Difference Between GFCI and AFCI
Differences between GFCI & AFCI – Ground Fault vs Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter
Faults generated in electrical wires can cause serious injuries to any person & damages to the property if they are left unattended. These faults happen so quickly & can cause accidents that could end up fatal in a matter or milliseconds. In order to prevent such accidents, we use various kinds of protection devices where GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) & AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) are two of these devices used for protection against ground fault & arc fault respectively. Both of these devices break the circuit in case of such fault & there are various differences between them.
- Related Post: Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
Before going into the list of differences between GFCI and AFCI, we are going to discuss about ground fault, arc fault & the basics of these two devices.
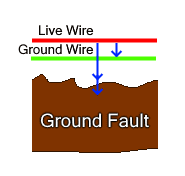
Ground Fault
The Ground fault means when the current flows in the unintended path. In a normal situation, the current should flow from the hot wire into the neutral wire. If the current leaks out of the circuit through a ground wire or any person’s body that came into contact with the ground is said to be a ground fault. The ground fault occurs when the phase wire completes the circuit with the ground. That’s why a proper earthing and grounding is needed in each and every electrical isntallations systems.
Arc Fault
An arc fault is a discharge of a very high power between two or more than two conductors. The arc is generated due to loose cable joints or damage in a flexible cable due to twisting or exposure to heat. Continuous arc generates heat energy that could result in an electrical fire. The arc varies in power & capacity. Normal arcs that are generated every time you toggle a switch or plug a device are not considered as arc faults because they do not cause damage.
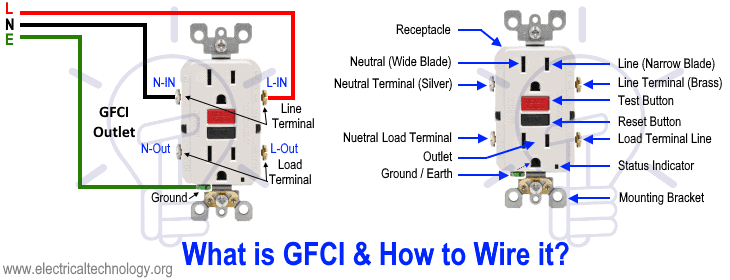
GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter)
GFCI is an abbreviation for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter, it is a protection device that offers protection against ground fault or leakage current. It pops off & breaks the supply when it senses any leakage current flowing out from the circuit. This leakage current caused by the ground fault flows through a human body & wet appliances. Therefore, GFCI helps in prevention against electrical shock & that is why they are installed in wet locations such as bathrooms, kitchen, outdoor etc.
It continuously monitors the current going into the load (appliance) “through hot or live wire” & flowing out of the load “through Neutral Wire”. If there is any difference between the two, the GFCI breaks the current supply. The difference occurs due to the leakage current flowing through the grounded body of a person when the appliance comes into contact with water.
The GFCI uses logic circuitry to sense the current flowing into & out of the appliance. The live wire & neutral wire both run through a CT (current transformer), that will generate no output under normal condition (equal current in live & neutral wire cancels each other effect). If there is an imbalance between them, the CT will generate some output & the logic circuitry detects it. If the current exceeds a certain limit, the logic circuitry breaks the circuit.
It is a very sensitive device that can sense very low current differences. It breaks the circuit when the leakage current exceeds 5 mA within 25ms. The current limit & the tripping time are crucial to protect any person from electrical shock. Because a minimum of 10mA of current through a person’s body is fatal if exposed for a prolonged period of duration.
It has “Test Button” & “Reset Button” usually in black & red colors respectively. It is the main indication of any outlet that has GFCI protection. The “test button” is used for verification of its operation. It momentarily connects the live wire with the neutral wire with in the outlet. The “Reset button” is used for resetting the power supply after it breaks. But you should not press it before disconnecting the appliances connected with it.
The GFCI will never trip due to overloading or any short circuit in the appliance connected. But it will trip the circuit breaker connected with the said GFCI outlet.
