Difference Between 1-Pole and 2-Pole Breakers – NEC & IEC
Difference Between Single-Pole and Double-Pole Breakers – Wiring and Applications in IEC (230V) and NEC (120V/240V) Circuits
If you look inside a household main panel or consumer unit, you will notice two common types of breakers e.g. single-pole and double-pole. While both serve the same fundamental purpose i.e. protecting people from electric shock and equipment from damage due to faults such as overcurrent or short circuits, there are key differences between them.
In the U.S. and Canada (according to NEC and CEC):
- Single-pole breakers are typically used for small loads, such as 15–20 amps at 120V. They connect to one hot wire and one neutral wire (plus a ground wire).
- Double-pole breakers are used for larger loads, typically 20–100 amps at 240V. They connect to two hot wires and a ground wire (with a shared neutral if required).
In countries following IEC standards:
- Both single-pole and double-pole breakers are used for small to heavy load circuits, usually rated from 6–63 amps at 230V.
- In a single-pole breaker at 230V, only the phase (live) wire is connected to the breaker.
- In a double-pole breaker at 230V, both the phase (live) wire and the neutral wire are connected to the breaker and then to the load.
So, if you’ve ever wondered about the differences between single-pole and double-pole breakers with their specifications, installation, and applications for 120V/240V or 230V circuits, the following explanation will clarify how each type of overcurrent protective device (OCPD) functions for short-circuit and overload protection.
- Related Post: Difference Between 15-Amp and 20-Amp Outlet?
Single-Pole Breaker – (NEC & IEC)
Specifications:
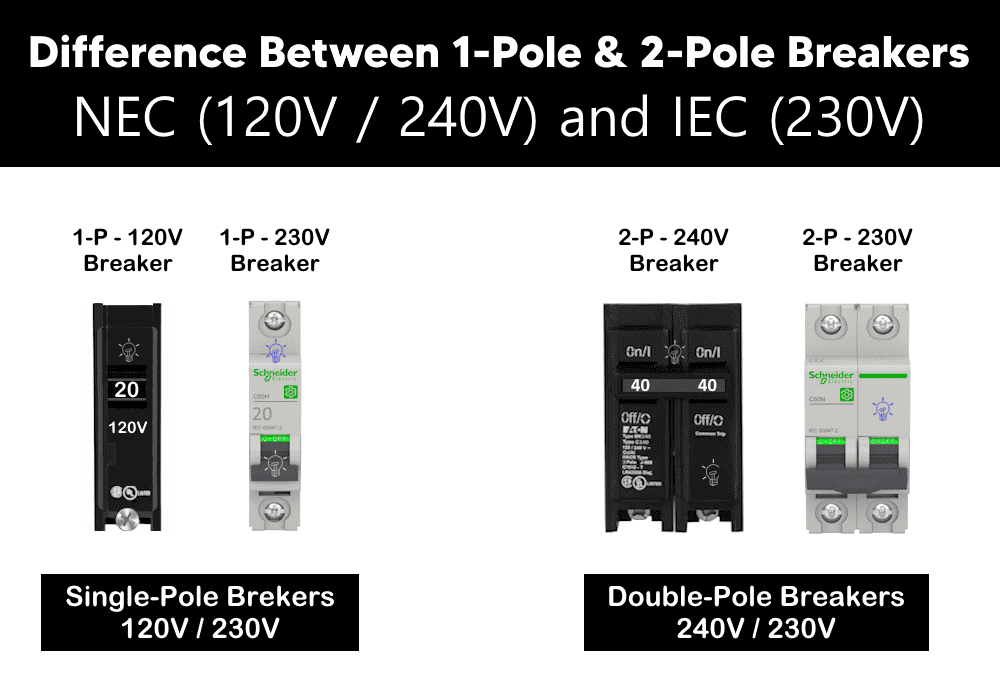
- Number of Poles: 1 (connects to one hot wire (red or black in the US followed by NEC or Phase wire (Brown in the UK, EU, AUS/NZ, ASIA, Middle East etc. following IEC standards).
- Voltage: Operated and protects 120V circuits in the U.S. (line-to-neutral). In the IEC following countries, it is used to protect the 230V AC circuits.
