What is a Transducer? Types of Transducers and Applications
Transducer, Types, Working, Advantages, Disadvantages and Applications
In electrical and electronics engineering students must come in contact with various electronic components while creating a project such as a microcontroller, sensor, transducer, actuator, transmitter, receiver, etc. The term sensor and transducer is usually used interchangeably and they are considered one and the same thing.
In general, transducer works on the principle of transduction. Transduction is the process of conversion of one form of energy into another form. While a sensor can only sense changes in any physical quantity.
Transducers, sensors and actuators are the backbones of instrumentation. They are used to measure and translate real-world quantities into the electrical and digital world.
What is a Transducer?
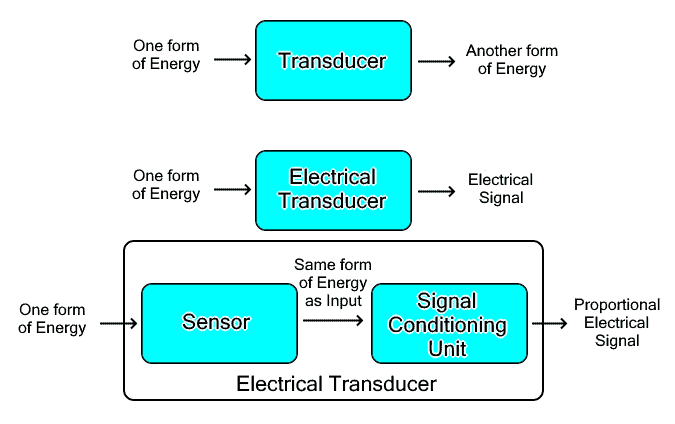
A transducer is a device that converts one form of energy into another form of energy. While an electrical transducer converts one form of energy into an electrical signal. A speaker is said to be a transducer as it can change an electrical signal into sound energy. But a microphone is an electrical transducer because it converts sound energy into an electrical signal.
The output of a transducer is proportional to the input or measured quantity applied to it. For instance, temperature, pressure, light, sound, position, and other quantities are converted into their proportional electrical signal using a transducer such as a thermometer, piezoelectric transducer, potentiometer, microphone, etc.
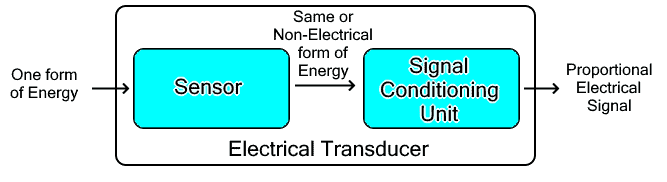
A transducer uses a sensor and signal conditioning unit to perform transduction. The sensor senses any change in the physical quantity or energy and provides a non-electrical output. It is then converted into a proportional electrical signal using a signal conditioning unit.
Parts and Working of Transducer
A transducer is generally made of two main parts.
- Sensor or Sensing Unit
- Transduction or signal conditioning Unit
The sensor unit is responsible for detecting any change in the physical quantity. The output of the sensing unit is non-electrical in nature.
The transduction unit converts the sensor’s output into an electrical signal that is proportional to the input quantity.
Advantages of Signal Conversion
There are various advantages of converting physical quantities into electrical signals. Some of them are mentioned below:
- The electrical signals can be easily processed using various electrical circuits and microcontrollers.
- The information can be stored in the form of an electrical signal and it can be recalled whenever it is needed.
- The electrical signal can be amplified, controlled and it can be visually displayed on a scale.
- The electrical signal is used to form a user-friendly interface to operate any instrument.
- The electrical signal is efficiently processed and helps in automating a complicated process.
Related Post: LVDT: Linear Variable Differential Transformer and Inductive Sensors
Types of Transducer
There are different types of transducers that are classified based on various characteristics.
Based on Power Source
Transducers can be divided into two types based on the external power being used
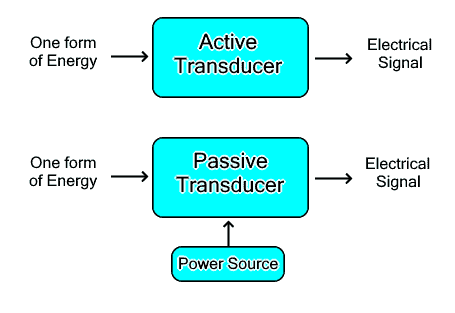
Active Transducer
The active Transducer does not require an external power source to work. It utilizes the energy from the physical change itself to operate and produce a proportional electrical signal. Various physical quantities can be converted into an electrical signals.
