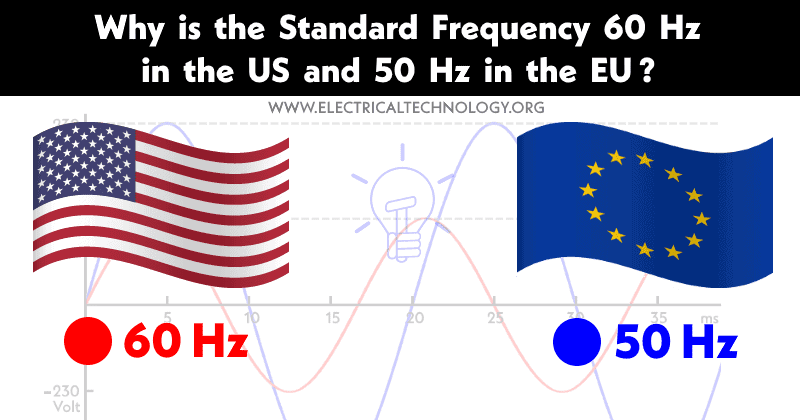
Why is the Standard Frequency 60 Hz in the US & 50 Hz in the EU?
Why is the Standard Frequency for Supply in the EU 50 Hz, But 60 Hz in the US? And Why Were Other Higher or Lower Frequencies Not Chosen?
In the U.S, the entire power system (including transmission and distribution for both residential and commercial applications) is somewhat complex and differs from systems used in other parts of the world. For example, the common household single-phase supply in North America is 120V (between Phase/Hot and Neutral) and 240V (between Hot 1 and Hot 2), operating at 60Hz. Similarly, other voltage levels, such as 208V, 277V, and 480V, are used in residential and commercial applications.
These systems, which comply with ANSI/NEMA standards, are used in North America (USA, Canada, Mexico) and parts of South America, such as Venezuela, Costa Rica, the Dominican Republic, Ecuador, Guatemala, Guyana, and Panama.
In contrast, the UK and IEC-standard countries follow a different system, where the single-phase residential supply is 230V, and the three-phase supply is 400V, operating at 50Hz.
The power supply frequency is one of the critical parameters in electrical power systems. It is essential to have a standard frequency across a particular region or country to ensure the compatibility of all electrical equipment and appliances.
The frequencies of 50 Hz and 60 Hz for power supply are standard because they have been selected as the most practical options for AC power systems. There are several reasons why only 50 Hz and 60 Hz frequencies have been chosen for power supply, and why other higher or lower frequencies were not selected.
In earlier days when AC took power over DC, the engineers found the suitable frequency for a typical power system between 87Hz to 133 Hz. Later, they lowered the frequency due to generated harmonics by higher frequency and strop effect in lamps due to lower frequencies. Thus, they revealed the most appropriate range somewhat between 50 Hz and 67Hz.
As the frequencies were not fixed at that time due to the limitation and unavailability of that wide range of appliances and machines, the IEC following countries (including most of them are in EU now) opted for 50 Hz in 1958 while the US adopted the 60 Hz frequency for the power system. The rest of the world opted for either EU and US standards (e.g. 50 Hz and 60 Hz).
The selection of standard frequency either 50 Hz or 60 Hz has a combination of factors such as historical, technical, and economic reasons for each region due to the system configuration, technology and compatibility with wide ranges of electrical machines. So now let’s see why the US opted for 60Hz and UK and EU selected the 50 Hz of supply frequency?
Good to Know:
- Westinghouse Electric by George Westinghouse is responsible for standardizing the 60Hz frequency for AC voltage levels in the US
- A German company AEG standardized the frequency of 50 Hz for 220 to 230V and later adopted it by UK and other IEC countries including Europe.
Related Posts:
- Difference Between 50 Hz and 60 Hz Frequency System
- Advantages & Disadvantages of 50 Hz and 60 Hz Frequency Power Supply
Selection of 60 Hz Frequency in the US & 50 Hz in the EU
The US, including North American countries, uses a standard power supply frequency of 60 Hz, which is different from the 50 Hz frequency used in the UK, EU and IEC following countries. Let’s why the US chose 60 Hz frequency and UK/EU opted for 50 Hz as the standard power supply and why other frequencies were not selected.
Historical Based Decision:
In the early days of the US power industry, there were many competing standards for power supply frequency. The first power plants used direct current (DC) generators, which did not have a fixed frequency. However, the development of alternating current (AC) generators made it possible to standardize the frequency of the power supply.
The earliest AC generators produced a frequency of 133 Hz, but this frequency was too high for most electrical equipment and appliances. In 1891, the US power industry settled on a standard frequency of 60 Hz, which was lower than 133 Hz but higher than the 50 Hz frequency later adopted by the UK and EU.
The choice of 50 Hz frequency as the standard power supply in the UK and EU has historical reasons. The UK was one of the first countries to establish a public electricity supply network, and in the late 1800s, the frequency of the electricity supply varied widely between different regions. The UK later settled on a frequency of 50 Hz in the early 20th century.
Similarly, in the EU, the frequency of the power supply varied widely between different countries, and a standard frequency was needed to ensure the compatibility of electrical equipment. In 1958, the EU settled on a standard frequency of 50 Hz.
Related Posts:
- Which One is More Dangerous? 50Hz or 60Hz in 120V/230V & Why?
- Which Transformer is More Efficient When Operates on 50Hz or 60Hz?
Selection Based on Technical Advancement:
The choice of 60 Hz frequency in the US and 50 Hz in the UK and EU was partly based on technical considerations. The early AC generators used a rotating armature design, which limited the speed at which the generator could operate. The frequency of the power supply is directly related to the speed of the generator, so a lower frequency requires a larger and heavier generator. A higher frequency, on the other hand, required a smaller and lighter generator.
At the time, 60 Hz was considered the optimal frequency for balancing the size and weight of the generator with the power output required by most electrical equipment and appliances. The 60 Hz frequency also provided better motor performance, particularly for motors used in industry and transportation. On the other hand, 50 Hz frequencies have their own advantages (mentioned below) as compared to the 60 Hz frequency.
Economically Suitable Choice
The choice of 60 Hz frequency in the US and 50 Hz in the EU and UK was also influenced by economic considerations. The US power industry was expanding rapidly in the early 1900s, and standardizing the frequency of the power supply made it easier to build a nationwide transmission network. A standard frequency also facilitated the interconnection of power systems, which improved reliability and reduced costs.
In addition, the US as well as UK and EU had a large and growing market for electrical equipment and appliances, and a standard frequency ensured compatibility and reduced costs for manufacturers and consumers.
Related Posts:
- Can We Operate a 60Hz Transformer on 50Hz Supply Source and Vice Versa?
- Is it Possible to Operate a 50Hz Transformer on 5Hz or 500Hz Frequency?
Power Generation and Transmission:
Electricity is generated by rotating turbines in power plants, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The turbines are driven by steam or water, and the speed of the turbines determines the frequency of the generated electricity. In the UK and EU, the standard frequency is 50 Hz, which means that the turbines in power plants rotate at 3000 RPM (revolutions per minute). Same is the case for North American 60 Hz frequency power supply systems.
The generated electricity is then transmitted to the consumers through a network of transmission lines and transformers. The frequency of the electricity remains constant throughout the transmission network. Any variation in the frequency can cause instability in the power system, leading to power outages and damage to electrical equipment.
Compatibility of Electrical Appliances with 50/60 Hz:
The frequency of the power supply is crucial in ensuring the compatibility of electrical appliances. Most electrical equipment and appliances are designed to operate at a specific frequency. Using a frequency other than the design frequency can cause the equipment to malfunction or even damage it.
As a major manufacturer, The US, UK and EU have a vast market for electrical equipment and appliances, and most of these products are designed to operate at 50 Hz and 60 Hz frequency. Changing the frequency would require significant modifications to the existing equipment, which would be costly and impractical.
Related Posts:
Advantages of 60 Hz Frequency:
The 60 Hz frequency provides several advantages in the US power system. Firstly, it is compatible with the majority of electrical machines, devices, equipment and appliances used in the US and North America, which reduces costs for manufacturers and consumers. Secondly, it provides better motor performance, particularly for motors used in industry and transportation. Thirdly, it is easier to synchronize the power supply across different regions and interconnect power systems.
Moreover, the 60 Hz of frequency has the following additional advantages.
- Size of electrical machines is smaller.
- Higher speed of electrical machines such as motors etc.
- Small size conductor is needed at 60 Hz, 240V as compared to 50 Hz, 230V AC.
Related Posts:
- Chart List of Standard Voltage and Frequency Around the World
- Difference Between 120V and 240V/230V AC Power Supply
Advantages of 50 Hz Frequency:
The 50 Hz frequency provides several advantages in the UK and EU power system over 60 Hz of frequency as follows:
- Higher power factor.
- Higher torque in electrical motors.
- Better cooling of electrical machines.
- Better life time of bearings.
- Reduced constant and variable power losses.
- Need small size of conductor
- Low noise in the machines.
- Low insulation is needed
- Overall efficiency of electrical machines is greater.
Lastly, 50 Hz is compatible with the majority of electrical equipment and appliances used in the UK, EU and other IEC following countries.
Related Interesting and Informative Questions & Answers:
- Difference Between Current and Voltage
- Difference between AC and DC (Current & Voltage)
- Difference Between Single Phase and Three Phase Power Supply
- Why 3-Phase Power? Why Not 6, 12 or More for Power Transmission?
- If a 1-Phase Supply is 230V, Why is 3-Phase 400V & Not 690V?
- Difference Between Socket, Outlet and Receptacle
- Why Do Prongs in Electrical Plugs Have Holes in Them?
- Why Don’t Birds and Squirrels Get Electrocuted on Power Lines?
- Why are Salt and Charcoal Added in Earthing Pit for Grounding?
- What are the Colored Aerial Marker Balls on Power Lines For?
- Which Bulb Glows Brighter When Connected in Series and Parallel & Why?
- Why Can’t a 12V Car Battery Electrocute You?
- Stranded Wire vs Solid Wire. Which One is Best and Why?
- Why are US Homes Wired Using Solid Wire rather than Stranded Wire?





Then we have Japan with half the country on 50 cycles and half on 60 cycles. The US now uses 240 volts for high current equipment. Would it not make sense to standardize globally on 240 volts 60 cycles?
Does this also explain why American kitchens boil a kettle on a gas stove, we in Britain, everyone uses an electric kettle 240 volts @2400 watts.
The frequency doesn’t affect electrical resistance devices like tea kettles. The voltage does.
At 120 volts, a typical appliance needs to draw less than 15 Amps, because older houses are wired with 14 AWG wire, and therefore have 15 Amp fuses or breakers, so most heating appliances are limited to 1500 Watts.
At 240 Volts with a current limit of 13 Amps (That’s a WTF all by itself) allows for much more powerful appliances. Remember that when these standards were being adopted, the predominant electrical appliances were lamps!
I’ve read about how domestic wiring is done in the UK,especially grounding, and it doesn’t make a lick of sense to me.
Not sure I agree with all the 50HZ advantages. Insulation difference is all about voltage, bearing life is about RPM and shaft loads such as caused by belts, conductor sizes based on motor HP, and the claim on power losses. Just be glad there is no push to convert the US to 50Hz as there is for metric.