- Amperage Rating: Rated from 15A to 100A+ in the US. The ranges can go from 1A to 63A in countries following IEC Standards.
- Wires Connected: One hot wire + neutral wire (and ground if present) in 120V circuits – U.S and 230V circuits in IEC following countries.
- Operation: Trips when there is an overload, short circuit, or fault on the single hot (or phase) wire.
- Application: Used for standard lighting, outlets, receptacles, sockets and small appliances.
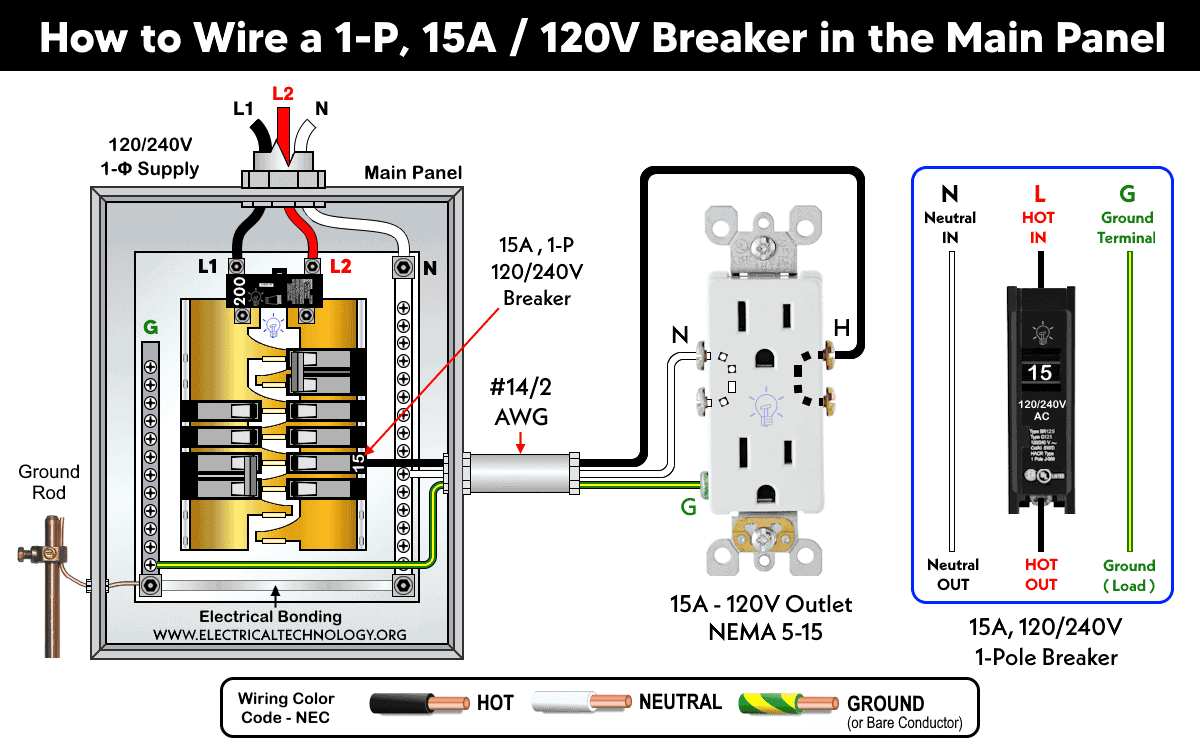
How to Wire a 1-Pole Breaker?
NEC & IEC
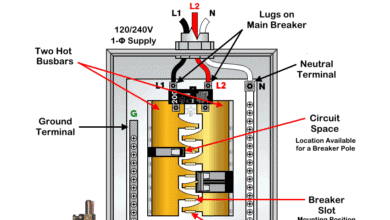
A 1-pole breaker fits into a single slot in a 120V/240V main panel (U.S.) or a 230V consumer unit (IEC countries). Only one hot wire (phase/line) is connected to its input and output terminals. In addition, the circuit requires one neutral and one ground wire.
In other words, a total of three wires (phase, neutral, and ground) are needed for 120V circuits protected by single-pole breakers. This breaker feeds and protects 120V (NEC) or 230V (IEC) circuits from overload and short-circuit faults.
