Why is an Air Conditioner and Refrigerator Rated in Tons instead of kVA or kW?
In today’s comprehensive HVAC technical article, we will discuss and help you gain an understanding of the following basic and important terms and expressions used in heating and cooling devices and applications.
Why is an AC Rated in Ton, Not in kW?
Refrigeration and air conditioning (AC) systems are typically rated in tons. The capacity of an air conditioner is specified in tons instead of kilowatts (kW) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA) because it is designed to remove a specific quantity of heat from a defined area, such as a room or a hall.
Air conditioners are rated in tons rather than kW or kVA because of their historical origins and the way cooling capacity was originally measured. The term “ton” in this context does not refer to weight but rather to the amount of heat required to melt one ton (2000 pounds) of ice in a 24-hour period, which is equivalent to 12,000 British Thermal Units (BTUs) per hour.
This measurement became popular in the early 20th century when ice was commonly used for cooling, and it provided a convenient way to describe the cooling capacity of early air conditioning systems.
Even though the use of ice for cooling has largely been replaced by mechanical refrigeration, the term “ton” has persisted as a unit of measurement for air conditioning capacity. It is a well-established convention in the HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) industry and is still widely used in the United States and some other countries.
While kilowatts (kW) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA) could technically be used to describe the cooling capacity of an air conditioner, the use of tons has become a standard practice and is often preferred for consistency and familiarity within the industry.
The term “ton” in reference to cooling capacity indicates the amount of heat energy a system can remove. If an air conditioner can remove 12000 BTUs (equivalent to 12,660.5 kJ, 30,26 kilocalories, or 3.517 kW-h) of heat in an hour, it is rated as a 1-ton AC unit.
The same measurement of ratings applies to all HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems, such as air conditioners (AC), heat pumps, chillers, freezers, refrigeration systems, and cooling towers etc.
Good to know:
- British Thermal Unit (IT) per pound per Fahrenheit degree (Btu (IT)/lb-°F) is a unit of measurement that has the dimension of L2T-2Q-1. Where: L is length, T is time, and Q is temperature.
- BTU = British thermal unit. A measurement of heat, specifically, the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of a pound of water by 1°F.
- 1 BTU = 0.252 kilocalories = 1055.05 joules = 0.293 W-hours = 0.0000833333 – ton.
- 12000 BTUs/hr = 1 Ton
Related Post: Why is a Transformer Rated In kVA, Not in KW?
Definition of Ton
A Ton of refrigeration (RT) is approximately equivalent to 12,000 BTU/h or 3,516.8528 W or 4.7142Hp.
A Ton of refrigeration (RT) is a unit of power used to describe the heat-extraction capacity of air conditioning and refrigeration equipment. It is defined as the heat of fusion absorbed by melting 1 short ton of pure ice at 0 °C (32 °F) in 24 hours.
In industrial HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning), a “ton” is a unit of cooling capacity. It is defined as the amount of heat absorbed or removed by one ton (2000 pounds) of ice melting over a 24-hour period. In terms of BTUs (British Thermal Units), one ton is equivalent to 12,000 BTUs per hour.
For example, a 2-ton air conditioner has a cooling capacity equivalent to 24,000 BTUs per hour, while a 3-ton unit has a capacity of 36,000 BTUs per hour, and so on.
Good to Know: 1 Ton = 12,000 BTU/h = 12,660.5 kilojoules = 30,26 kilocalories = 3.517 kilowatts-hours
How Many kW, kWh and HP are Equivalent to 1 Ton?
1 Ton = 3.5168525 kWh = 4.714Hp
Explanation
1 Ton = 12,000 BTU/h
1 Watt = 3.412141633 BTU/h
1 Ton = 12,000 ÷ 3.412141633 = 3,516.8528 Watts = 3.5168528 kW.
1 Ton = 3,516.8528 Watts = 3.516 kW.
And
1 Ton = 3,516.8528W ÷ 746 = 4.7142798928 Hp →→→ (1 Hp = 746 Watts)
1 ton is equivalent to:
- Approximately 3.517 kilowatts (kW) of cooling capacity.
- Approximately 3.517 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of energy consumption per hour (assuming a coefficient of performance (COP) of 1, meaning 1 kW of electricity produces 1 kW of cooling).
