How to Install a 50A -125V Receptacle (NEMA 5-50R) with GFCI / Breaker
The NEMA 5-50R is a 125 V, 50 A receptacle, once used for heavy-duty 120V equipment but now nearly obsolete. It’s not standard or recommended for new residential or commercial installations under modern NEC practices. Most 50A applications today use 240V receptacles like NEMA 6-50R or 14-50R instead.
NEMA 5-50R receptacles were used for large 120V appliances (e.g., heavy-duty commercial equipment, welders, or industrial vacuum cleaners), some RV park pedestals (older installations) and commercial or shop environments which requires high current at 120V. Nowadays, NEMA 5-50R are rare and uncommon (now mostly obsolete) in new installations.
The NEMA 5-50 Receptacle
A NEMA 5-50 is a 125-volt, 50-amp (2-pole, 3-wire) grounding receptacle, used for welders and generators. The “5” in the designation indicates a 3-wire, 125-volt configuration (hot, neutral, and ground), while the “50” specifies the 50-amp rating.
A NEMA 5-50 receptacle is not compatible with other NEMA configurations, such as a NEMA 14-50 or NEMA 6-50, which operates at 240V.
Similarly, NEMA 5-50R are not used in residential setting as there’s no household equipment designed for NEMA 5-50.
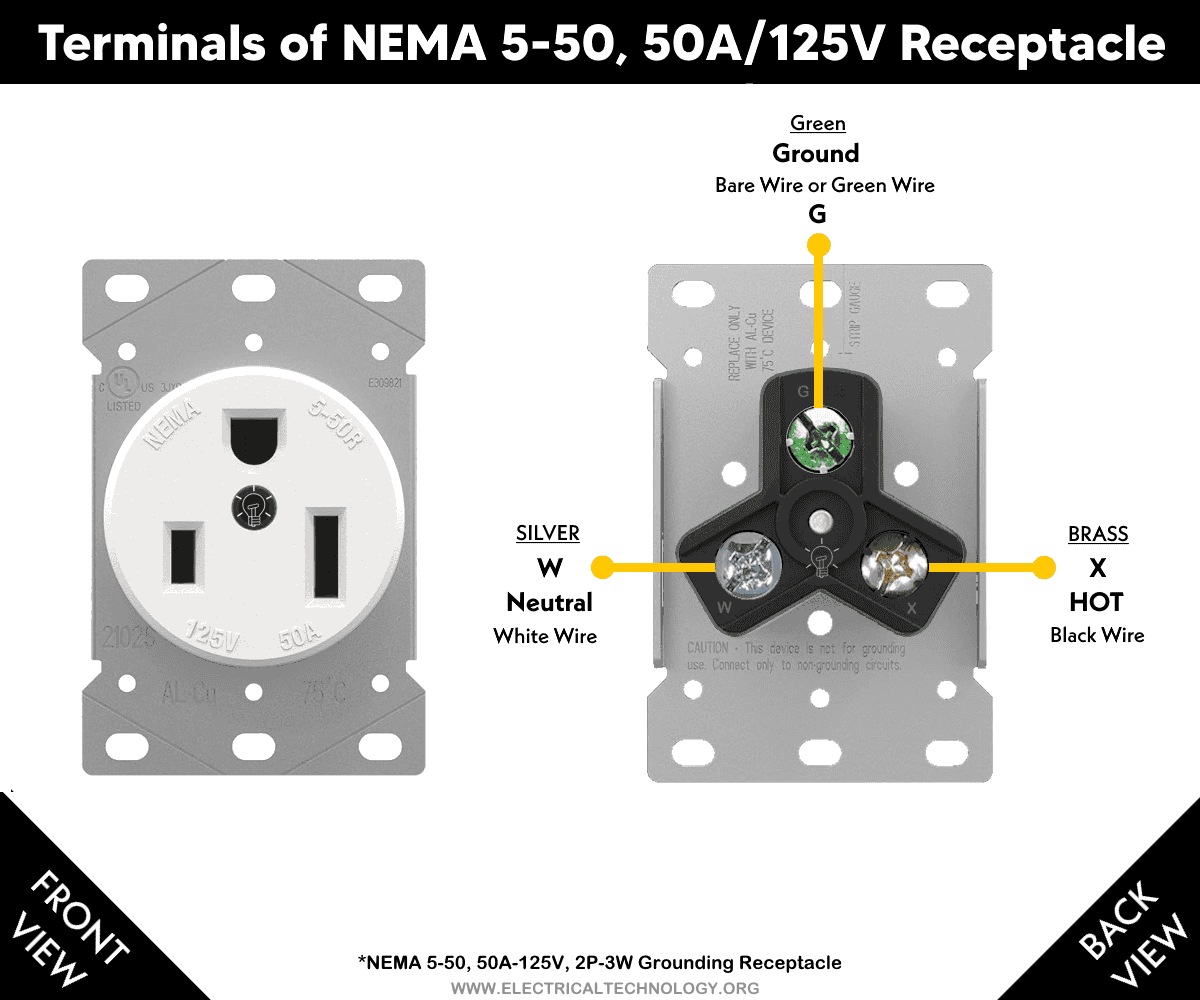
