Thermal Power Plant – Components, Working and Site Selection
How a Thermal Power Plant Works?
What is a Thermal Power Plant?
According to energy conservation law, energy is neither created nor destroyed. But we can convert one form of energy into other forms of energy. Electrical energy can be derived from many other sources of energy. And the plant that is used to generate a bulk amount of electrical energy is known as a power plant or power station.
In the thermal power plant, the electrical energy is transformed from heat energy. Heat energy can be derived from different heat sources like; coal, diesel, biofuel, solar energy, nuclear energy, etc.
The power plant that uses coal to generate heat is known as the thermal power plant. The thermal power plant is a conventional power plant. Sometimes, the thermal power plant is also known as a steal-turbine power plant or coal power plant.
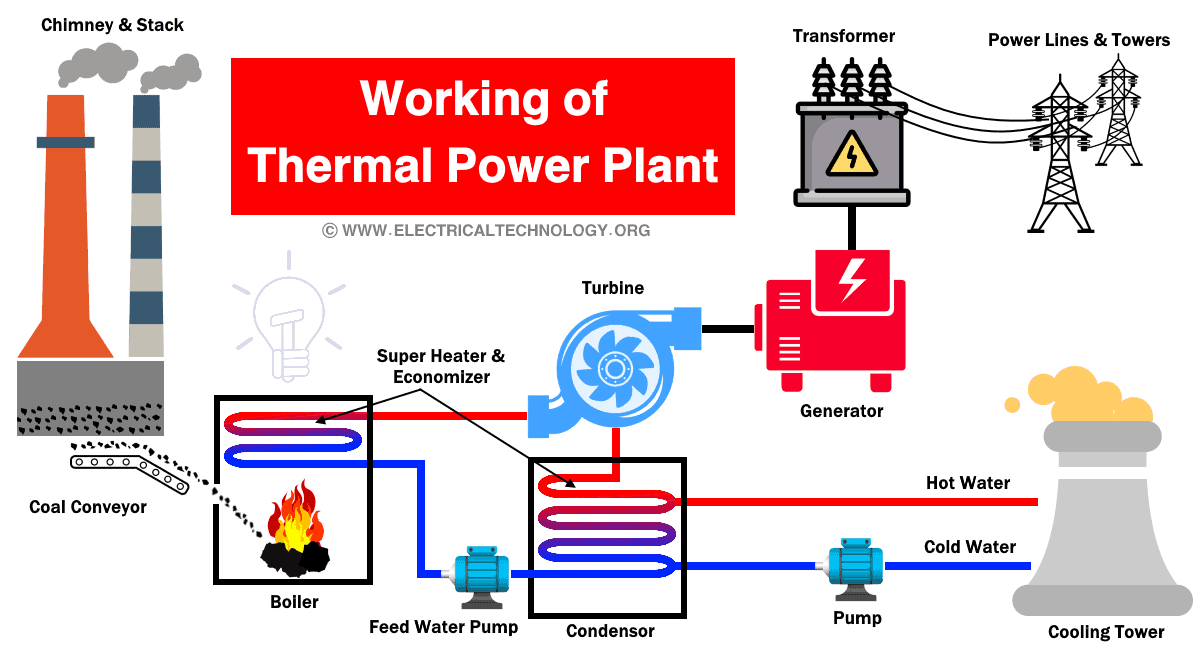
Working of Thermal Power Plant
The thermal power plant works on the Rankine cycle. A one-line diagram or layout of the thermal power plant is as shown in the below figure.
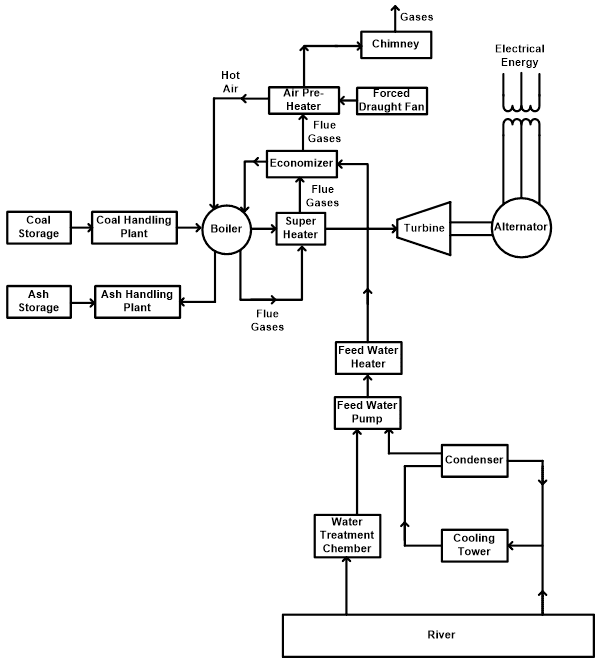
In a thermal power plant, a very large amount of fuel (coal) is required. Therefore, the coal is transported via trains to the fuel storage space. The size of coal is very large that is not suitable for the boiler. So, the coal is crushed in small pieces via crusher and fed to the boiler.
To produce steam in the boiler, a high amount of water is also required in the thermal power plant. The water is treated with filters and free from impurities and air. After that, the water is fed to the boiler drum. In the boiler drum, the combustion heat from the fuel is transferred to the water. And the water converts into steam.
This steam is high-pressure and high-temperature steam. Further, this steam is supplied to the superheater. And this super-heated steam is supplied to the turbine blades.
So, the heat energy is converted into rotational energy of mechanical energy by the turbine. The turbine is mechanically connected to the same shaft as the alternator. So, the turbine rotates the rotor of the alternator. An alternator is used to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy.
Further, the electrical energy is converted into high voltage using a transformer and transfer the electrical energy to the load via a transmission line in a typical power system.
The steam released from the turbine is supplied to the condenser. In the condenser, the exhaust steam is condensed by means of cold-water circulation. And the steam releases pressure and temperature. This will increase the efficiency of the cycle.
The condensed water again fed to the boiler with the help of the feedwater pump and used in the cycle.
The ash is produced after the combustion of coal. So, it was taken out from the boiler furnace. And it is necessary to dispose of properly without damage the environment.
While combustion of coal in a boiler, the flue gases exhaust the atmosphere from the chimney.
Components of Thermal Power Plant
In a thermal power plant, various components are used in the cycle. Here we have listed, main components of the thermal power plant.
- Boiler
- Turbine
- Super-heater
- Condenser
- Economizer
- Feedwater pump
- Alternator
- Chimney
- Cooling tower
Boiler
The pulverized coal is fed to the boiler with preheated air. The boiler is used to produce high-pressure steam.
The boiler in the thermal power plant is used to convert the chemical energy of coal into thermal energy or heat energy. During the combustion of coal, a high temperature is produced inside the boiler. This temperature is high enough to convert water into steam.
The size of the boiler depends on the amount of heat required for the thermal power plant. And there are several types of boiler used in a thermal power plant like; Haycock and wagon top boiler, firetube boiler, Cylindrical fire-tube boiler, water-tube boiler, etc.
Turbine
The high pressure and high-temperature steam are fed to the boiler. This superheated steam is a strike on the turbine blade. And the turbine starts rotating. The turbine is a mechanical device that is used to convert the heat energy of steam into rotational energy or kinetic energy.
The turbine is mechanically coupled with an alternator via a shaft. When the steam release from the turbine, the temperature and pressure is reduced. And this steam is passed to the condenser.
Super-heater
In a steam turbine, super-heated steam is used to rotate the turbine. The wet and saturated steam is supplied to the super-heater. And it is a device that converts it into dry and superheated steam.
The super-heater’s temperature is the highest among all components of the thermal power plant. In the thermal power plant; there are three types of superheaters used; convection, radiant, and separately fired.
The superheater is used to increase the temperature of the steam generated from the boiler. This will increase the thermal energy of the steam.
Condenser
When the steam release from the turbine, the temperature and pressure is decreased. The exhaust steam of the turbine reuse in the cycle. To increase the turbine efficiency, we need to condense this steam to maintain a proper vacuum.
