AFCI: Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working & Applications
What is an AFCI (Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter) and How Does it Work?
Each year, thousands of people are injured and hundreds lose their lives due to accidents related to electrical wiring. Faults that develop in electrical conductors can cause severe injuries and significant property damage if they go unnoticed or are left uncorrected.
One of the leading causes of residential electrical fires is an arc fault. To reduce the risk of such fires, the National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA) recommends installing Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupters (AFCIs) in homes and buildings.
What is an Arc Fault?
An arc fault is a powerful electrical discharge that occurs between two or more conductors. The intensity of the arc depends on the fault current and the duration of the discharge. It can generate enough heat to damage or completely break down insulation, creating a serious risk of electrical fire.
In addition, arc faults produce irregular waveforms that can interfere with or even damage sensitive electronic equipment.
Related Post:
- GFCI: Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter. Types, Working and Applications
- Difference Between GFCI and AFCI
Types of Arc Faults
Arc faults can occur in two different ways, and therefore are classified into two types:
Parallel Arc Fault
This type occurs between two different conductors, typically due to damaged insulation or a small gap between the wires. Parallel arc faults can occur between two phases or between phase and neutral.
Series Arc Fault
A series arc fault occurs within the same conductor and is usually caused by a loose connection, damaged wire, or a break in the conductor that is in series with the load.
Among these two types, the parallel arc fault is considered the more dangerous because it can generate higher fault currents and is more likely to cause electrical fires.
Related Posts:
- How to Wire an AFCI Outlet? – Arc Fault Interrupter Outlet Wiring
- How to wire a GFCI Outlet? – GFCI Wiring Circuit Diagrams
Causes of Arc Fault
Arc faults can occur for several reasons. Some common causes:
Loose Wire Connections: Loose screw terminals on wall outlets or switches can cause wires to move and make unintended contact with other conductors. Connections may also loosen over time due to frequent plugging and unplugging of devices.
Overheated Wires: Excessive heat can degrade or melt the insulation around a conductor, creating a small gap. When current jumps across this gap, an arc fault occurs.
Damaged Wires: Wires can become damaged for various reasons, such as nails driven into walls with hidden wiring, twisting or kinking of cables, or pushing heavy furniture against power cords. Any damage that pierces or weakens the insulation can lead to an arc fault.
Damaged Terminals: Terminals and conductors can corrode or wear out over time, reducing conductivity and increasing the risk of arcing.
Liquids Near Electrical Tools: Exposure to liquids (especially water) can create conductive paths or degrade insulation, making arc faults more likely.
What is an AFCI?
AFCI stands for Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter (aka AFDD – Arc-Fault Detection Device). It is a protective device designed to prevent fire hazards caused by arc faults. An AFCI continuously monitors the circuit, detects dangerous arcing conditions, and disconnects the electrical supply before the arc can start a fire.
In addition to arc-fault protection, an AFCI also provides overload and short-circuit protection through the same thermal and magnetic mechanisms used in a standard circuit breaker.
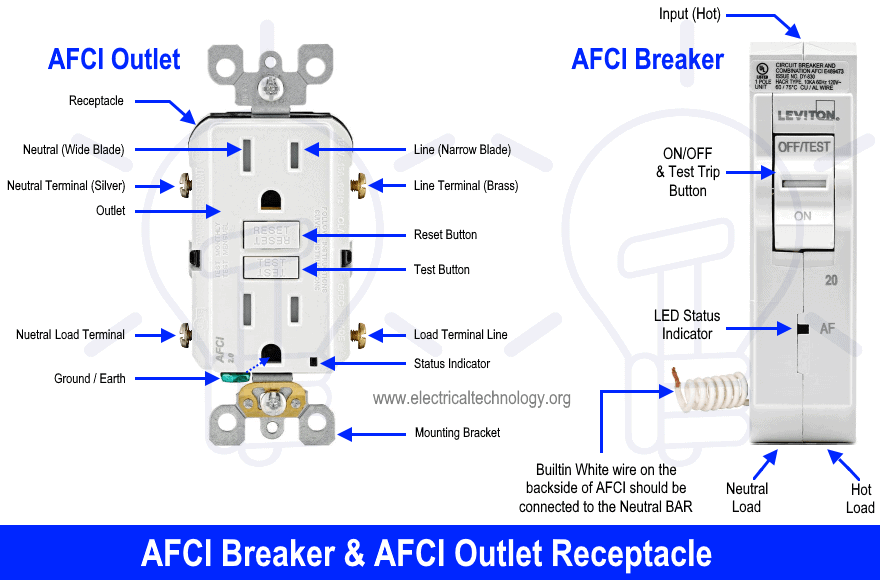
The following figure shows the basic construction and labeled components of Arc-Fault Circuit Breakers and AFCI Outlets.
