Comparison Between Direct-On-Line (DOL) and Star Delta Motor Starting Methods
It is well known that induction motors draw a high inrush current during the initial starting phase. This temporary transient current is 6-8 times more than the full load current. To limit this high starting current and safely start and run the motor, a starter is required in the motor circuit. Among the various types of motor starters, two commonly used starters for controlling and starting motors are the Direct-On-Line (DOL) Starter and the Star-Delta Starter.
Now the question arises: when and where should we use a DOL Starter or a Star-Delta Starter with three-phase motors? To answer this, let’s first differentiate between them by discussing their advantages, disadvantages, characteristics, and applications.
What is DOL Starter?
A Direct-On-Line (DOL) starter is the simplest motor starting method where the motor is connected directly to the power supply at full or rated voltage. That’s why it is also known as “across the line” starter. It consists of a contactor, overload relay, and start/stop buttons.
As in DOL starting method, the motor directly connects the motor windings at full voltage to the power supply, This way, it draws very high as much locked-rotor current (LRC), typically 6-8 times the motor’s full load current. Consequently, the starting torque is high. Hence, it is suitable for applications where strong initial torque is needed.
When the start button is pressed in DOL starter, the contactor energizes, applying full voltage to the motor. The motor starts instantly with high inrush current (5-8 times the full load current). The overload relay protects the motor from excessive current (Overload) while the breaker or fuse protects the motor’s branch circuit conductors from overcurrent and ground faults.
Where to Use DOL Starter
DOL starters are typically used in small to medium load applications where the motor size is up to 5 HP to 10 HP (~3.7 kW – ~7.5 kW) in industrial installations depending on the supply capacity.
Direct-On-Line Starters are suitable to use when the electrical supply network can handle high inrush currents without significant voltage drop and permissible by the power regulatory authority. It is also used where mechanical systems connected to the motor can withstand a sudden torque surge during starting.
Common applications of DOL starters include small water pumps, compressors, fans, blowers, conveyor belts and small workshop machinery with low inertia loads.
Advantages & Disadvantages of DOL Starters
Advantages
- Simple design and easy installation with fewer components.
- Low cost compared to other starters.
- Quick acceleration to full speed.
- Provides full starting torque, which is beneficial for applications that require high starting torque.
Disadvantages
- High starting current (6 to 8 times full-load current), which can cause voltage dips in weak supply systems.
- Mechanical stress on the motor shaft, coupling, and driven equipment due to sudden torque.
- Not suitable for large motors or sensitive supply networks as excessive inrush current can trip circuit breakers.
- Increases wear and tear on mechanical parts due to abrupt starting.
What is a Star Delta Starter?
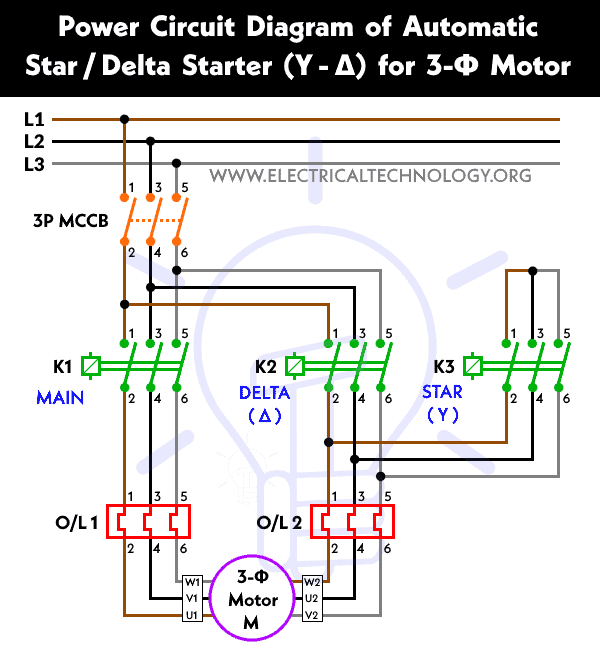
A Star-Delta Starter is a reduced voltage starting method used for starting large three-phase induction motors. Unlike DOL starter, Star-delta starting method is used to minimize inrush current during motor startup. In this method, the motor windings are initially connected in a Star (Y) or “Wye” configuration during startup to reduce the voltage across each winding to 1/√3 (about 58%) of the line voltage. After the motor reaches a certain speed at a set time, the winding connection changes to Delta (Δ) configuration to apply full line voltage.
The main components of a star-delta starter consists of three contactors i.e. Main, Star, and Delta contactors. Additional components are timer or automatic controller, overload relay and circuit breaker or fuse for overcurrent protection.
In operation when the start button is pressed:
- Star (Y) Connection: Initially it connects the motor windings in a star (Y) configuration. Hence, motor starts with reduced voltage (≈58% of line voltage), which reduce the starting current.
- Delta (Δ) Connection: After a preset time, the motor switches to Delta (Δ) mode for full voltage operation.
Where to Use a Star Delta Starter?