Terminals
There are three terminals in a NEMA 5-50R receptacle as follows:
- (I) = Narrow Vertical Terminal (Brass Screw) on the Left Side: Connects to the Hot – Black Wire
- (|) Longer Vertical Terminal (Silver Screw) on the Right Side: Connects to the Neutral – White Wire
- (U) Shaped “G” Terminal (Green Screw): Connects to the Ground (EGC) – Bare or Green Wire
Electrical Ratings & Specifications
- NEMA: 5-50R – Straight-Blade Receptacle
- Poles: 2-Poles, 3 Wires Grounding
- Voltage: 125V Single-Phase AC Supply – 60 Hz
- Current: 50A – 40A
- Breaker / GFCI: 50A
- Wattage: 6,000 W
- Wire Size: #6 AWG Copper
- Grade & Material: Commercial Grade – Thermoplastic/Composite
- Mounting: Flush / Screw Mounting
- Outdoor Box: 2-gang outdoor box – NEMA 3R rainproof enclosure
- Wiring: Hardwired / Dedicated Circuit
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
Wiring NEMA 5-50R Receptacle
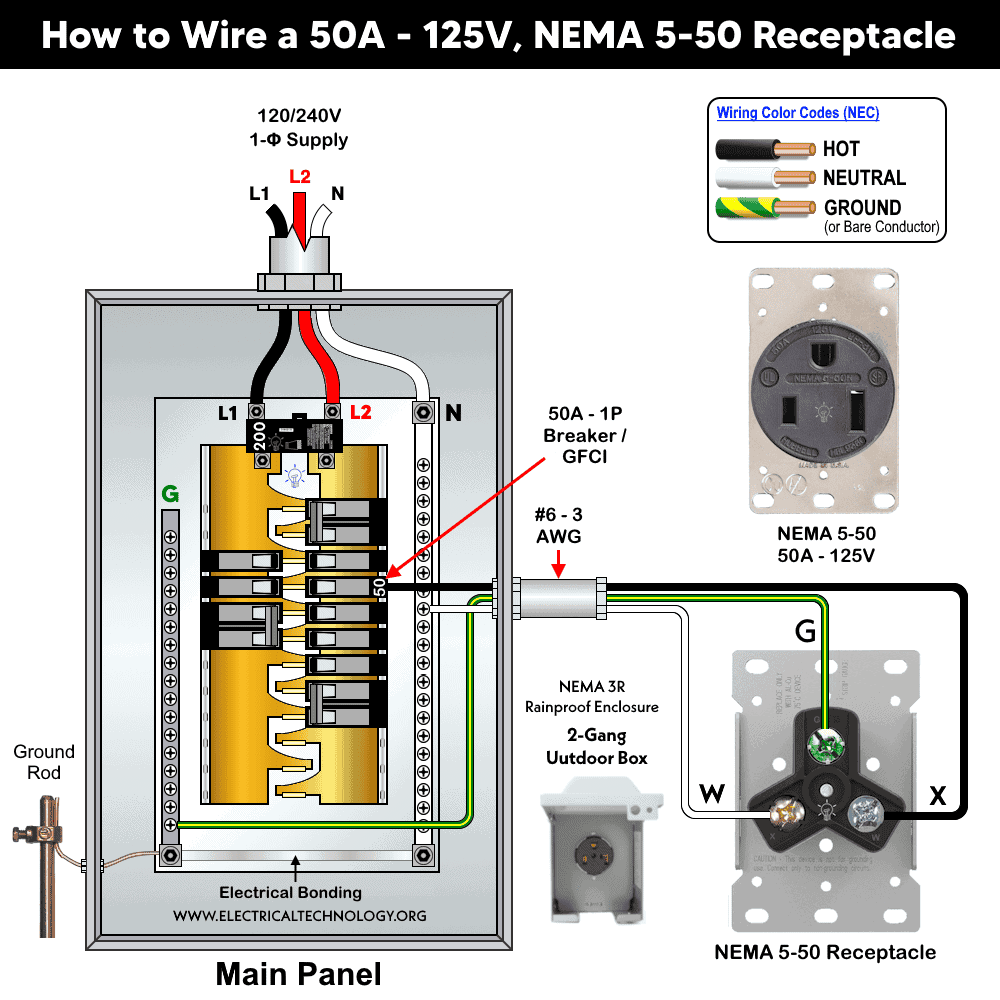
Wiring 50A-120V Outlet using 1-P Breaker / GFCI
The following wiring diagram illustrates the wiring connections of a 50A, 125V outlet (NEMA 5-50R) to a single-pole, 120V – 50A breaker or GFCI in a 120/240V main panel, as shown below:
To wire a NEMA 5-50R, follow the following simple steps:
- Strip 1 inch (25mm) of insulation from the conductors.
