Parallel Connection of Solar Panels and Batteries with Automatic UPS System – 12V Installation
The 12V system is the most common solar panel wiring configuration used with batteries for small load residential application. Typically, to achieve a 12V DC to 120V/230V AC system, both the photovoltaic (PV) panels and batteries are connected in parallel. This setup is widely used with a 12V solar charge controller and an automatic inverter/UPS to support AC loads (120–230V), battery charging, and direct DC loads such as DC-operated appliances.
Solar panels and batteries wiring configuration system are commonly used for 12V, 24V, 36V, and 48V variants. If you want to increase the system’s capacity (either to run the load for a longer time or to handle a higher load), you must wire the components in a parallel configuration.
For example, if a single 12V battery powers a ceiling fan for 6 hours, connecting a second identical battery in parallel will allow the fan to run for approximately 12 hours. Similarly, using two solar panels connected in parallel will result in faster battery charging and the ability to support more load.
This parallel wiring method is essential for 12V systems, including 12V charge controllers and inverters. Therefore, two or more solar panels and batteries (each rated at 12V DC) are connected in parallel to maintain system voltage while increasing current capacity.
Good to Know: Depending on the system requirements, multiple solar panels and batteries can also be wired in series, parallel, or series-parallel configurations to create 12V, 24V, 36V, or 48V DC systems.
We know that in a parallel connection, the voltage remains the same, while the current increases. In other words, currents are additive in a parallel configuration.
V1 = V2 = V3 … = Vn
IT = I1 + I2 + I3 … + In
This means that when solar panels or batteries are connected in parallel, the voltage level stays the same, but the current capacity increases. For batteries, this increase is measured in ampere-hours (Ah), and for solar panels, in amperes (A).
For example:
If you connect two solar panels or two batteries, each rated at 12V DC, 120W, and 10A, in parallel, the combined output will be:
- Voltage (V) = 12V (same as a single unit)
- Current (I) = 10A + 10A = 20A
- Power (P) = 12V × 20A = 240W
Similarly, for batteries, if each is rated at 12V, 100Ah, then two connected in parallel will result in:
- Voltage (V) = 12V
- Capacity (Ah) = 100Ah + 100Ah = 200Ah
It shows that the voltage level is same for both solar panels and batteries while the ampere hour (Ah) capacity of batteries is increased when connected in parallel.
Warning: When connecting batteries in series or parallel, all batteries should have the same voltage rating and ampere-hour (Ah) capacity to ensure safe and efficient operation. Similarly, for solar panels, the voltage rating should match when connecting in parallel.
In a parallel configuration, the voltage remains constant at 12V (both for PV panels and batteries), while the current capacity increases. This configuration is ideal for systems using a 12V UPS/inverter and solar charge controller. It allows both energy generation (via solar panels) and energy storage (via batteries) to operate efficiently and seamlessly.
During normal daylight conditions, the DC to AC inverter is powered by the solar panels directly. In case of low sunlight, shading, or at night, the inverter draws power from the battery bank. The inverter then converts 12V DC into 120V/240V AC (for US systems) or 230V AC (for UK/EU systems), depending on the regional AC voltage requirements. This AC power can then be used to run standard electrical loads such as light bulbs, fans, etc.
Additionally, DC-operated devices can be connected directly to the DC load terminals of the charge controller for efficient and lossless operation.
Wiring Parallel Solar Panels and Batteries:
To connect two or more solar panels and batteries in parallel, simply connect the positive terminal of one panel or battery to the positive terminal of the other, and the negative terminal to the negative terminal, as shown in the diagram below.
In the following wiring diagram:
- Two 12V, 10A, 120W solar panels are connected in parallel.
- They charge two 12V, 100Ah batteries that are also connected in parallel.
- During the day, solar panels power the AC load via the inverter and charge the battery bank.
- During night or cloudy conditions (no sunlight), the stored energy in batteries powers the inverter, which continues to supply AC power to the load.
- The entire process is automatic, handled by the UPS/inverter, with no manual switching or ATS (Automatic Transfer Switch) required.

Related Posts:
- A Complete Guide about Solar Panel Installation. Step by Step Procedure with Calculation and Image
- Blocking Diode and Bypass Diodes in a Solar Panel Junction Box
- Basic Components Needed for Solar Panel System Installation
- How Much Watts Solar Panel You Need for Home Appliances?
- How to Design and Install a Solar PV System? With Solved Example
- Solar Panel Wiring and Installation Diagrams
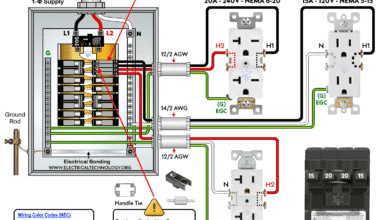 How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits
How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits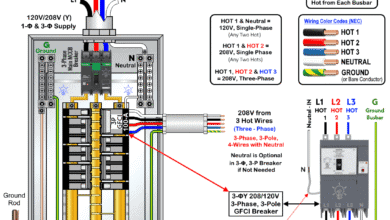 How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel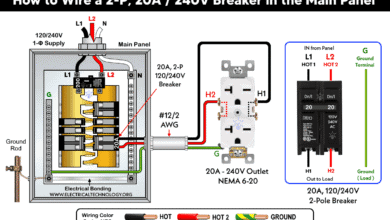 How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel