How to Wire a 20A – 250V Outlet – NEMA 6-20 Receptacle
How to Install a Standard 20A – 250V Receptacle (NEMA 6-20) with Breaker and GFCI Protection
A NEMA 6-20 receptacle is a 250V – 20A, 2-P, 3-W grounding outlet. The 20A – 240V outlet is used for heavy-duty 240V appliances and equipment that do not require a neutral connection. In other words, It only requires two hot wires and a ground. These outlets are generally found in residential, commercial and industrial buildings and specific appliances operates on 240V supply.
Example loads are air conditioners (window or split units), compressors, kitchen countertops, bathroom and laundry rooms for washers and dryers, commercial lighting equipment, motors, water heaters, HVAC control units, welders, workshops and other dedicated circuits.
The NEMA 6-20 Outlets and Receptacles
A NEMA 6-20 receptacle is a 20A – 250V (often called 240V) outlet designed primarily for single-phase, 2-pole, 3-wire grounding circuits.
It differs from a standard 120V outlet by having two hot slots for blades and one ground pin instead of one hot, one neutral, and one ground pin. The horizontal slot is used for Hot 1 and the T-shaped slots is used for hot 2. The round ground (u-shaped) slot is used for ground pin.
This configuration is designed where both 15A and 20A operated at 240V plugs can be inserted into the outlet. It is used for demanding high-power devices in both residential and commercial applications. NEMA 6-20R (20A version) is more frequently used for new 240V equipment instead of older versions such as NEMA 6-15R.
The corresponding plug to use with NEMA 6-20R is a NEMA 6-20P. It means, it is only allowed for 250V equipment and not for 120V loads. In addition, it must be installed on a dedicated 20A / 240V circuit.
In simple terms, a standard 20-amp outlet can accept both 15-amp and 20-amp plugs, but a 15-amp outlet cannot accept a 20-amp plug.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
Terminals
There are three terminals in a 6-20R outlet in accordance with UL/CSA.
- Hot 1 (L1): Black Wire → Right Side Brass Screw – Horizontal Slot (➖)
- Hot 2 (L2): Red Wire → Left Side Brass Screw – T-Shaped Slot (⊣)
- Ground (G) for EGC (⏚): Green or Bare wire → Green Screw – (U) Shaped Terminal.
Electrical Ratings & Specifications
- NEMA: 6-20R – Straight-Blade, Duplex Receptacle
- Poles: 2-Poles, 3 Wires Grounding
- Voltage: 250V Single-Phase AC Supply – 60 Hz
- Current: 20A – 16A
- Breaker / GFCI: 20A – 2P
- Wattage: 4,800 W
- Wire Size: #12AWG Copper
- Grade & Material: Commercial Grade – Thermoplastic Nylon Face & Zinc-Plated Steel
- Termination: Back & Side Wired
- Mounting: Flush / Screw Mounting
- Wiring: Hardwired / Dedicated Circuit
Wiring NEMA 6-20R Outlet
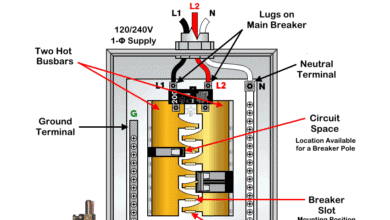
Wiring 20A – 240V Outlet using 2-P Breaker
The following wiring diagram illustrates the wiring connections of a 20A, 250V outlet (NEMA 6-20R) to a two-pole, 240V – 20A circuit breaker in a 120/240V main panel.
Wiring Instructions for NEMA 6-20R Outlet
- Strip the Insulation: Remove about 3/4 inch (19 mm or 1.9 cm) of insulation from the side wire, and about 1/2 inch (12.7 mm or 1.27 cm) from the back wire.
- Connect the ground wire: Attach the bare or green wire to the green screw, which is the centered, round, or U-shaped “G” terminal.
- Connect Hot 1 (black): Secure the black wire to the brass screw on the left horizontal slot terminal.
- Connect Hot 2 (red): Secure the red wire to the brass screw on the right “T-shaped” slot terminal.
- Tighten all terminal screws: Torque each screw to approximately 14-18 lb-in (1.6-2 N·m) to ensure a solid electrical connection.
For this installation, use #12 AWG copper wire, which is the correct conductor size for a 20A circuit and compatible with the NEMA 6-20R outlet.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
Wiring a 20A – 240V Switched Outlet
Following the same wiring diagram shown above, a 20A – 240V outlet can be wired and controlled using a double-pole, single-throw (DPST) 20A switch.
As illustrated in the figure:
- The Hot 1 (black) wire from the two-pole 20A breaker is connected to the Line 1 (L1) terminal of the DPST switch.
- The outgoing Hot 1 (com 1) wire from the switch is then connected to the brass terminal (Hot 1 side) of the outlet.
- Similarly, the Line 2 (L2) terminal from the breaker to the switch and then (Com 2) from switch is connected to the Hot 2 (T-shaped slot) side of the outlet using a red wire.
- Finally, the ground (bare or green) wire is connected to the ground terminal of the outlet, just as in a standard outlet wiring setup.
This way, the ON/OFF operation of the 20A – 240V outlet can be controlled using a switch. When the switch is ON, the outlet will be energized (operational), and when the switch is OFF, the outlet will be de-energized (off).
If the breakaway fin tab between the brass terminals of the outlet remains intact, both receptacles will be controlled simultaneously by the switch for ON/OFF operation. However, if the tab between the hot terminals is removed, only the upper receptacle of the duplex outlet will be controlled by the switch, while the lower receptacle will remain continuously energized, regardless of the switch position.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
In certain applications, this breakaway tab may be removed to split the receptacle, allowing each outlet to be powered independently. This configuration is commonly illustrated in wiring diagrams for various outlet and receptacle installations.
Wiring 20A – 120V Receptacle with GFCI
According to NEC 210.8, GFCI protection is required for receptacles installed in garages, basements, outdoors, laundry areas, and other wet or damp locations. Specifically, NEC 210.8(A)(1) through (A)(11) mandates that all outdoor receptacles must be installed downstream of GFCI protection, in accordance with Articles 426.28 and 427.22.
Currently, only 15A and 20A GFCI receptacles rated for 120V are available, typically in NEMA 5-15 and NEMA 5-20 configurations. For 240V outlets, GFCI protection must be provided using GFCI circuit breakers, as 240V GFCI receptacles are not yet available.
To wire a 20A, 240V outlet in any location where GFCI protection is required by code, simply replace the standard two-pole 20A breaker with a GFCI circuit breaker (two-pole, 20A, 240V). The rest of the wiring remains unchanged, as shown in the following wiring diagram.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge

FAQs:
How Many Amps Can a 20A – 240V Outlet Handle Safely?
A 20A, 240V outlet can safely handle up to 20 amps of continuous current. However, according to the NEC 80% rule (NEC 210.19(A)(1)), continuous loads (lasting more than 3 hours) should not exceed 16 amps on a 20A circuit.
- This guideline is in accordance with NEC Articles 210.19(A), 210.20(A), 215.2(A), 215.3, and 230.42(A), which require branch circuits and feeders to be sized based on the continuous and non-continuous load conditions.
How Many Watts Can a 20A – 240V Receptacle Hold?
At full capacity (non-continuous load):
- 240V × 20A = 4,800W
For continuous loads (80% rule):
- 240V × 16A= 3,840W
So, a 20A–240V outlet can handle up to 4,800 watts, but only 3,840 watts continuously.
Which Breaker Size is Suitable for a 20A – 240V Receptacle?
The suitable breaker size is 240V, 20A, double-pole circuit breaker or GFCI for a 20A–240V outlet. The double-pole breaker ensures both hot legs are simultaneously disconnected during faults or maintenance.
What is the Correct Wire Size and Cable Type to Use with a 20A – 240V Outlet?
As per NEC Table 310.16, Table 210.24(1), and NEC 240.4(D)(6), the minimum required wire size for 20A – 240V outlet is 12 AWG copper.
- Cable Type: Use 12/2 with ground cable (THHN or NM-B type depending on installation) for 240V circuits.
- For longer runs (over 100 ft), consider 10 AWG to reduce voltage drop.
In short, 20-amp circuit should use #12 AWG copper or #10 AWG aluminum (minimum) for safe operation – based on NEC. Moreover, the equipment grounding conductor (EGC) can be #12 AWG copper, as specified in NEC Table 250.122 for the protection of a 20A circuit.
Can I Use a 20A Outlet on a 15A Circuit Breaker and Vice Versa?
- No, you cannot install a 20A outlet on a 15A breaker. The outlet’s T-slot design allows 20A plugs, which can overload the 15A circuit.
- You can use a 15A outlet on a 20A breaker only if there are multiple outlets on the same circuit (per NEC 210.21(B)(3)).
Can I Use a 20A Outlet on a 15A Circuit and Vice Versa?
Same rule applies i.e.
- No for a 20A outlet on a 15A circuit.
- Yes for a 15A outlet on a 20A circuit if it’s part of a branch circuit with multiple receptacles.
Can a 15A Device be Plugged into a 20A Outlet?
Yes. Most 20A receptacles (such as NEMA 6-20R) are designed to accept both 15A (6-15P) and 20A (6-20P) plugs. The device will only draw the current it needs, up to its rating.
Can a 20A Device be Plugged into a 15A Outlet?
No. A 20A plug will not physically fit into a 15A outlet, preventing potential overloading of the 15A circuit.
Can You Install a NEMA 6-20R in a 120V AC Circuit?
No. A NEMA 6-20R is rated for 240V only and has two hot terminals with no neutral. Installing it on a 120V circuit is unsafe and violates NEC requirements. For 120V applications, use a NEMA 5-20R receptacle instead.
Instructions, Precautions & Codes
- 20A – 240V (NEMA 6-20R) outlet cannot supply 120V i.e. it is strictly 240V-only. Do not connect 120V equipment (such as lamps or electronics) to it.
- It is permissible to use 15A receptacles on a 20A circuit if there are two or more receptacles (such as duplex outlets) connected on the same branch circuit. In simple terms, a 15A device can safely be plugged into a 20A outlet.
- it is against the code to connect a 20A load to a 15A receptacle. A 20A plug will not fit into a 15A outlet, and forcing it is dangerous.
- A standard 20A outlet (NEMA 6-20R) accepts both 15A and 20A plugs, but the reverse is not true i.e. a 15A outlet cannot accept a 20A plug.
- According to the NEC Table – 310.16 , Table 210.24.(1) and NEC 240.4(D)(6), the correct Breaker and Wire size for a 20-Amp, 120V (6-20R) outlet is #12 AWG copper or #10 AWG Aluminum.
- Use #12/2 cable (hot, neutral, and ground) for wiring a 20A-240V breaker and outlet.
- A 20A outlet can supply up to a 16A continuous load and a maximum of 20A non-continuous load, as per NEC 210.19(A), 215.2, and 230.42(A).
- It is not permitted to use a 20A receptacle on a 15A breaker, or to use undersized conductors (e.g., 14 AWG or 16 AWG) on a 20A circuit. Use the correct size of 12AWG for 20A outlets and breakers.
- A 20A, 240V outlet must be installed only on a 20A circuit breaker.
Resources:
Related Wiring Tutorials
NEMA Family Outlets/Receptacle Wiring
NEMA 5 -Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-50 Receptacle
NEMA 6-Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-20 Receptacle … (You are Here)
- How to Wire a 30A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-50 Receptacle
NEMA 10-Series
- How to Replace a 20A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-20R?
- How to Replace a 30A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-30R?
- How to Replace a 50A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-50R?
NEMA 14-Series
- How to Wire a 20A – 125/250V Outlet – NEMA 14-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125/250V Outlet – NEMA 14-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 125/250V Outlet – NEMA 14-50 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 60A – 125/250V Outlet – NEMA 14-60 Receptacle
NEMA General Outlets/Receptacle
- How to Replace a 15A – 125V Outlet – NEMA 1-15 Receptacle
- How to Replace a 20A – 250V Outlet – NEMA 2-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125V Outlet – NEMA TT-30 Receptacle
General Wiring Installations:
- How to Size a Breaker and Wires in AWG with EGC for Load?
- How to Wire an Outlet Receptacle? Socket Outlet Wiring Diagrams
- How to a Wire 3-Way Combination Switch and Grounded Outlet?
- How to Wire Combo Switch and Outlet? – Switch/Outlet Combo Wiring Diagrams
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Wire 277V & 480V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase, Commercial Main Service Panel?
- How to Wire 240V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Continuous?
- How to Wire 3-Phase Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
- How to Wire ST01 Timer with Relay & Contactor for 120V/240V Motors?
- How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
Switches Wiring
- How to Wire Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) as 2-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) as 3-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Double Pole, Single Throw Switch? Wiring DPST
- How to Wire Double Pole, Double Throw Switch? Wiring DPDT
- How to Wire Double Switch? 2-Gang, 1-Way Switch – IEC & NEC
- How to Wire 4-Way Switch (NEC) or Intermediate Switch as 3-Way (IEC)?
GFCI/AFCI Breaker/Outlet Wiring
- How to Wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker?
- How to wire a GFCI Outlet?
- How to Wire GFCI Combo Switch and Outlet – GFCI Switch/Outlet
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker?
- How to Wire an AFCI Outlet?
Related Posts:
- What is the Suitable Wire Size for 20A Breaker and Outlet?
- What is the Difference Between 15-Amp and 20-Amp Outlet?
- Difference Between Socket, Outlet and Receptacle
- Difference Between NEMA 14-50 Standard Vs EV Receptacle
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- Can you use 15A Breaker on 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You use a 15A Outlet on a 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Ground Terminal Up or Down: Which Way Should Outlets Face?
- What Do the Green Dot or Orange Triangle Outlets Mean?
- What Do the Different Colors of Electrical Outlets Indicate?
- Why are Outlets and Receptacles in Hospitals Upside Down?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panelboard?
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker? Breaker Size Calculator & Examples
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation?
- Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
- What Will Happen If You Connect a Male-to-Male Plug Between Outlets