The condenser decreases the operating pressure. So, the vacuum is increased. And this will increase the volume of steam that results in more amount of work available at the turbine. And due to this, the plant efficiency will increase with the increase in turbine output.
Economizer
The economizer is a heat exchanger device that is used to reduce energy consumption. In the boiler, flue gases are exhausted into the atmosphere. These gases have a high temperature. So, the economizer uses the heat of flue gases to heat the water.
The water release from the condenser is again used in the cycle. With the help of a feedwater pump, this water is transferred to the economizer. An economizer uses the heat of flue gases to increase the temperature of the water.
The economizer uses the waste heat of flue gases. Hence, it is used to increase the efficiency of the entire cycle.
Feedwater pump
A feedwater pump is used to supply water into the boiler. The water may be from the condenser or freshwater. This pump is used to pressure the water. Generally, the feedwater pump is a centrifugal type or positive displacement type of pump.
Alternator
The alternator and turbine are connected on the same shaft. The turbine rotates with the flow of steam and the turbine rotates. The rotor of the alternator rotates and generates electrical energy. Therefore, the alternator is a device that converts kinetic energy or rotational energy into electrical energy.
Chimney
In most of the thermal power plants, coal is used as fuel. During the combustion of coal, the flue gases are generated in the boiler. The chimney provides a path to the flue gas and exhaust to the atmosphere.
The chimney works based on the natural draft and stack effect. The hot air is light in weight and it goes up. The height of the chimney is high. The taller height, the more draft or draught is created.
Cooling tower
As the name suggests, the cooling tower is used to reject waste heat in the atmosphere. Different heat transfer methods are used in the cooling tower. The heat of the water evaporates into the atmosphere. And remains cool water that further use in the cycle.
The condenser converted steam into water. And the water that comes from the condenser is supplied to the cooling tower. Generally, forced flow cooling towers are used in the thermal power plant. And the air is circulated from bottom to top of the tower.
- Related Post: What is Nuclear Power and How Nuclear Power Plant Works?
Site Selection of Thermal Power Plant
Various factors affect for selection of the site of a thermal power plant. The following factors should be considered while a selection of thermal power plants.
Availability of fuel:
In most of the thermal power plants, coal is used as a fuel. The power plants are used to generate a bulk amount of electrical energy. And for that, a greater amount of coal is required. Therefore, the thermal power plants are placed near the coal mine to reduce the cost of transportation.
Transportation facility:
There are several pieces of machinery used in the thermal power plant. These machineries are very big in size. So, the location is selected where adequate transportation facility available. For transportation of coal, rail or road transportation is required. The power plant is handled by several technicians, workers, and engineers. So, the location of the plant is selected where the public transport easily available.
Availability of water:
In a thermal power plant, to produce high pressure and high-temperature steam, a huge amount of water is required. So, it is necessary that the plant must be located near the bank of a river or at a place where a continuous supply of water is available.
Availability of land:
To install a thermal power plant large space is required. And the cost of land must be low. The land was chosen with consideration of future expansion if necessary. The plant requires many heavy types of machinery. Hence, the ground should be bearing the load of machinery and the foundation must be strong.
Far from populated area:
The thermal power plant exhausts flue gases, ash, dust, and smoke. And these things are a danger for a human being. So, it is necessary that the plant must be placed far from the city area. The surrounding atmosphere and land may damage due to ash and gases. So, the place chosen for a plant is kept as far as from the populated area and farms.
The plant has several types of machinery like the alternator, power transformer, fans, pumps, turbines, etc. Therefore, it produces noise in the surrounded area.
Ash disposal facility:
After the combustion of coal, the ash generated 30-40% of total coal consumption. And the ash is the main byproduct of the thermal power plant. And it is necessary to proper disposal of ash.
The ash is collected from the bottom of the boiler furnace and most of the ash particles are flue with gases. So, there is two ash handling systems; one is the bottom ash handling system and the second is the fly ash handling system.
Near to the load center:
The electrical energy is generated from the alternator. And the alternator is connected with the power transformer to step up the voltage level. High voltage power is transmitted to the load center via a transmission line. So, to reduce the transmission cost, the plant is located near the load center.