Functions of AFCIs
Apart from providing protection against overloads and short circuits, the primary function of an AFCI is to protect electrical circuits from arc faults.
An AFCI performs the following three key functions:
- Arc-Fault Protection: The main purpose of an Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter is to detect dangerous arcing conditions and prevent the damage and fire hazards caused by arc faults.
- Overload Protection: Overloading occurs when the current exceeds the rated limit for an extended period. This excessive current produces heat that can damage equipment, wiring, and may lead to fire hazards. An AFCI protects the circuit from overload conditions using a bimetallic thermal strip.
- Short-Circuit Protection: A short circuit occurs when phase conductors come into contact with each other or with the neutral conductor, resulting in an extremely high and destructive current flow. An AFCI provides short-circuit protection using a magnetic (instantaneous) trip mechanism.
Related Posts:
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker? Arc Fault Circuit Interrupter Wiring
- How to Wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker? 1, 2, 3 and 4 Poles GFCIs Wiring
Operation of an AFCI Breaker
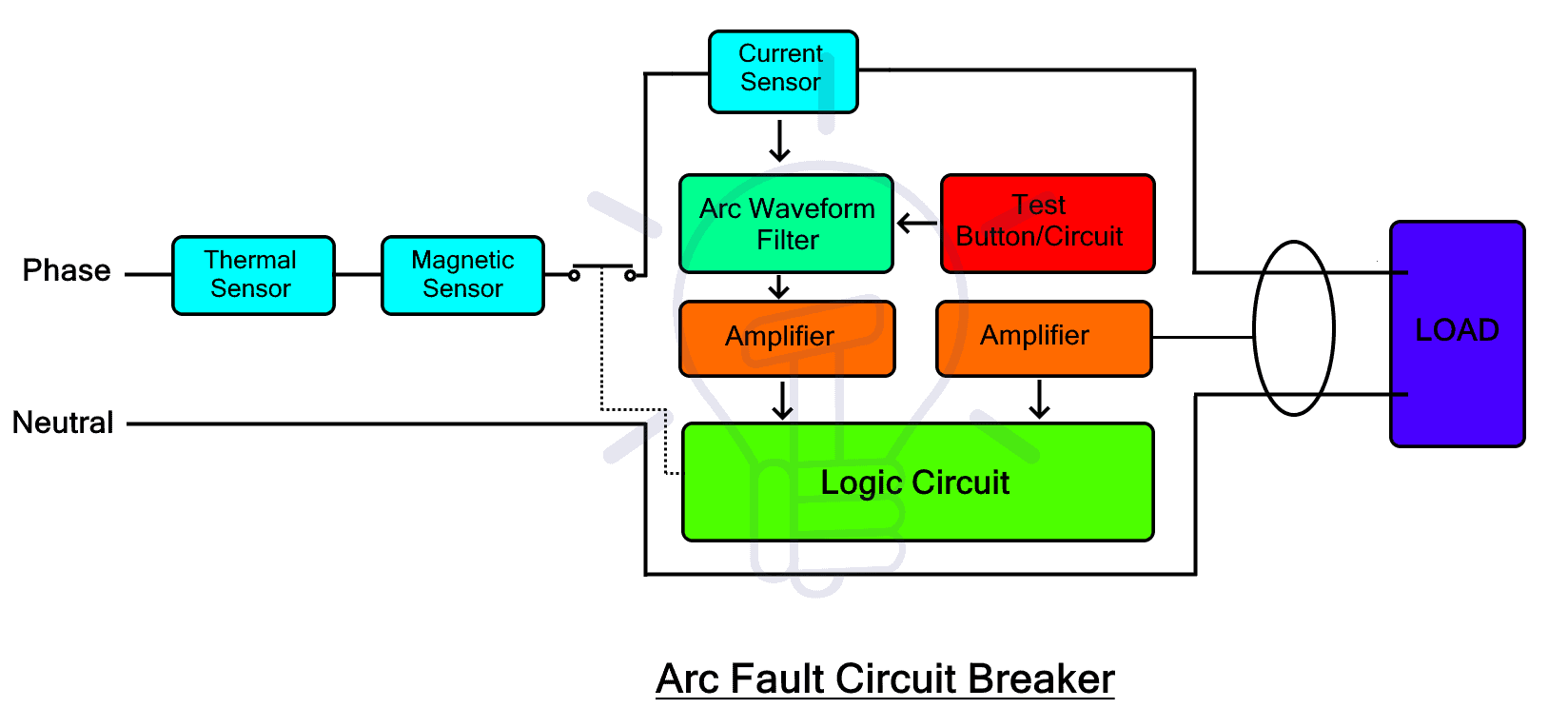
The AFCI continuously monitors the current flowing through the circuit to identify arc-fault waveforms and the magnitude of arcing current. If a dangerous arc is detected, the device immediately interrupts power to the load to prevent further damage or potential fire.
An Arc-Fault Circuit Interrupter also incorporates the thermal and magnetic trip mechanisms found in conventional circuit breakers.
- The thermal mechanism uses a bimetallic strip that bends when heated by excessive (overload) current, releasing the trip latch and opening the circuit.
- The magnetic mechanism uses an electromagnetic coil that reacts instantly to high short-circuit currents, causing the breaker to trip.
The AFCI contains logic and sensing circuits that analyze the current waveform. It can distinguish between normal arcs (such as the brief, low-level arcs produced during switching or when plugging in appliances) and dangerous arcing faults.
Faulty arcs have non-periodic, erratic waveforms with discontinuities and high-amplitude current spikes. Various detection techniques are used, and more advanced methods continue to be developed
To achieve this, the AFCI includes a waveform-filtering circuit that isolates the relevant components from the main current signal. The filtered waveform is amplified and sent to the logic circuitry, which evaluates the signal. If the waveform matches the characteristics of a hazardous arc, the AFCI opens the contacts and disconnects the circuit.
The TEST button is provided to verify proper operation. When pressed, it generates a simulated arc-fault waveform. If the AFCI is functioning correctly, it will trip and open the circuit.
Related Posts:
- How to Wire an AFCI Combo Switch – AFCI Switch Wiring Diagrams
- How to Wire GFCI Combo Switch and Outlet – GFCI Switch/Outlet Wiring Diagrams
Types of AFCIs
There are different types of Arc fault circuit interpreters that depend on the type of its application.
Combination AFCI
Combination AFCI provides protection against both parallel and series arc fault. The parallel arc occurs between phase to phase, phase to neutral and phase to ground. While the series arc occurs along the same conductor.
They are the most used arc fault circuit interrupters in the main distribution panels to protect the branch circuit including the loads connected to it.
Dual-Function AFCI
The dual function AFCI is a device that offers protection against both arc-fault and ground faults. It has both the function of AFCI and GFCI. Therefore, it is the most reliable protection device and to be used at home. It is also cheaper and takes less space than using individual AFCI and GFCI.
Branch / Feeder type AFCI
The branch or feeder type AFCI is the oldest arc fault circuit breaker that is used at the start of a branch circuit or feeder at the distribution panel. It protects against only parallel arc faults in the connected branch circuit i.e. phase to phase, phase to neutral, phase to ground.
Such AFCI is no longer in use and have been replaced by a combination of AFCI
AFCI Outlet / Receptacle
It is an outlet included with an AFCI protection circuit. It offers protection against arcing to appliances, power cord and cables connected to the said outlet.
Portable AFCI
It is a plug-in device like an extension cord with an AFCI plug that is plugged into any normal outlet/receptacle (that has no AFCI protection). The portable AFCI provides protection to any appliances or load connected to it.
Advantages and Disadvantages of AFCIs
Advantage
Here are some of the advantages of Arc fault circuit interrupters
- The AFCI can differentiate between the normal and unwanted arc.
- It helps in the prevention of damage and injuries caused by electrical fires.
- It also offers protection against overcurrent.
- It is more efficient than a standard circuit breaker.
- It can protect the while branch circuit from arc faults.
Disadvantages
Here are some of the disadvantages of Arc fault circuit interrupters
- AFCI is expensive than a conventional circuit breaker
- It cannot stop the first arc.
- It has a more complex design and structure.
Applications of AFCIs
50% of the electrical fires are caused by arcing. Therefore, the Arc fault circuit interrupter is used to break the circuit during arcing to prevent any damage. The NEC also requires that all the receptacles installed in a dwelling bedroom must be protected with AFCI. This includes all receptacles even including the bathroom and kitchen etc.
Related Posts:
- Types of Circuit Breakers – Working and Applications
- Air Circuit Breaker: Construction and Operation
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Working, Types and Uses
- MCCB (Molded Case Circuit Breaker) – Construction, Types and Working
- Difference between MCB, ELCB, RCBO and RCD Circuit Breakers
- HRC Fuse: Construction and Operation
- Resistor and Types of Resistors
- Fuse and Types of Fuses
- Types of Switches









Like the information you provided, but you do not explain what is the remedi to repair the issuse if you have a a arcfault problem.
Simply, Install an Arc Fault Circuit Breaker. That’s it.