- Related Post: How to wire a GFCI Outlet? GFCI Wiring Circuit Diagrams
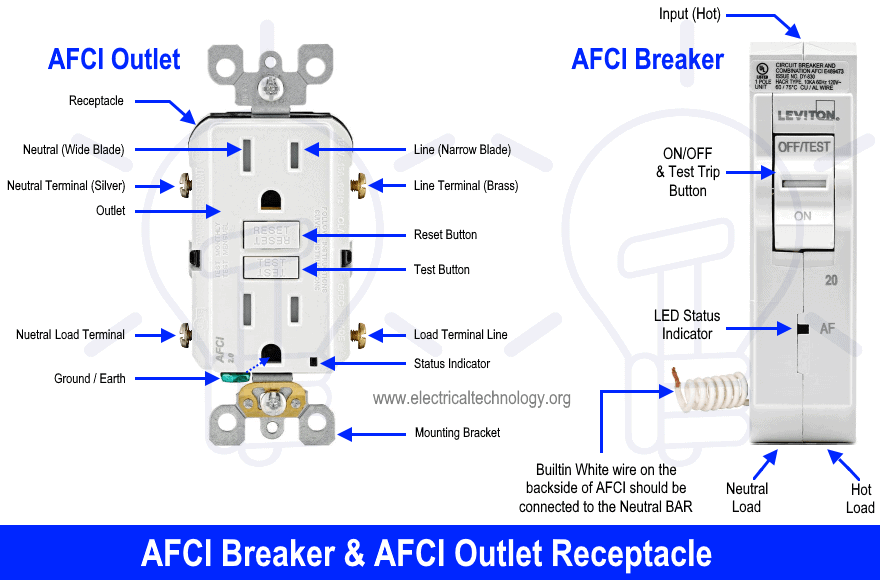
AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter)
AFCI stands for Arc Fault Circuit interrupter; it is a protection device that offers protection against Arc faults. The arc faults are high power discharges between two conductors. The continuous arc can generate enough heat to start a fire & could cause serious damage to property & life. The AFCI breaks the circuit upon sensing any arc in the circuit.
The arcs are generated due to incorrect or loose joints in cables or damaged cables by nail, twisting, kinking, etc. Any loose connection in a power point or old cables may also cause an electrical arc. These continuous arcs can generate enough heat to start a fire & it can disrupt the operation of any sensitive electronic device.
The arcs generate a non-periodic waveform that is detected by using a sensitive logic circuit. It discriminates between a normal arc & an arc fault. As soon as the arc is detected the circuitry trips the power supply but it cannot prevent the first arc. Although it can prevent the ones that follow & avoid a potential fire hazard.
The AFCI has a “Test & Reset button” that is used for verifying its operation & resetting the power supply after it trips. The test button feeds an arc-like waveform to the arc detector in its logic circuit. If the AFCI is switched on, pressing the test button will trip the circuit if it works properly, otherwise, it is defected & you should ask for a professional to inspect it.
Main Differences between GFCI and AFCI
| GFCI | AFCI |
| it is a protection device that offers protection against Ground faults. | It is a protection device that offers protection against Arc fault. |
| It stands for Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. | It stands for Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. |
| It breaks the circuit when there is a leakage current. | It breaks the circuit only when there is an electrical arc in the circuit. |
| It helps in the prevention of electrical shocks. | It helps in the prevention of electrical fire caused by an electrical arc. |
| It must be installed in only wet areas such as bathrooms, pools, kitchen etc. | It is required to be installed in a branching circuit that provides power to outlets in the residential room, dining room, etc. |
| GFCI Receptacles are more preferred than its breaker. | The AFCI breakers are more preferred than its receptacles. |
| The GFCI usually prevents electrocution from the connected load. | The AFCI usually protects from arcs in branching circuits. |
| It protects from accidents that happen outside the walls. | It prevents accidents from happening inside the walls. |
| GFCI is often installed at the power outlets in wet areas. | The AFCI breakers are installed at the main electrical panel. |
The conclusion of this article is that the GFCI is used for prevention of electrical shocks & the AFCI is used for the prevention of electrical fires.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCB, RCD or RCCB Circuit Breakers
- Main Difference between Contactor and Starter
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit & Vice Versa?
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference Between Neutral, Ground and Earth
- How to wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker?









This interesting and very useful
This is the best web page. Thank you for making it so simple to understand. Super great help.
this is a great work and educative