.e. there is no power factor (P.f) in DC circuits due to zero frequency and phase angle difference (Φ) between current and voltage.
What is Power Factor?
Power factor may be defined by three definitions and formals as follow.
- You may also read: Is Reactive Power Useful?
1). The Cosine of angle between Current and Voltage is called Power Factor.
- P = VI Cosθ OR
- Cosθ = P ÷ V I OR
- Cosθ = kW ÷ kVA OR
- Cosθ = True Power ÷ Apparent Power
Where:
- P = Power in Watts
- V = Voltages in Volts
- I = Current in Amperes
- W = Real Power in Watts
- VA = Apparent Power in Volt-Amperes or kVA
- Cosθ = Power factor
2). The ratio between Resistance and Impedance in AC Circuit is known as Power Factor.
Cosθ = R ÷ Z
Where:
- R = Resistance in Ohms (Ω)
- Z = Impedance (Resistance in AC circuits i.e. XL, XC and R known as Inductive reactance, capacitive reactance and resistance respectively) in Ohms (Ω)
- Cosθ = Power factor
Impedance “Z” is the total resistance of AC Circuit i.e.
Z = √ [R2 + (XL + XC)2]
Where:
- XL = 2πfL … L is inductance in Henry
- XC = 1 ÷ 2πfC … C is capacitance in Farads
Related Post: Difference Between Active and Reactive Power
3).The ratio between Active Power and Apparent Power in volts-amperes is called power factor.
- Cosθ = Active Power ÷ Apparent Power
- Cosθ = P ÷ S
- Cosθ = kW ÷ kVA
Where
- kW = P = Real Power in kilo-Watts
- kVA = S = Apparent Power in kilo-Volt-Amperes or Watts
- Cosθ = Power factor
Power Factor Formula in Three Phase AC Circuits
Power Factor Cosθ = P ÷ √3 VL × IL… Line Current & Voltage
Power Factor Cosθ = P ÷ √3 VP × IP… Phase Current & Voltage
Power Factor Triangle and Examples
Beer analogy of active or true power, reactive power, apparent power and power factor.
Chips bag analogy of true or real power, reactive power, apparent power and power factor.
Good to know:
In pure resistive circuit, power factor is unity (1) due to zero phase angle difference (Φ) between current and voltage.
In pure capacitive circuit, power factor is leading due to the lagging VARs. i.e. Voltage is lagging 90° behind the current. In other words, Current is leading 90° from voltage (Current and voltage are 90° out of phase with each others, where current is leading and voltage is lagging).
In pure inductive circuit, power factor is lagging due to the leading VARs i.e. Voltage is leading 90° from current. In other words, Current is lagging begging 90° behind the voltage (Current and voltage are 90° out of phase with each, others where voltage is leading and current is lagging).
Related Posts:
- Causes of Low Power Factor
- Disadvantages of Low Power Factor
- Advantages of Power factor improvement and Correction
- Power Factor improvement Methods with Their advantages & Disadvantages
- Active, Reactive, Apparent and Complex Power.
- Difference Between Active and Reactive Power – Watts vs VA
- How to Calculate the Suitable Capacitor Size in Farads & kVAR for PF Improvement
- How to Convert Capacitor Farads into kVAR & Vice Versa
- Capacitor banks – Characterless and Applications
- What is Electrical Power? Types of Electric Power and their Units
- kVAR to Farad Calculator – How to Convert kVAR to μ-Farads?
- μ-Farad to kVAR Calculator – How to Convert Farads to kVAR?
- Analysis of Reactive Power in Power System
- Is Reactive Power Useful? Importance of Reactive Power
- Introduction of Custom Power Devices For Power Quality Improvement
- What is Static VAR Compensator (SVC)? Construction, Working and Applicators

 Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle?
Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle? Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V?
Why Does the High Leg Measure 208V Instead of 120V? Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors?
Why are 1-Phase Motors Not Self-Starting Like 3-Phase Motors? Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage?
Why are High-Power Devices Not Designed to Run on DC Voltage? How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings?
How Do Some Devices Have Dual Input Voltage Ratings? Why is AC Commonly Used in Households Instead of DC?
Why is AC Commonly Used in Households Instead of DC?