Simple Battery Charging Time and Current Formula for Batteries (with 120Ah Battery Example)
In this simple tutorial, we will explain how to determine the appropriate battery charging current and how to calculate the required charging time in hours. To make it easy to understand, even for non-technical users or beginners, we’ll use a basic example of a 12V, 120Ah lead-acid battery.
Below are the formulas for calculating the required battery charging time (in hours) and the necessary charging current (in amperes):
Charging Time of Battery = Battery Ah ÷ Charging Current
t = Ah ÷ A
and
Required Charging Current for battery = Battery Ah × 10%
A = Ah × 10%
Where:
- t = Time in hrs.
- Ah = Ampere-Hour (Ah) Rating of a Battery:
- A = Current in Amperes
Example:
What is the suitable charging current in amps and the required charging time in hours for a 12V, 120Ah battery?
Solution:
Battery Charging Current:
First, we will calculate the charging current for a 120Ah battery. As a general rule of thumb, the charging current should be ≈ 10% of the battery’s Ah rating.
Therefore,
Charging Current for 120Ah Battery = 120 Ah × (10 ÷ 100) = 12 Amperes.
However, considering losses such as heat and internal resistance, it’s common practice to use a slightly higher charging current (typically around 12 to 14 amps) instead of the exact 10% (i.e., 13 or 14 amps) of the battery’s Ah rating.
Related Posts
- Battery Capacity Rating Calculator Formula and Equations
- Battery Life Calculator (Formula and Equations)
Battery Charging Time:
Suppose we choose 13 amps as the charging current.
Then,
Charging Time for a 120Ah Battery (Ideal Case) = 120 ÷ 13 = 9.23 hours
However, this is an ideal case without considering any losses.
In practice, it’s observed that approximately 40% energy is lost during the charging process due to heat, resistance, and other factors.
To account for these losses:
Losses = 120Ah × (40 ÷ 100) = 48Ah
So, the total effective capacity to be charged becomes:
120 Ah + Losses
i.e.:
120Ah + 48Ah = 168Ah
Now, to calculate the practical charging time:
Charging Time = Total Ampere-Hours ÷ Charging Current
Charging Time = 168 ÷ 13 = 12.92 hours (approximately)
Therefore, a 120Ah battery would take approximately 13 hours to fully charge when using a 13-Amp charging current, considering practical losses.
Related Posts:
- How to Size and Find the Back-up Time of Battery in a Solar Panel Installation – Examples
- Batteries MCQs with Explanatory Answer
- Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
- Batteries Wiring Connections and Diagrams
- Series, Parallel and Series-Parallel Connection of Batteries
- What Happens if a Battery is Connected to the AC Supply?
- What Happens to the Battery with Reverse Polarity Wiring Connection
- How to Design and Install a Solar PV System with Batteries? Solved Example
- How to Wire Solar Panel to 12V DC Load and Battery?
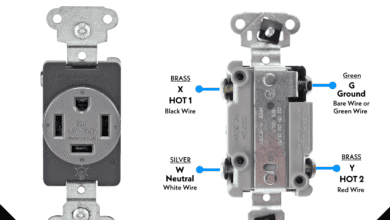 How to Wire a 20A, 125V/250V – NEMA 14-20 Receptacle
How to Wire a 20A, 125V/250V – NEMA 14-20 Receptacle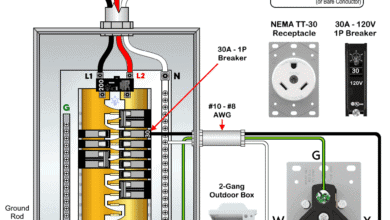 How to Wire NEMA TT-30 Receptacle for RVs & Travel Trailers
How to Wire NEMA TT-30 Receptacle for RVs & Travel Trailers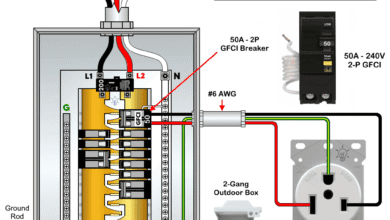 How to Wire a 50A – 250V, NEMA 6-50 Receptacle
How to Wire a 50A – 250V, NEMA 6-50 Receptacle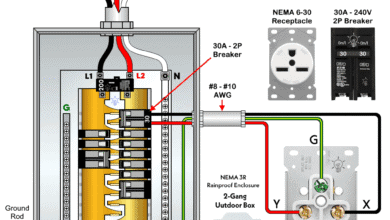 How to Wire a 30A – 250V, NEMA 6-30 Receptacle
How to Wire a 30A – 250V, NEMA 6-30 Receptacle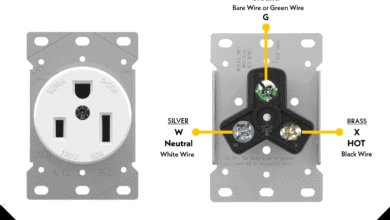 How to Wire a 50A – 125V – NEMA 5-50 Receptacle
How to Wire a 50A – 125V – NEMA 5-50 Receptacle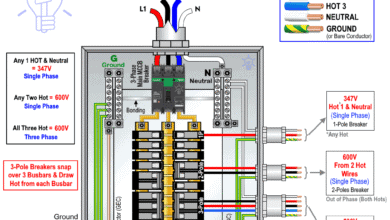 How to Wire 600/347V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase Main Service Panel
How to Wire 600/347V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase Main Service Panel