- Approximately 4.714 horsepower (HP) of cooling capacity (1 HP is equivalent to 0.7457 kW).
1 Ton = 4.714 Hp
- Related Post: Why is an Electric Motor rated in kW instead of kVA?
How to Convert Ton to kW / kWh and vice versa?
One RT (Refrigeration Ton) = 3.5168528 kW
1 RT = 3.5168528 kWh
1 kWh = 0.284345 RT (Refrigeration Ton)
1 kWh = 0.28434517 RT
Therefore,
The power “P” in kW = Power “P” in RT (Refrigeration Ton) times 3.5168528.
Conversion of Ton into kW
P(kW) = P(RT) × 3.5168528
Conversion of kW / kWh into Tons
P(RT) = P(kW-h) ÷ 3.5168528
Example 1:
Convert 3 Ton AC into kW i.e. Convert 3 RT to kW or kWh.
Solution:
P(kW) = 3 RT × 3.5168528
P(kW) = 10.55 kW
Therefore,
3 Ton AC = 10.55 kW
So, a 3-ton air conditioner has a cooling capacity of approximately 10.551 kilowatts.
Example 2:
Convert 0.5275 kW or kWh into Tons
Solution:
P(RT) = 0.5275 kW ÷ 3.5168528
P(RT) ≈ 1.5 Tons
Therefore,
0.5275 kW Ton AC = 1800 BTU = 1.5 Tons of AC
Please note that these formulas assume a coefficient of performance (COP) of 1, meaning 1 kW of electricity produces 1 kW of cooling. In reality, COP varies depending on the efficiency of the cooling system. Adjustments may be needed for systems with different COP values.
- Related Post: Why is a Battery Rated in Ah (Ampere hour), Not in VA.
How Much Current in Ampere Will a 2 Tons AC Draw in 1-Phase & 3-Phase System?
Current Drawn by 2 Tons AC in a Single Phase Circuit
Suppose, the single phase supply voltage are 230V having a power factor = Cos ϕ = 0.95
1 Ton = 3,516.8528 Watts = 3.516 kW.
2 Ton = 2 × 3.516 kW = 7.032kW = 7032W
Power in a Single Phase AC System
P = V × I Cos Φ and current…
I = P ÷ (V × Cos Φ)….. Where Cos Φ = Power factor
I = 7032W ÷ (230V × .95)
I = 32.18 A
Therefore, a 2 Ton AC (Air-conditioner in Single Phase AC system will draw 31.18 Ampere Current
Current Drawn by 2-Ton AC in a Three-Phase Circuit
Suppose, There are 440V and Power factor = Cos Φ = 0.85 in Three Phase AC system…
Power in a Three Phase AC System
P =√3 × VL × IL CosΦ and current….
I = P ÷ ( √3 × V × CosΦ)
I = 7032W ÷ (1.732 × 440V × .85) Where Cos Φ = Power factor and √3 = 1.732
I = 10.855 A
Therefore, a 2 Ton AC (Air-conditioner in Three Phase AC system will take 10.855 Ampere Current.
Good to Know:
These calculation are based on basic electrical formulas and the assumptions and reference values may change with real life applications. For example, an air conditioner current depends a lot on operating conditions such as ambient temperature, refrigerant pressure, Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) etc. for instance, if EER is 6, then input power for 2 Tons Air conditioner is 24000BTU/6 = 4000 watts
In case of single-phase 230 volt system, the air conditioner load current would be = 4000 ÷ (230V × .95) = 18.5 A
Another similar rating is Coefficient of power (COP) which is the output power in watts divided by input power, so with a COP = 1.8, for instance, input power for 2 Tons Air conditioner is 7032W ÷ 1.8 = 3906 watts. Now you can find current by using the above method which is equal to 18A approx.
- Related Post: Why is a Generator & Alternator rated in kVA. Not in kW?
How Many 2-Ton Air Conditioners Can I Run on a 30 kVA Generator?
To determine how many 2-ton air conditioners you can run on a 25 kVA generator, you first need to calculate the total power consumption of the air conditioners and compare it to the generator’s capacity.
A 2-ton air conditioner typically requires around 3.516 kW ( ≈ 3500 watts) per hour. Since 1 ton is approximately equal to 3.5 kW, a 2-ton unit would be around 7032W (≈7 kW).
2 Ton = 2 × 3.516 kW = 7.032kW = 7032W
The efficiency of utility power generators are 90% approximately.
Efficiency of Generator = 30 kVA × (90 ÷ 100) = 27 kVA
Now the Number of 2 Ton AC (Air conditioners) which you can run on a 25 kVA Generator smoothly:
27kVA ÷ 7032W = 3.8
So, you can run three air conditioners, each rated at 2 tons, on a 30 kVA generator. Do not add an additional unit to avoid overloading the circuit.
What is the Suitable Rating of an MCB for a 1-Ton and 2-Tons Air Conditioner (AC)?
Note: For calculations in depth, you may refer to the premium technical resource on sizing a circuit breaker for various electrical devices and applications.
Sizing MCB for 1 Ton AC
A 1-ton AC usually has a running current of around 5 to 7 amps and a starting current that could be around 15 to 20 amps or higher. As the starting current is high during the initial switching, hence it takes more current at full load than the normal running current.
1 Ton = 3516.85 W
Full Load Current of 1 Ton AC in 230V AC circuit can be calculated using Ohm’s Law.
I = P ÷ V
3516.85W ÷ 230V
I ≈ 15.3
The circuit breaker should be connected to the load at 80% of its rated amperes. In other words, the rating of the circuit breaker should be 1.25 times the load circuit current.
- 15.3A Load Circuit × 1.25 ≈ 19.125A Breaker Size
- 19.125A Breaker × (80/100) = 15.3A Load Circuit
Now, the next standard size of 20A Class “C” MCB (miniature circuit breaker) is perfect for 1 Ton AC (air-conditioner) which is capable to run the AC smoothly in both the full load high starting current as well as the normal running current without tripping the circuit.
And 20 A Class “C” MCB would be better for 1 Ton AC (air-conditioner)
Sizing MCB for 2 Ton AC
A 2-ton AC typically has a running current of around 10 to 12 amps and a starting current (also known as inrush current) that can be significantly higher, possibly reaching 30 to 40 amps or more for a brief period during startup.
As we have calculated the load current for 2 Ton Air conditioner (AC) above which is 32A.
Calculated Current for 2 Ton A.C = I = 32 A
The circuit breaker should be connected to the load at 80% of its rated amperes. In other words, the rating of the circuit breaker should be 1.25 × load circuit current e.g.
- 32A Load Circuit × 1.25 = 40A Breaker Size
- 40A Breaker × (80/100) = 32A Load Circuit
Now 40A Class “C” MCB (miniature circuit breaker) would be suitable for 2 Ton AC (air-conditioner) as it will smoothly handle both the high starting starting and ruining current in the circuit.
Good to Know:
Class “’C’ Type of CBs
Class “C” type MCBs are suitable for installations with high inrush current during the initial switching time. In other words, they are ideal for equipment and devices with inductive loads, such as air conditioners, induction motors, fluorescent lamps, transformers , etc.
A general AC (Air-conditioner) Name plate rating Data
- kVA to Amps Calculator – How to Convert kVA to Amps?
- Amps to kVA Calculator – How to Convert Amps to kVA?
- Amps to Watts Calculator – Conversion – DC/AC (1 & 3 Phase)
- Watts to Amps Calculator – Conversion – DC/AC (1 & 3 Phase)
- Difference between Analog and Digital Multimeter
- Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor



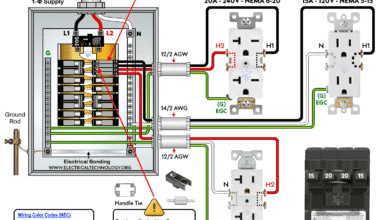 How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits
How to Wire a Tandem Breaker for 120V and 240V Circuits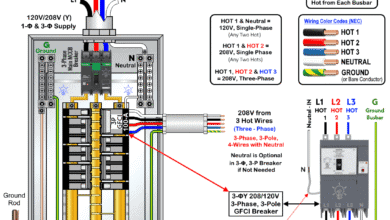 How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel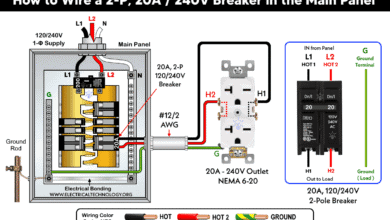 How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel