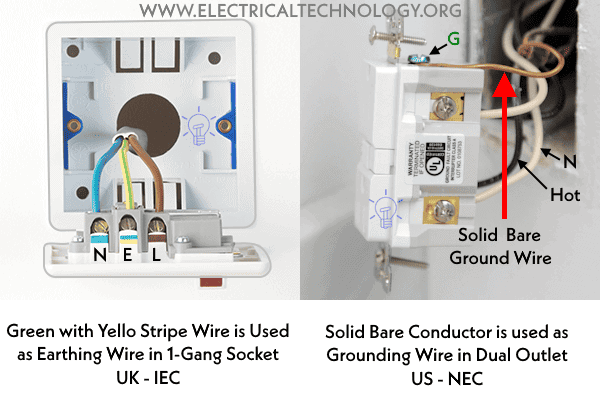
Why is the Grounding Wire Bare and Not Insulated?
Why is Mostly Solid Bare Conductor Used for Grounding Instead of Insulated Wire?
A ground wire, also known as a grounding wire or ground conductor (GEC and EGC), as the name implies, is an electrical wire connected from the transformer and main panel (or distribution board) to the ground rod or earthing plate via ground electrode conductor (GEC), also known as an earthing lead buried in the ground or Earth. It is connected to all metallic parts that may come into contact with the human body to prevent electric shocks in case the hot (phase or line) wire accidentally touches the machine or electrical device.
A grounding conductor is known a Ground Wire (G) in NEC and Protective Earth (PE) in IEC.
A ground wire in the grounding/earthing system is used to provide a safe path for electrical currents to flow into the earth. As a safety measure, it is used to prevent electric shock and fires in case of fault currents flowing in the circuit, such as a short circuit or leakage current.
As per National Electrical Code (NEC) sections 250.118(A) and 250.119(A) Both Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC) and Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC) can be bare, covered or insulated. Copper, aluminum or copper-clad aluminum in the form of solid or stranded form can be used for grounding conductors. In addition, GEC (grounding electrode conductor shall not be used a equipment grounding conductors per NEC 250.118(B).
While covered or insulated wires can be used, solid bare copper is preferred for grounding conductors. Electrical drawings use common color codes to indicate ground wires. For example, insulated grounding wires are denoted with green or green with a yellow stripe when used instead of a bare copper conductor. According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), the color code for the earth wire is light blue (which replaced black in the UK prior to 2004).
Why Use a Bare Grounding Wire Instead of an Insulated Wire?
The most valid reason for using a solid bare conductor as a ground wire is cost-efficiency. While the price difference may be negligible for bare and insulated wires on a small scale (neglecting the small price difference), it provides significant cost savings when used in heavy industrial applications and even more so for large-scale manufacturers.
Grounding wires are sometimes not insulated for several reasons:
- Cost: Grounding conductors are often bare to save cost. Adding insulation to grounding wires would increase the cost of materials and installation without providing any significant benefit for their intended function.
- Leakage Current Capacity: The use of a bare conductor for below-ground grounding is to maximize the “leakage current” capacity and to maximize the sphere-of-influence of the grounding system.
- Alternative Grounding Methods: In some wiring methods, there are no ground wires because the metal cable armor or the conduit itself serves as the ground. Keep in mind some wiring systems need a sperate bare or insulated ground wire in metal conduit.
- Heat dissipation: In the event of a fault or overload, grounding wires may carry high currents for a very short time of period. The lack of insulation allows for efficient heat dissipation, reducing the risk of the wire overheating or melting. Insulation could trap heat and increase the risk of fire or damage to the wire.
- Easy Identification: Grounding wires are often color-coded or identified by their lack of insulation, making them easily distinguishable from other conductors in an electrical system. This is important for safety and maintenance purposes, as it helps electricians and maintenance personnel quickly identify and work with these wires.
It’s important to note that there are situations where ground conductors may be enclosed in conduit or insulating materials to protect them from physical damage, but in most cases, the ground wire itself is left uninsulated for the reasons mentioned above. For example, a metal-clad cable where both insulated and bare grounding conductors are used based on the system requirements.
Related Posts:
- Why is Copper Rod Used as Ground Rod in Grounding System?
- Why are Overhead Power Transmission Lines Not Insulated?
- What is the Purpose of Ground Wire in Overhead Transmission Lines?
- Why is the Ground Wire Always Positioned Above the Overhead Power Lines?
- Difference Between Grounding, Earthing and Bonding
- Difference Between Real Ground and Virtual Ground
- Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth?
- Why are Salt and Charcoal Added in Earthing Pit for Grounding?
- Why Earth Pin is Thicker and Longer in a 3-Pin Plug?
- Why are US Homes Wired Using Solid Wire rather than Stranded Wire?
- Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
- Can you Combine AC and DC Ground in a Solar Installation?
- Will I Get an Electric Shock If I Touch the Ground Wire?
- Can the Neutral Wire Cause Electric Shock? Different Cases
- Why Doesn’t DC System Require a Grounding System Similar to AC System?
- Why is the Ground Wire Size Smaller than the Hot Wire?
- Why is the Ground Wire Always Positioned Above the Overhead Power Lines?
- Why Must Neutral and Ground Wires Be Bonded in the Main Panel?
- Why are Neutral and Ground Wires Separated in a Subpanel?
- Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground
- Is It Possible to Get Electrocuted by an Electric Vehicle?
- How Does the Grounding System Work in Aircraft & Submarines?