Where to Use 1-Pole Breakers?
120V, 1-pole breakers in 120V (NEC) or 230V (IEC) are used for small load appliances such:
- Lighting points
- outlets and receptacles / sockets.
- Celling Fans
- TV & laptop chargers outlets
- Vacuum
- microwave
- blenders
- Air-compressors
- Hair dryers
- Power tools
Related Post: Main Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
Double-Pole Breaker – (NEC & IEC)
Specifications:
- Number of Poles: 2 (connects to two hot wires i.e. (red and black in the US – NEC or Phase wire and Neutral wire (Brown and Sky Blue) in the IEC following countries including UK and EU.
- Voltage: Protects 240V circuits in the U.S. (line-to-line). In the IEC following countries, it is used to protect the 230V AC circuits (similarly to 1-Pole breaker in 230V circuits.)
- Amperage Rating: Usually rated from 15A up to 100A or more in the US. The ranges can go from 1A to 63A in countries following IEC Standards.
- Wires Connected: Two hot wires (and often a neutral and ground depending on the circuit) in the U.S. in the IEC following countries, one Phase and one Neutral is required to connect to the breaker and 230V load circuits. (Similar to 1-pole breaker in 230V circuits).
- Operation: Both poles are mechanically tied together i.e. if one trips, both disconnect simultaneously, ensuring complete protection.
- Application: Used for large appliances and equipment such as water heaters, dryers, ovens, central AC units, and subpanels in 240V circuits. In 230V circuits, It is used for mains switch in garage and consumer unit or when full isolation is required for both Phase and Neutral such as in motors and generators circuits.
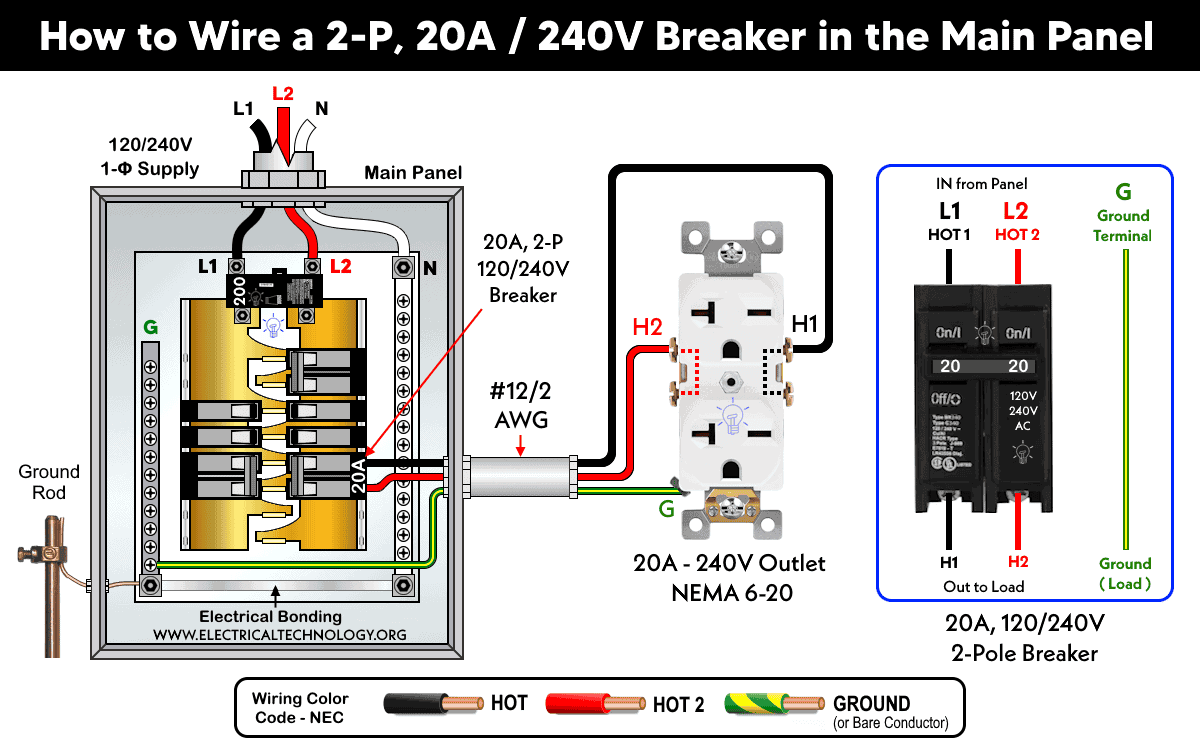
How to Wire a 2-Pole Breaker?
