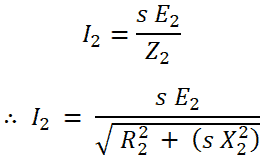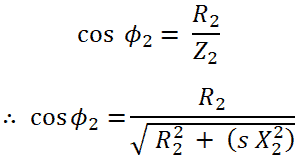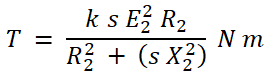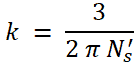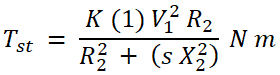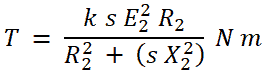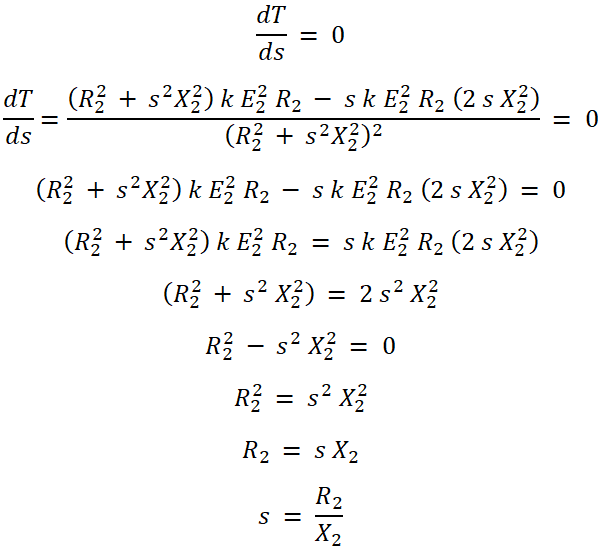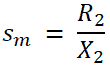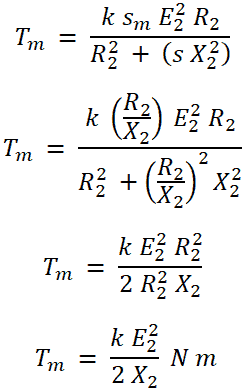Torque Equation of Induction Motor
Starting Torque, Full Load Torque, Torque at Synchronous Speed & Condition for Maximum Torque Equations of an Induction Motor
An induction motor is widely used in industries as it produces good torque. The torque of an induction motor depends on the three factors;
- Rotor power factor under running condition (cos ϕ2)
- Rotor current under running condition (I2)
- Part of a rotating magnetic field that induces EMF in the rotor winding (ϕ)
Therefore, the equation of torque is proportional to the above factors and equate as;
T ∝ ϕ I2 cos(ϕ2)
The flux produced in the rotor is directly proportional to the stator voltage E2;
ϕ ∝ E1
But, the transformation ratio (K) is;
Hence,
E2 ∝ ϕ
Rotor current I2;
Rotor Power factor (cos ϕ2);
Now submit these values in the torque equations;
We can write the above equation by adding a proportionality constant.
This equation is known as a torque equation of induction motor.
Related Post:
- Torque-Slip & Torque-Speed Characteristics of Induction Motor
- Power, Voltage and EMF Equation of a DC Motor
Full Load Torque
The slip of an induction motor depends on the loading condition. If we consider full load slip is s, the equation of full load torque is defined as the below equation.
Where k is a proportionality constant and the value of k is;
Where Ns’ is synchronous speed (RPS) = NS / 60
Related Post:
Torque at Synchronous Speed
At synchronous speed, the slip of a motor is zero (s = 0). If we put the value of slip in the torque equation, we get the torque produced by the motor is zero. Hence, the induction motor is an asynchronous motor that can be run at synchronous speed.
Starting Torque
Starting torque is defined as a torque produced at starting of the motor (consider rotor speed is zero). Hence, the speed N = 0 and slip s = 1. The starting torque is denoted as Tst. And we get the equation of starting torque by substituting s = 1 in the torque equation.
At the time of starting, the motor is in standstill condition. Therefore, starting torque is also known as standstill torque.
For an induction motor; we can write;
Put this value in torque equation;
E1 is nearly equal to V1;
At starting condition, slip s = 1;
Tst ∝ V12
Hence, the starting torque is proportional to the square of the applied stator voltage.
- Related Post: EMF Equation of an Alternator and AC Generator
Condition for Maximum Torque
When a motor is running, the equation of starting torque is defined as;
It is clear from the above equation that the torque depends on the slip when a motor is in running condition. Now, we need to find the condition at which the torque is maximum. For that, we differentiate the above equation with respect to slip and compare it with zero.
Therefore,
This equation shows the value of slip that corresponds to maximum torque Tm. And it is a ratio of rotor resistance and reactance at standstill. The slip at maximum torque condition is denoted as sm.
Now, put this value in the equation of for to find the equation of maximum torque Tm.
From the above equation, we can conclude that, the maximum torque;
- Does not depend on the rotor resistance R2. But the value of slip sm at which maximum torque Tm occurs is directly proportional to the rotor resistance.
- Directly proportional to the square of rotor voltage E2.
- Inversely proportional to the rotor reactance.
Related Posts:
- Types of Electric Motors – Classification of AC, DC & Special Motors
- Applications of Electric Motors
- Single-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Three-Phase Induction Motor – Construction, Working, Types & Applications
- Motor Starter – Types of Motor Starters and Motor Starting Methods
- Direct Online Starter – DOL Starter Wiring Diagram for Motors
- Cable Size Calculation for LT & HT Motors
- Speed Control Methods of of a DC Motor
- DC Machine – Construction, Working, Types and Applications
- Servo Motor – Types, Construction, Working, Controlling & Applications
- Brushless DC Motor (BLDC) – Construction, Working Principle & Applications
- Stepper Motor – Types, Construction, Operation & Applications
- What is Motor Efficiency and How to improve it?
- Induction Motor & Linear Induction Motors Formulas & Equations
- What is Motor Generator Set and How Does it Work?
- How to Run a Three-Phase Induction Motor on a Single-Phase Power Supply?
- Electrical & Electronics Engineering Formulas & Equations
- Electric Motors Symbols