- Connect the ground (bare or green) wire to the green screw – the centered, round or U-shaped “G” terminal.
- Connect the hot (black) wire to the brass screw – the shorter or narrow vertical slot terminal.
- Connect the neutral (white) wire to the silver screw – the longer vertical terminal.
- Once fixed in the slots, tighten all terminal screws to approximately 30 lb-in (3.4 N·m) of torque.
For this circuit, use #6 AWG copper wire, which is the correct size for a 50A circuit and the associated NEMA 5-50R outlet.
For outdoor installations, use a NEMA 3R weatherproof 2-gang enclosure for NEMA 5-50 to protect the receptacle from moisture and environmental exposure.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
In the case of a 50A outlet used for RV park pedestals (older installations) or outdoor wiring where GFCI protection is required, simply replace the single-pole breaker with a single-pole, 50A-125V GFCI breaker. While replacing the standard breaker with GFCI, don’t forget to connect the built-in pigtail (white wire) from the GFCI to the neutral busbar in the main panel.
Good to Know:
According to NEC 210.8, GFCI protection is required for receptacles installed in garages, basements, outdoors, laundry areas, and other wet or damp locations.
Specifically, NEC 210.8(A)(1) through (A)(11) mandates that all outdoor receptacles must be installed downstream of GFCI protection, in accordance with Articles 426.28 and 427.22.
FAQs
Are NEMA 5-50R Receptacles Still Used Today?
They are very rare and seldom used in modern installations. Most new 50A outlets are 240V, i.e. NEMA 6-50R (for welders) or NEMA 14-50R (for ranges, EV chargers, RVs). A 50A, 125V circuit is inefficient and unusual and only few appliances require that much current at 120V.
Is It Allowed to Install NEMA 5-50R in New Installations?
The NEC does not prohibit NEMA 5-50 receptacles outright i.e. any listed and labeled device can be used if the load requires it. However, it’s not standard practice for residential or commercial wiring because:
- No common household appliance requires 50 A @ 120V.
- Most 50A branch circuits are 240V, not 120V.
Hence, inspectors may question or reject a 5-50R unless it’s clearly required by manufacturer specs.
How Many Amps Can a 50A – 125V Receptacle Handle Safely?
A 50-amp outlet is designed to handle up to 50 amps continuously under normal conditions.
However, per NEC 210.19(A)(1) and NEC 210.20(A), continuous loads (lasting more than 3 hours) should not exceed 80% of the circuit rating.
Safe continuous current: 50A × 0.8 = 40A
So, a 50A-120V outlet can safely handle 40 amps continuously and up to 50 amps for non-continuous loads.
How Many Watts Can a 50A – 125V Receptacle Hold?
To find wattage capacity:
P = V × I
120V × 50A = 6,000W
The maximum (non-continuous) power a 50A -120V outlet can handle is 6,000 watts (6 kW).
Safe Continuous Power (80% rule):
120V × 40A = 4,800W
So, it can safely deliver 4.8 kW continuously or up to 6 kW total.
Which Breaker Size is Suitable for a 50A – 125V Receptacle?
Based on the breaker sizing and selection, 1-Pole, 120V – 50A thermal-magnetic circuit breaker (or GFCI if required by NEC 210.8 for outdoor, garage, or wet locations) is required for a 120V, 50A (NEMA 5-50) receptacle.
What is the Correct Wire Size and Cable Type to Use with a 50A – 125V Receptacle ?
For a 50A circuit, the minimum required conductor size is #6AWG copper which can safely handle 50 amps per NEC Table 310.16 and Table 210.24(1). Similarly, use #10AWG for 50A circuit as EGC per NEC Table 250.122.
For NEMA 5-50R, you may use NM-B 6/2 for indoor dry locations, UF-B 6/2 for outdoor direct burial and THHN/THWN 6 AWG in conduit.