Two-pole breakers for 230V and 240V are wired differently according to IEC and NEC standards
NEC (U.S. & Canada)
In the U.S. and Canada, 2-pole breakers are mainly used to protect 240V circuits from overload and short circuits. The breaker occupies two slots in the main or subpanel. Two hot wires (commonly red and black) are connected to the breaker and the load.
A total of 3 or 4 wires are required: two hot wires and a ground wire, with an additional neutral wire if the circuit requires it. In case of a fault, both hot wires are disconnected from the supply. This ensures the breaker fully protects 240V circuits.
The following diagram shows single-pole and 2-pole breakers wiring in a 120V/240V main panel.
Click image to enlarge or open in a new tab
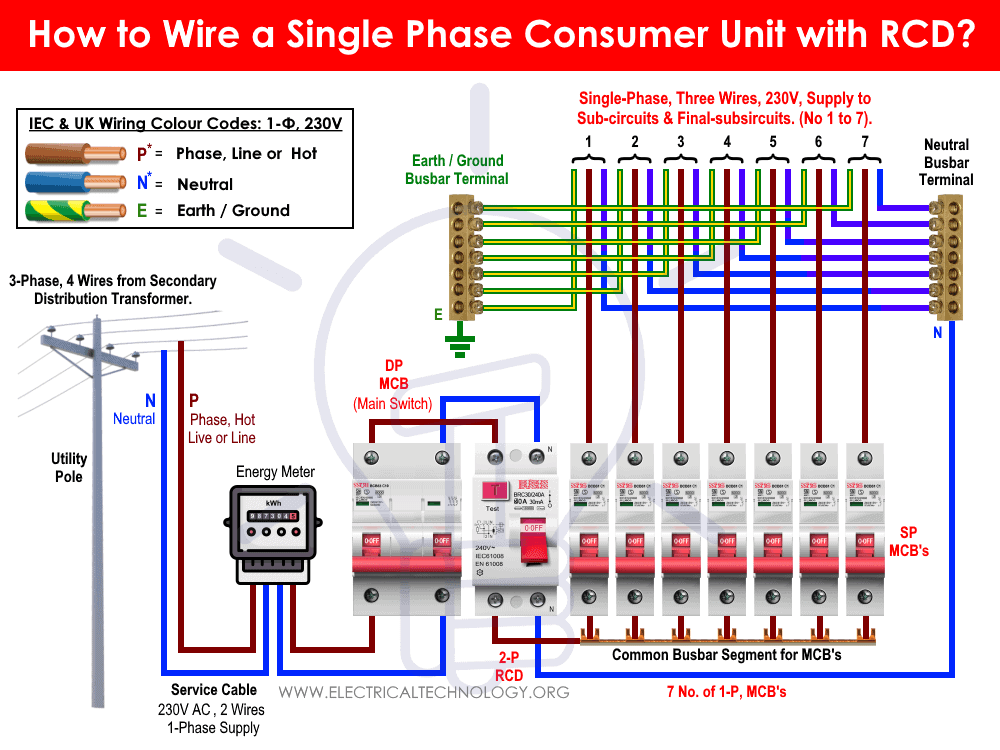
IEC (International)
In IEC countries (UK, EU, Australia/New Zealand, Asia, Middle East, Russia, and China), 2-pole breakers are wired with one phase (live) wire and one neutral wire (plus a ground wire). The breaker occupies two slots in the consumer unit.
In case of a short circuit or overload, it disconnects both the phase and neutral wires, providing complete circuit isolation and protection.
The following fig shows single-pole and 2-pole breakers wiring in a 230V consumer unit.
Click image to enlarge or open in a new tab
Where to Use 2-Pole Breakers?