Star-Delta starters are used in large load applications where the motor size is large, generally above 5 HP (~3.7 kW) and commonly up to 150 HP (~110 kW) or more. It is used where reducing the starting current is necessary to avoid supply voltage dips. Y/Δ starters also suitable to use when the load does not require full starting torque. Keep in mind that star-delta starters are not suitable for heavy-load starting.
Common applications for star/delta starter includes large water pumps, air compressors, Industrial fans, blowers, crushers, processing machinery and large industrial applications. At all, start delta starters are suitable for low to medium voltage and light starting torque with high inertia loads induction motors.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Star Delta Starters
Advantages:
- Reduces starting current to about 1/3 of that in DOL starting. In other words, it limits inrush current to 2-3 times full load current.
- Reduces voltage dips and mechanical stresses on the motor and driven equipment.
- Cost-effective solution for large motors where soft starters or variable frequency drives (VFDs) are not used.
- Ideal for high-inertia loads
Disadvantages
- Provides only 33% of the starting torque, which may be insufficient for high-torque applications.
- Requires more components (three contactors and a timer), making the circuit more complex than DOL.
- There is a brief power interruption during the changeover from star to delta, potentially causing mechanical shock if the load is not light.
- Not suitable for motors that need full torque at startup i.e. it may fail to start heavy loads in Star mode.
Comparison Between DOL and Star Delta Motor Starters
The following table shows the comparison between Direct-On-Line (DOL) and Star-Delta motor starters.
| Feature | DOL Starter | Star Delta Starter |
| Components | 1 Contactor, 1 Overload Relay | 3 Contactors, 1 Timer, 1 Overload Relay |
| Starting Method | Direct connection to full line voltage | Initial star connection, then delta |
| Starting Current | 6–8 times full load current | 1/3 of DOL i.e. 2–3 times full load current |
| Starting Voltage | Full line voltage | Reduced voltage (58%) in Star mode |
| Starting Torque | 100% of rated torque | 1/3 i.e. ~33% of rated torque during Star mode |
| Motor Size Suitability | Small motors (up to 5–10 HP) | Medium to large motors (above 5 HP) |
| Complexity | Simple | More complex (multiple contactors & timer) |
| Voltage Drop | Can cause significant voltage dips | Less impact on supply voltage |
| Mechanical Stress | High due to sudden start | Lower than DOL due to smooth transition |
| Transition During Start | None | Possible transient during star-delta switching |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost due to additional components |
| Application | Small to medium motors (<5 HP or up to ~7.5 kW), high initial torque | Larger motors (above >5 HP or ~7.5 kW), light initial load, current limitation |
Resources & Tutorials:
- Difference between Star and Delta Connections – Comparison Of Y/Δ
- Main Difference Between Contactor and Starter
- Difference Between NEMA and IEC Motor Starters & Contactors
- Difference Between Soft Starter and Star Delta Starter
- Difference Between DOL Starter and Soft Starter
- Difference Between Soft Starter & VFD (Variable Frequency Drive)
- 3-Point Starter – Circuit and Working of Three-Point Starter
- 4-Point Starter – Circuit and Working of Four-Point Starter
- Understanding NEMA Motor Nameplate Data and Marking
- Motor Load Circuits: NEC Terms and Terminologies
- NEC Requirements for Motor Circuits
- Star to Delta & Delta to Star Conversion. Y-Δ Transformation
Wiring and Calculations
- How to Size a Motor Starter, Contactor and Controller? NEMA – NEC
- How to Size Star-Delta Starter for Motors?
- How to Size DOL Starter for Three-Phase Motors?
- How to Size Disconnecting Means for Motor & Controller
- How to Size Overcurrent Protection for Motor Control Circuits
- VFD Bypass DOL Starter – Power, Wiring and Control Circuits
- VFD Bypass Star-Delta Starter – Power and Control Circuits
- Automatic & Manual Control of Motor Using VFD & DOL Starter
- ON / OFF 3-Phase Motor Using 14-PIN Relay and DOL Starter
- Wiring of DOL Starter for Automatic / Manual Control Using Digital Timer
- Star – Delta Starter Using Different PLCs – Wiring and Ladder Diagram
- Automatic Star – Delta Starter Motor Control Circuit Using LOGO! V8 PLC
- Star – Delta Starter Motor Control Circuit Using S7-1200 PLC
- Star-Delta Starter for Reverse – Forward Operation Without Timer
- How to Start & Stop a 3-Phase Motor Using Direct-On-Line (DOL) Starter?
- Reverse-Forward of 3-Phase Motor using DOL Starter – Wiring, Power & Control Circuit
- Wire Twin Timer in Repeat Cycle & One-Shot Mode for 120V/240V Motors?
- How to Toggle between Two Heat Pumps using 240V Twin Timer & Contactor?
- How to Control 120V & 240V Water Heater using ST01 Timer and Contactors?
- 1-Phase Automatic Changeover (ATS) using Contactors and Timer
- 3-Phase Automatic Changeover (ATS) using Contactors and Timer


 How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 3-Φ Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel
How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole Breaker in a Three-Phase Panel How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Two-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel How to Wire a Single-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Wire a Single-Pole Circuit Breaker in a 120/240V Panel