For example, a photo-voltaic cell can convert the light energy into an electrical signal without the use of any external power source. Similarly, a piezoelectric crystal is sensitive to pressure change and converts pressure into electrical energy without any external power.
Passive Transducer
A passive transducer requires an external power source to operate. It converts physical quantity into proportional resistance, capacitance, or inductance that is further converted into an electrical signal using an external power source. Therefore, the transducers that work on these principles are passive transducers. Such as potentiometer vary the resistance with a change in position or length that is converted into voltage and current using a power supply.
Based on the Output Conversion
The transducer is divided into primary and secondary types based on the output of the transducer
Primary Transducer
A primary transducer converts the physical quantity into a mechanical signal. They include mechanical as well as mechanical devices. The output of the primary transducer is further converted by the secondary transducer.
Secondary Transducer
A secondary transducer converts the mechanical signal of the primary transducer into an electrical signal. They are electrical circuits whose output signal magnitude is proportional to the mechanical signal.
- Related Post: Capacitive Sensor and Transducer and Its Applications
Analog and Digital Transducer
Analog Transducer
An analog transducer converts physical quantities into an electrical signal that is analog in nature i.e. its magnitude is continuous with time. Its output is a continuous function. Examples of analog transducers are thermistor and thermocouple for temperature measurement, a piezoelectric sensor for pressure measurement, etc.
Digital Transducer
A digital transducer converts a physical quantity into an electrical signal that is digital in nature i.e. the output signal is discrete and non-continuous both in magnitude and time. The output signal is in binary form “1” and “0” called bits. It is used for interfacing the transducer directly with a microcontroller.
Transducer and Inverse Transducer
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts any other form of energy or physical quantity into an electrical signal such as a thermistor, microphone, etc.
Inverse Transducer
An inverse transducer is a type of device that converts electrical energy into any other form of energy. Its name suggests its function is opposite of the transducer. Example of an inverse transducer is speaker, screen, servo motor, etc.
Types of Transducer based on the Principle of Operation
Transducers are divided into different types based on the principle of operation.
Photovoltaic Transducer
A photovoltaic cell is an active transducer that converts light energy into electrical energy. It is made of semiconductor material having a PN junction. When a light particle enters the junction, it energizes the junction and releases current into the connected load. The current is known as photoelectric current.
It is also known as solar cells used in solar panels. They are used for converting solar energy into electrical energy to power electrical equipment. They are the source of green energy.
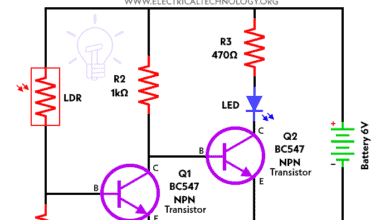
Photoconductors Transducer
A photoconductor transducer is a device whose conductivity depends on the light intensity. LDR (light-dependent resistor) is a photoconductor whose conductivity increases with an increase in the intensity of light. LDR can be used to convert the light intensity into an electrical signal.
Piezoelectric Transducer
A piezoelectric transducer works on the principle of the piezoelectric effect. It generates electrical energy that is proportional to the pressure, force, and strain on it.
There are various materials that produce the piezoelectric effect. One of the most used substances is quartz crystal made from silicon oxide SiO2. It produces a charge on its surface when a force is applied on it. The charge can be utilized by connecting electrodes to its surface.
A piezoelectric transducer is used for measuring the change in pressure, acceleration, etc. They are used in automatic doors for sensing footsteps. It is also used in a lighter to generate necessary sparks to ignite the fuel. Microphone also operates on piezoelectric effect to sense the sound energy pressure and convert it into an electrical signal.
Electromagnetic Induction
An inductive transducer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction. It measures the change in inductance between the two coils. This can be done by either self-induction or mutual induction. A movable core is used between the coils of a transducer to vary the inductance between them. Physical quantities such as displacement, force, torque, acceleration can be measured.
Hall Effect Transducer
Such transducer works on the principle of the Hall Effect. it can detect a magnetic field and convert it into an electrical signal that is proportional to the magnitude of the magnetic field.
Hall Effect transducers are used for proximity and position sensing, speed detection in the tachometer, etc.
Thermoelectric Transducer
It is a temperature transducer that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. A thermocouple is a thermoelectric transducer that has two terminals. It produces electrical energy based on the temperature difference between its terminals.
Electrostatic Transducer
An electrostatic transducer is made of two electrodes i.e. fixed and movable electrode charge with opposite polarities. When the movable electrode moves, it changes the capacitance between the electrodes that varies the applied voltage. The voltage change is proportional to the electrode displacement.
Electromechanical
An electromechanical transducer converts the mechanical motion into an electrical signal. It is used for sensing and measuring mechanical displacement and positioning.
Based on Quantity to be measured
There are different types of transducers used for measuring various physical quantities.
Pressure Transducers
The transducer that converts the pressure exerted into an electrical signal is called a pressure transducer. It consists of an elastic material that bends when pressure is exerted on it. The bending is translated into an electrical signal.
Pressure transducers are used for the following applications.
- It is used to measure the pressure inside a gas tank and detect any leak in case pressure drops.
- It is used for monitoring the flow of substances.
Temperature Transducers
The temperature transducers convert the surrounding temperature into an electrical signal. It can measure the temperature as well as any change in it. A thermocouple, thermistor is example of a temperature transducer used for temperature measurement.
It is used for monitoring the temperature of equipment. It is also used to control and maintain the temperature inside a room.
Ultrasonic Transducers
An ultrasonic transducer converts ultrasonic waves into an electrical signal. The ultrasonic waves are reflected from a surface that is detected by this transducer.
It is used for detecting an object in front of it. It is also used for measuring the distance between the object and the transducer. The speed of ultrasonic waves is equal to the speed of sound that is used in the calculation of distance.
Displacement Transducers
A displacement transducer converts linear motion or vibration into an electrical signal. It can sense change in displacement and also measure the precise position of an object. It uses different principles of operation to measure the change in displacement such as resistive, capacitive, and inductive etc.
An LVDT (linear variable differential transformer), potentiometer is an example of displacement transducer used for measuring linear displacement.
Flow Transducers
A flow transducer converts the flow of a gas, liquid into an electrical signal. It is used for measuring the flow velocity of any gas or liquid.
Inductive Transducer
An inductive transducer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction to detect a change in its self-inductance. It has a coil that develops a magnetic field due to its own current flow. When an object such as a metal comes in its magnetic field, its inductance varies that is detected by a deflecting needle.
It is used in proximity sensors, metal detectors, object counters, etc.
Strain Gauge Transducer
A strain gauge transducer converts physical quantity like mechanical stress or strain into an electrical signal. It is made of an elastic material with trace of conductor that does not break when force is applied on it. It works on the principle of change in electrical conductivity or resistivity of the conductor.
When force is applied, it bends and the conductor lengthens and gets narrower. Therefore, the resistivity of the conductor changes. The change in resistivity is translated into the electrical signal using a formula that is proportional to the stress applied on it.
Strain gauge transducers are mainly used for measuring stress and strain in the field of civil engineering.
Acceleration Transducer
Acceleration transduces or accelerometer is a transducer that converts the acceleration of a body into an electrical signal. It can sense the change in velocity. Accelerometer uses various operating principles.
Acceleration is caused when force is applied on an object. A piezoelectric crystal can sense the force acting on it and generate an electrical signal proportional to the force. Therefore, it can translate the acceleration into an electrical signal.
Characteristics of Transducer
There are some characteristics of a transducer that determines the overall performance of a transducer.
It is divided into two types;
- Static Characteristics
- Dynamic Characteristics
Static Characteristics
These characteristics do not depend or vary with variation in the input signal or with time. Here are some of the static characteristics.
Accuracy
The accuracy of a transducer is the maximum difference between its actual value and the indicated value. It is expressed in a percentage of the actual value. A transducer must have high accuracy to measure the physical quantity accurately.
Linearity
The ability of a device to vary its output linearly with the input signal is called linearity. The output is in proportional with the input signal. A transducer having linearity has a more accurate reading and it can easily translate the signal to its corresponding output value.
Robust
A transducer must be able to withstand extreme environmental conditions and mechanical stress. A rugged and robust transducer’s performance Is not affected by its environment.
Repeatability
The ability of a transducer to generate an identical output signal multiple times when applied with the same input signal. The output signal must repeat itself and do not vary with time.
Stability
The capability of a transducer to provide a stable output and does not fluctuate.
Sensitivity
The ability of a device to sense the smallest change in a physical quantity and translate it efficiently into an electrical signal is called sensitivity. A device having higher sensitivity can measure more accurately and precisely.
Size
A transducer having a small size is crucial for installing compact devices without taking much space.
Dynamic Characteristics
The dynamic characteristics of a transducer are dependent of time and they may vary little. Here are some of the dynamic characteristics of a transducer:
Dynamic Range
The dynamic range is the ratio between the highest amplitude and the lowest amplitude the device can efficiently convert. A transducer having a high dynamic range has better performance and sensitivity.
Error
The error is the difference between the measured reading and the actual reading. The error can be caused by various factors.
Speed
The speed of a transducer plays a vital role in its performance as it shows how quickly it translate a physical quantity into a stable electrical signal.
Noise
Noise is a random unwanted signal that distorts and inflicts error in the original signal. A transducer adds noise in its signal. A low amplitude signal is more affected by noise than a high amplitude signal.
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the ability of a device whose output not only depends on its current input but the previous input as well.
Efficiency of Transducer
The efficiency of a transducer is the ratio of output power to input power. The percentage efficiency of a transducer is never 100% as some of the energy is wasted during the process of conversion. For example, the efficiency of a photovoltaic cell is below 30%. Most of the energy is wasted in the form of heat and reflection.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Transducers
Advantages
Here are some advantages of Transducer
- The electrical signal of a transducer can be easily and quickly processed using electrical circuits and microprocessors.
- It requires less energy to control electrical signals thus more energy efficient.
- The electrical signal is easier to transmit and receive over long distances.
- The electrical signal can be easily amplified, added, mixed with other signals.
- Modern tech is becoming smaller and more compact day by day. Thus electrical signals can be processed and stored using very small gadgets and devices.
- There are no mechanical parts involved, thus it reduces the mechanical wear and tear problem.
Disadvantages
Here are some disadvantages of a transducer
- Some transducers especially the more accurate ones are relatively very expensive.
- Transducers are not reliable as compared to mechanical instruments in long-term use.
- Noise in an electrical signal can affect the accuracy of the measurement.
- The battery-operated transducer’s performance is affected by the charge remaining in the battery.
Applications of Transducer
The conversion of any physical quantity into an electrical signal is used in almost every field. Here are some applications of transducers.
- In Biomedical Instrumentation, different transducers are used to help patient diagnosing such as ultrasound machines, thermometers, ECG, ECHO, CT, MRIs, and other instruments. They convert various signals generated from our body into electrical signals and display them on a screen.
- In civil construction, stress gauges are used to measure the stress on a building, bridge, etc.
- The temperature is converted into an electrical signal that is processed to maintain temperature in a room. They are also used in fire alarms.
- A transducer such as an antenna converts the electromagnetic signal into an electrical signal that enables data transmission over a long distance.
- The pressure of any liquid or gas is easily measured using a transducer.
- Transducers such as microphones convert sound waves into electrical signals that can be amplified as well as processed, modified, and stored.
- Photoelectric transducer such as solar cells is a source of green energy. They are used to produce electrical energy from solar energy. Other LDR, photodiodes and photo-transistors are used in various electrical projects.
- Modern driverless cars operate on transducers that convert different signals from its surrounding into electrical signals and process them to make decisions.
- In robotics, Robots depend on transducers to understand and process real-world quantities using their microprocessors.
In general, we use multiple transducers in our daily life such as the lighter we use in our kitchen has a piezoelectric crystal that generates a spark when hit with a spring-loaded hammer. Almost every electrical equipment or gadget has a transducer embedded in it. different types of transducers are used in electronic measurement devices.
Related Posts:
- What is Thermocouple? – Types, Construction, Working and Applications
- What is a Thermistor? Types of Thermistors and Applications
- Infrared Motion Detector Circuit – Diagram, Working and Applications
- Rain Alarm Sensor– Snow, Water and Rain Detector Project
- Simple Touch Sensitive Switch Circuit using 555 Timer and BC547 Transistor
- Automatic Bathroom Light Switch Circuit Diagram and Operation
- Internet of Things (IoT) and Its Applications in Electrical Power Industry







Thank you for a the detailed and informative article.
Your article on transducers’ role in automotive safety systems was compelling.
Fantastic article on the latest innovations in transducer technology! The advancements in materials and design, such as the development of piezoelectric ceramics and MEMS (Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems) sensors, are truly transformative.
A great read for any car owner. The section on fuel efficiency and engine tuning was especially helpful!
Transducers have transformed how we measure, monitor, and control systems—from medical devices to aerospace engineering.