NEC
In the U.S and Canada, two-pole breaker are used for heavy load appliances operated at 240V such as:
- Electric water heaters
- Dryers , laundry and heavy-duty washers
- Electric Ranges, stoves, & ovens
- Central air conditioners
- Subpanels
- EV Charging and outlets
- and heavy power tools.
IEC
In IEC countries, 2-pole breakers are mainly used to ensure proper isolation of both the phase and neutral conductors. They also protect users against risks such as reversed wiring and electric shock from touching the neutral wire. For maintenance, switching off a 2-pole breaker guarantees that the power supply is fully disconnected.
In addition, a 2-pole breaker is more reliable, with a breaking capacity of up to ICU = 20kA, compared to 1-pole or 1-pole + Neutral breakers, which typically have ICU = 10kA. Furthermore, phase-pole-only breakers (two-pole breakers where only the phase is protected) are commonly used in TT, TN-S, and IT earthing systems.
Some common Applications of 2-Pole Breakers in 230V Circuits:
- Main switch in the consumer unit
- Main switch in the garage unit
- Electric motor circuits
- Back-up generators
- UPS and Inverters
- Electric Vehicles charging sockets
- Extension cords used for power tools
In IEC 230V/400V systems, breakers are designed with specific tripping curves. For example, Type B breakers are commonly used in residential applications, while Type C breakers are suited for circuits with higher inrush currents, such as motors and commercial inductive loads, to prevent nuisance tripping.
However, if a single-pole breaker is used instead of a 2-pole breaker on a 230V supply, it will trip and stop the connected load but may not fully isolate the supply, especially when corded plugs are in use.
- Related Post: Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
Standard Current Rating of 1-P & 2-P Breakers – IEC / NEC
NEC – Current Ratings of 1P & 2P Breakers (120V/240V and up to 600A AC)
Single-pole and double-pole breakers in the U.S. and Canada are available in the following standard current ratings, as specified under NEC 240.6:
15A, 20A, 25A, 30A, 35A, 40A, 45A, 50A, 60A, 70A, 80A, 90A, 100A, 110A, 125A, 150A, 175A, 200A, 225A, 250A, 300A, 350A, 400A, 450A, 500A, 600A, 700A, 800A, 1000A, 1200A, 1600A, 2000A, 2500A, 3000A, 4000A, 5000A, 6000A
IEC – Current Ratings of 1P & 2P Breakers (230V/400V AC)
Single-pole and double-pole breakers are available in the following standard current ratings as per IEC standards:
- IEC 60898-1 (Low-voltage circuit breakers for household applications (≤ 1000V): 1A, 6A, 10A, 16A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 63A, 100A, 200A, 400A
- IEC 60947-2 (Low-voltage circuit breakers for industrial applications (≈ 1kV–52kV): 250A, 400A, 630A, 800A, 1250A, 1600A, 2000A, 2500A, 4000A
- IEC 62271-100 (High-voltage circuit breakers for medium & high-voltage applications (> 52kV): 1250A, 2000A, 2500A, 3000A, 4000A, 5000A
Comparisons Between Single-Pole and Double-Pole Breakers
| Feature | 1-Pole Breaker | 2-Pole Breaker | ||
| NEC | IEC | NEC | IEC | |
| No. of Poles | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 |
| Operating Voltage | 120V
(Line-to-Neutral) |
230V
(Phase-to-Neutral) |
240V
(Line-to-Line) |
230V
(Line-to-Neutral) |
| Amps – Rating | 15,20,25..100A | 1A up to 63A | 15A – 100A+ | 1A up to 63A |
| Hot Wires Controlled | 1 ( One Phase) | 1 ( One Phase) | 2 (Two Phases) | Phase and Neutral |
| Wiring | One Hot + Neutral (+ Ground) | One Phase + Neutral (+ Ground) | Two Hots (+ Neutral and Ground if required) | One Phase + Neutral (+ Ground) |
| Tripping Action | Trips only One Wire | Trips only One Wire | Trips both Hot Wires together (mechanically tied) | Trips both Phase and Neutral together (mechanically tied) |
| Space in Panel | Occupies 1 Slot | Occupies 1 Slot | Occupies 2 Slots | Occupies 2 Slots |
| Applications | Lighting, outlets, receptacles, small appliances | Lighting, outlets, sockets, small appliances | Water heaters, dryers, ovens, Central AC, Subpanels, Heavy Equipment | Heavy load e.g. motors, mains, garage or when isolation is required. |
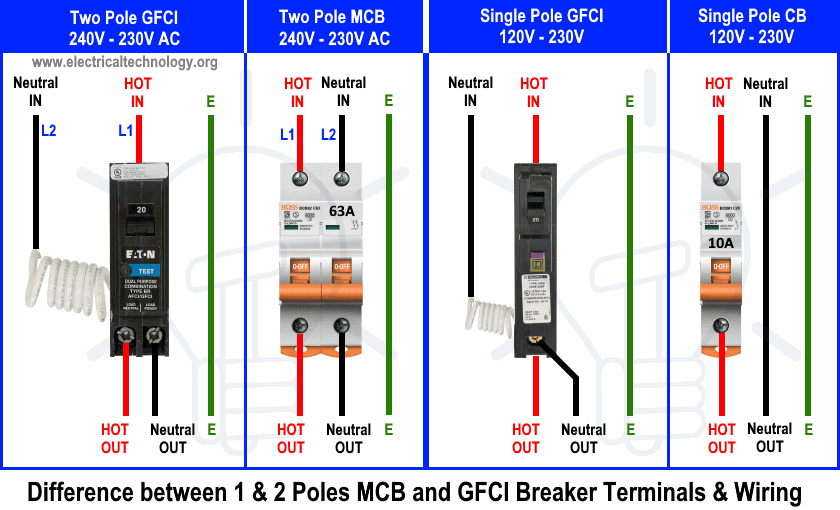
The following fig shows differences and terminal wiring of single-pole and two-pole standard breakers and GFCI breakers – US – NEC.
Click image to enlarge or open in a new tab
Resources & Tutorials:
- Can I Use a 240V Breaker on a 120V Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You Use 15A Breaker on 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You use a 15A Outlet on a 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- What Happens if You Use a 120V Device on 240V & Vice Versa?
- Can I Use a 1-Phase Breaker on a 3-Phase Supply & Vice Versa?
- Can an AC Device Operate on DC Supply, and Vice Versa?
- Can We Use AC Circuit Breaker for DC Circuit & Vice Versa?
- How Does a Standard Breaker Respond to Electrical Fault?
- Why Doesn’t a Standard Breaker Protract Against Ground Faults?
- How Do GFCI and Standard Breakers Respond to Ground Faults?
- Difference Between Socket, Outlet and Receptacle?
- Difference Between GFCI and AFCI
NEC – Wiring Guides for Breakers Installations
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker? Breaker Calculator & Examples
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire 240V, 208V & 120V, 1 & 3-Phase, High Leg Delta Main Panel?
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Install EV Charging Outlet using GFCI Breakers
- How to Wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker?
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panel Board?
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
- Sizing Motors FLC, HP, Voltage, Breaker Size and Wire Size
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation?
- How to Wire Double Switch? 2-Gang, 1-Way Switch
- How to Wire Double Pole, Double Throw Switch? Wiring DPDT
- How to Wire Double Pole, Single Throw Switch? Wiring DPST
- How to Wire Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) as 3-Way Switch?
- How to Find the Right Wire Size for 100A Service 120V/240V Panel?
- How to Toggle Electric Water Heater Between 120V and 240V?
IEC – Wiring Guides for Breakers Installations
- How to Wire 1-P & 2-P, 1-Phase & 3-P, 3-Phase GFCI Breakers
- How to Wire Single-Phase, 230V Consumer Unit with RCD? IEC, UK & EU
- How to Wire 1-Phase Split Load Consumer Unit? – RCD+RCBO
- How to Wire 230V Dual Split Load Consumer Unit? – RCD+MCB
- Wiring of the Distribution Board with RCD
- Wiring of the Distribution Board without RCD
- How to Wire a Three Phase, 400V Distribution Board? IEC & UK
- How to Wire Combo of 3 & 1-Φ, 400V/230V Distribution Board?
- How to Wire a Garage Consumer Unit?
- How to Wire an RCBO? Residual Current Breaker with Overcurrent
- How to Wire Wi-Fi & RF Smart Wireless Remote Control Switch?