Questions – Answers
Electrical and Electronics Engineering Interview Questions and Answers
-

Ferrite Bead: Tiny Cylinder in Power Cords & Cable. Why?
What is the Tiny Cylinder in Power Cords and Cables? Ever noticed a small, cylindrical lump on a power cord or cable? You might have seen it on your laptop…
Read More » -
What is a Solenoid and Solenoid Magnetic Field
What is a Solenoid and Solenoid Magnetic Field What is a Solenoid? Solenoid is an enamel wire (coil wire) wound on a round shaped, made of solid materials like Steel…
Read More » -
Types of Solar Panels and Which Solar Panel Type is Best?
Different Types of Solar Panels and Photovoltaic Cells Note: This is an up-to-date article about Different types of Solar Panels and Photovoltaic Cells and we will update it in the…
Read More » -
Magnetic Terms used in Magnetic Circuits – Definition & Formulas
Magnetic and Magnetism Important Terms, Definition and Formulas Magnetic Field or Magnetic Induction (B) Magnet or Electromagnet produces a Magnetic field. The field where the magnet attracts or repels magnetic…
Read More » -
Why is a Motor Rated in kW instead of kVA?
Why are Electric Motors Rated in kW or Horsepower (hp) and Not in kVA? We already know that transformer ratings may be expressed in kVA instead of kW. The same…
Read More » -
Why are Air-Conditioners (AC) Rated in Tons, Not in kW or kVA?
Why is an Air Conditioner and Refrigerator Rated in Tons instead of kVA or kW? In today’s comprehensive HVAC technical article, we will discuss and help you gain an understanding…
Read More » -
Difference Between AC and DC Resistance – Which One is Greater?
Difference Between AC & DC Resistances & How to Calculate it? Resistance The property of a substance or material which oppose the flow of electricity through it is called resistance…
Read More » -
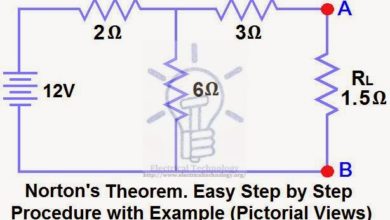
Norton’s Theorem. Easy Step by Step Procedure with Example
Norton’s Theorem in DC Circuit Analysis Norton’s Theorem is another useful technique for analyzing electric circuits, similar to Thevenin’s Theorem. Both methods simplify linear, active circuits and complex networks into…
Read More »