Efficiency of Thermal Power Plant
In a thermal power plant, the electrical energy is generated from two energy conversion. The chemical energy of coal is converted into thermal energy of heat energy. After the thermal energy is converted into kinetic energy or mechanical energy. And finally, the mechanical energy is converted into electrical energy. So, due to the number of energy conversions, the efficiency of thermal power plants is very low around 20-29%.
The efficiency of a thermal power plant is also depending on the size of the plant and the quality of coal. In a thermal power plant, the heat energy is lost in the condenser. There are two types of efficiency in thermal power plants.
- Thermal efficiency
- Overall efficiency
Thermal efficiency:
Thermal efficiency is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent mechanical energy available at the turbine to the heat energy available at the combustion of coal in the boiler.
The thermal efficiency of the thermal power plants is 30% approx. Most of the heat energy (approx. 50%) is wasted in the condenser. The rest of the heat energy is wasted in the flue gases, ash etc.
Overall efficiency:
The overall efficiency is defined as the ratio of heat equivalent of electrical output to the heat of combustion of coal.
The overall efficiency includes the losses that occur at all stages of a cycle. It also includes the efficiency of an alternator.
The overall efficiency of a thermal power plant depends on its size and rating of a power plant in MW. Lower the capacity, lower the efficiency.
| Installed Plant Capacity | Average Overall Thermal Efficiency |
| Up to 1 MW | 4% |
| 1 MW to 10 MW | 12% |
| 10 MW to 50 MW | 16% |
| 50 MW to 100 MW | 24% |
| More than 100 MW | 27% |
Related Posts:
- What is HVDC? High Voltage Direct Current Power Transmission
- Differences Between HVAC and HVDC Power Transmission
- Advantages of HVDC over HVAC Power Transmission
Advantages & Disadvantages of Thermal Power Plant
Advantages
The advantages of a thermal power plant are listed below.
- The initial cost of this plant is less compared to other power plants.
- The cost of fuel is less.
- Running cost is less compared to a diesel power plant.
- It is less depending on the seasons. Most thermal power plants running throughout the year.
- The coal is easily available and easy to transport in bulk quantity.
- Compared to hydropower plants, it requires less space.
- The maintenance of thermal power plants is less compared to the other power plants.
- This plant can be installed in any location where adequate transport facility and bulk water is available.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of the thermal power plants are as listed below.
- The thermal power plant uses coal as a fuel. And it is a conventional source of energy. So, we need to use less conventional sources for a better future.
- Coal is a commodity. So, the price of coal depends on the commodity market and it varies day by day.
- The running cost of this plant is high compared to a hydro power plant.
- It produces ash as a by-product. And it is necessary to dispose of ash without harming the environment.
- Due to the combustion of coal, flew gases and smoke are released into the atmosphere. Therefore, this plant is not environmentally friendly.
- It produces harmful noise in the surrounded area. So, it affects workers and the people leave nearby areas.
- The overall efficiency of the thermal power plant is very less. It is approx. 30%.
Related Posts:
- What is Electricity? Types, Sources & Generation of Electricity
- What is Electrical Power? Types of Electric Power and their Units
- Energy and Power Consumption Calculator – kWh Calculator
- FACTS – Flexible AC Transmission System – Types of FACTS Controllers & Devices
- Why Electric Power Transmission is Multiple of 11 i.e. 11kV, 22kV, 66kV etc?
- Corona Effect & Discharge in Transmission Lines & Power System
- Why Power Transmission Cables & Lines are Loose on Electric Poles & Transmission Towers?
- Difference between AC and DC Transmission System & Power Lines
- Design and Installation of EHV/EHV and EHV/HV Substations

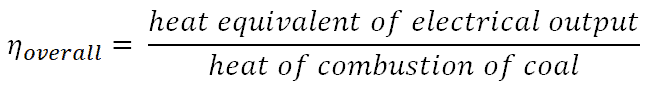






This article does a fantastic job explaining the principles, working, and key functions of thermal power plants! The section on the functions of different components is particularly clear and easy to follow, making it a great resource for anyone studying power generation.