Instructions, Precautions & Codes
- The 5-50R should not be used with single-gang wall boxes. Use a 2-gang outdoor box and NEMA 3R rainproof enclosure, especially for outdoor applications.
- According to NEC Table – 310.16, and Table 210.24(1) the correct wire size for a 50A circuit and outlet is #6 AWG copper. Likewise, the appropriate breaker size is a 50A, 120V single-pole breaker (or 50A 1-P, GFCI breaker) when wiring a NEMA 5-50R receptacle, using the same wire size (#6 AWG) copper conductors.
- A 50A outlet can supply up to a 40A continuous load and a maximum of 40A non-continuous load, as per NEC 210.19(A), 215.2, and 230.42(A).
- Use #10/2 cable (hot, neutral, and ground) for wiring a 50A-120V breaker and outlet.
- Use 50A, 120V outlet as a dedicated circuit for single unit.
Warning
- Always turn off the power supply by switching OFF the circuit breaker in the main electrical panel before performing any electrical work.
- If you are unsure or inexperienced, it is strongly recommended to contact a licensed electrician to perform the work in accordance with local electrical codes and safety regulations.
- The author assumes no responsibility or liability for any losses, injuries, or damages resulting from the use, misuse, or improper application of the information provided. Please be safe because playing with electricity is extremely dangerous.
Resources:
Related Wiring Tutorials
NEMA Family Outlets/Receptacle Wiring
NEMA 5 -Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 120V NEMA 5-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 120V – NEMA 5-50 Receptacle… (You are Here)
NEMA 6-Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 240V – NEMA 6-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 240V – NEMA 6-50 Receptacle
NEMA 10-Series
- How to Replace a 20A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-20R?
- How to Replace a 30A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-30R?
- How to Replace a 50A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-50R?
NEMA 14-Series
- How to Wire a 20A – 125/250V NEMA 14-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125/250V NEMA 14-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 125/250V NEMA 14-50 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 60A – 125/250V – NEMA 14-60 Receptacle
NEMA General Outlets/Receptacle
- How to Replace a 15A – 125V Outlet – NEMA 1-15 Receptacle
- How to Replace a 20A – 250V Outlet – NEMA 2-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125V – NEMA TT-30 Receptacle
General Wiring Installations:
- How to Size a Breaker and Wires in AWG with EGC for Load?
- How to Wire an Outlet Receptacle? Socket Outlet Wiring Diagrams
- How to a Wire 3-Way Combination Switch and Grounded Outlet?
- How to Wire Combo Switch and Outlet? – Switch/Outlet Combo Wiring Diagrams
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Wire 277V & 480V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase, Commercial Main Service Panel?
- How to Wire 240V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Continuous?
- How to Wire 3-Phase Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
- How to Wire ST01 Timer with Relay & Contactor for 120V/240V Motors?
- How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
Switches Wiring
- How to Wire Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) as 2-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) as 3-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Double Pole, Single Throw Switch? Wiring DPST
- How to Wire Double Pole, Double Throw Switch? Wiring DPDT
- How to Wire Double Switch? 2-Gang, 1-Way Switch – IEC & NEC
- How to Wire 4-Way Switch (NEC) or Intermediate Switch as 3-Way (IEC)?
GFCI/AFCI Breaker/Outlet Wiring
- How to Wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker?
- How to wire a GFCI Outlet?
- How to Wire GFCI Combo Switch and Outlet – GFCI Switch/Outlet
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker?
- How to Wire an AFCI Outlet?
Related Posts:
- What is the Right Wire Size for 50A Breaker and Outlet?
- What is the Difference Between 15-Amp and 20-Amp Outlet?
- Difference Between Socket, Outlet and Receptacle
- Difference Between NEMA 14-50 Standard Vs EV Receptacle
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- Can you use 15A Breaker on 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You use a 15A Outlet on a 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Ground Terminal Up or Down: Which Way Should Outlets Face?
- What Do the Green Dot or Orange Triangle Outlets Mean?
- What Do the Different Colors of Electrical Outlets Indicate?
- Why are Outlets and Receptacles in Hospitals Upside Down?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panelboard?
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker? Breaker Size Calculator & Examples
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation?
- Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
- What Will Happen If You Connect a Male-to-Male Plug Between Outlets
 How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel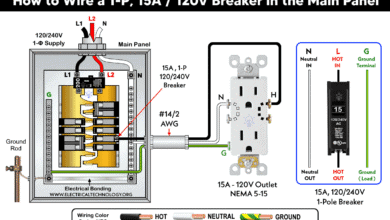 How to Wire a Single-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel