Induction Motor & Linear Induction Motors Formulas & Equations
Formulas and Equations for Linear and Induction Motors
The following equations and formulas related to linear and induction motors can be used to calculate the basic parameters while analyzing and designing a single phase and three phase induction motor.
Formula and Equations for Induction Motor:
Induced EMF:
eind = vBl
where
- eind = induced EMF
- v = velocity of the rotor
- B = magnetic flux density
- l = length of conductors inside magnetic field
Rotor Current:
The rotor current is given by:

Torque Induced:
Terms used in Motor Torque Equations and formulas.
- Ns = Synchronous speed
- s = slip of the motor
- sb = breakdown or pull-out slip
- E1 = stator voltage or input voltage
- E2 = Rotor EMF per phase at a standstill
- R2 = Rotor Resistance Per Phase
- X2 = Rotor Reactance Per Phase
- V = supply voltage
- K = rotor/stator turn ration per Phase
Starting Torque
- Maximum Starting Torque Condition
R2 = X2
- Starting Torque Relation With Supply Voltage
Tst α V2
- Torque In Running Condition
- Gross Torque
- Maximum Running Torque Condition
R2 = sX2
- Maximum Running Torque
- Breakdown Slip
- Torque Relation With Max Torque
Slip Speed & Slip of Induction Motor:
Slip speed is the difference between synchronous speed and rotor speed;
- Nslip = Ns – N (Speed in RPM)
- ωslip = ωs – ω (Angular speed in Rad/sec)
Where
- Nslip = Slip speed
- Ns = Synchronous speed = 120f/P
- N = Rotor speed of motor
The slip of induction motor is a relative term expressed in percentage. It is given by:
Where
- S is the slip of induction motor
Rotor Speed:
The rotor speed of induction motor is given by
- N = (1-s)Ns (Speed in RPM)
- ω = (1-s) ω s (Angular speed in Rad/sec)
Electrical Frequency on the Rotor:
Where
- fr = Rotor Frequency
- f = Line Frequency
- P = Number of Poles
Power of Induction Motor:
Related terms used in Motor Power Formulas and Equation.
- P1 = Stator input Power
- P2 = Rotor Input power
- Pm = Rotor Gross Output Power
- Pout = Output Power
- Tg = gross torque
- Tsh = shaft torque
Rotor Input Power:
P2 = Tgωs
- Rotor Gross Output Power:
Pm = Tgω
- Output Power:
Pout = Tshω
P1 = P2 + stator Losses = Pm + Rotor Copper Losses = Pout + Windage & friction Losses
Rotor Input Power: Output Mechanical Power: Rotor Cu loss ratio:
Where
- Pcr = I2R = rotor Copper loss
Synchronous Watt:
The torque at which the machine at synchronous speed will generate one watt;
Efficiency of Induction Motor:
- Rotor Efficiency:
- Overall Efficiency
Formula & Equations for Linear Induction Motor:
Synchronous Speed:
- vs = linear synchronous speed
- w = width of one pole-pitch
- f = line frequency
Slip:
Where
- vs = linear synchronous speed
- v = Actual speed
Thrust or Force:
Where
P2 = Rotor input Power
Rotor Cu Loss:
Gross Mechanical Power: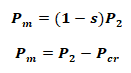
Related Formulas and Equations Posts:
- Transformer Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Engineering Formulas and Equations
- Basic Electrical Quantities Formulas
- Power Formulas in DC and AC Single-Phase & Three-Phase Circuits
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Electric Motors Symbols



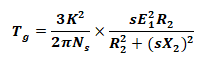
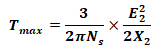


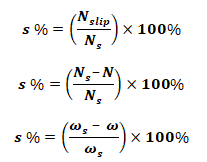
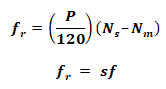
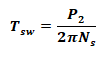
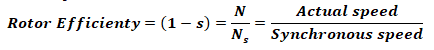
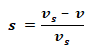
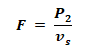




In the article “Voltage And Power Equations of a DC Motor” the iron losses are also important. Those losses can not be neglected in real cases instead of ideal cases. By the way, it is interesting to use these equations to simplify the circuit analysis and calculations.