Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor
Difference Between Capacitor and Supercapacitor / Ultra-Capacitor
Both supercapacitors and conventional capacitors store electrical charge in the form of an electrostatic field. They are passive components, meaning they do not generate energy but rather store and release it. A supercapacitor is a type of polarized capacitor, requiring correct polarity during connection, much like electrolytic capacitors.
While the basic function of both conventional capacitors and supercapacitors is the same (i.e. to store and release electrical energy), there are several key differences between them, which we will discuss below.
- Related Post: Difference Between Conductor and Superconductor
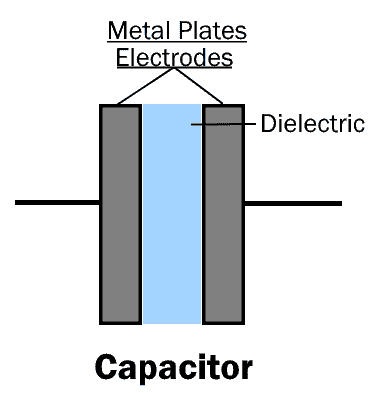
Capacitor
A capacitor is a two-terminal passive electronic component that stores electrical charge in the form of an electric field between its metal plates. It is constructed using two conductive plates (acting as the anode and cathode) separated by an insulating material known as the dielectric.
When a voltage source is applied across the terminals of a capacitor, the current attempts to flow; however, the dielectric (insulating material) opposes the flow of electrons, which prevents direct current from passing through. As the voltage builds up across the capacitor’s plates, electrons accumulate on one plate, creating a potential difference. Once the voltage across the capacitor equals the applied voltage, the current flow stops, but the electric field remains.
This opposition to electron flow and accumulation of charge creates an electrostatic field across the dielectric, thereby storing energy in the capacitor.
- Related Post: Difference Between a Battery and a Capacitor
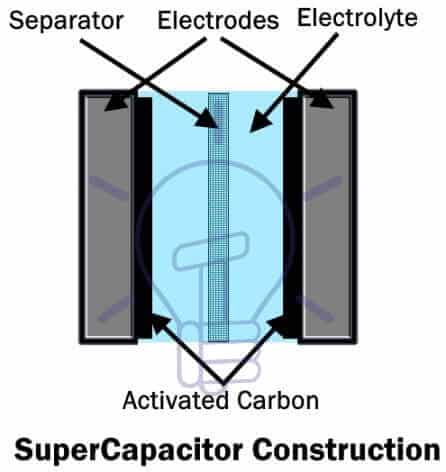
Supercapacitor
A supercapacitor, also known as a supercap, electrochemical double-layer capacitor (EDLC), or ultracapacitor, is a high-capacity energy storage device that bridges the gap between conventional capacitors and rechargeable batteries.
In supercapacitors, the electrodes are coated with activated carbon, which significantly increases the surface area, enhancing the charge storage capability. Unlike conventional capacitors that use a dielectric material between the plates, supercapacitors use a separator (an ion-permeable membrane) placed between the anode and cathode. This separator allows the movement of ions in the electrolyte while preventing electrical contact between the electrodes.
Supercapacitors store energy through two mechanisms:
- Electrostatic double-layer capacitance (EDLC): Where charge is stored physically at the electrode-electrolyte interface without any chemical reaction.
- Electrochemical pseudocapacitance: Where charge is stored through fast surface redox (oxidation-reduction) reactions.
Some advanced designs combine both mechanisms, resulting in what’s called hybrid capacitance.
The structure of a supercapacitor typically consists of metal foil electrodes, each layered with activated carbon, with a separator (such as modern graphene membranes) sandwiched in between. This setup provides insulation and enables efficient ion exchange within the electrolyte.
Supercapacitor is also known as Super Cap, Double Layer Capacitor or Ultra-capacitor. The electrodes of supercapacitor is coated with active carbon as electrode material. A separator is used between Anode and Cathode in Supercapacitor, whereas a dielectric materials are used in conventional capacitor.
The supercapacitors store charge either using electrostatic double-layer capacitance (EDLC) or electrochemical pseudocapacitance or both known as hybrid capacitance.
Supercapacitors are made of metal foil (electrodes), each layered with activated carbon. These foils sandwich the separator in between. The separator is an ion-permeable membrane such as graphene (used in modern supercapacitor) which provides the insulation and exchange of ions of the electrolyte between the electrodes.
Supercapacitors are often considered a hybrid between capacitors and batteries. They charge rapidly like capacitors, yet they offer higher energy storage capacity and slower discharge rates, similar to batteries. This makes them ideal for applications requiring quick bursts of energy and frequent charge/discharge cycles.
- Related Post: Difference Between Relay and Circuit Breaker
Comparison Between Capacitors and Supercapacitors
There are several key differences between a conventional capacitor and an ultra-capacitor (supercapacitor), which are summarized in the comparison table below.
| Characteristic | Capacitor | Supercapacitor (Ultracapacitor) |
| Construction | Two metallic terminals (electrodes) separated by a dielectric material. Stores energy in an electrostatic field. | A type of polar capacitor that uses an electrolytic solution. Electrodes are coated with activated carbon to enlarge surface area. |
| Definition | Stores potential energy in the form of an electric field (electrostatically), releasing it as electrical energy. | Lies between a capacitor and a battery. Also called Super Cap, Double Layer Capacitor, or Ultracapacitor. Offers high capacitance and low voltage. |
| Working Principle | Stores energy as an electric field between two plates. | Stores energy between electrolyte ions and electrodes through a double layer of charge (EDLC or pseudocapacitance). |
| Types | Electrolytic, Film, Tantalum, Integrated Capacitors | Electrostatic Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLCs), Electrochemical Pseudocapacitors, Hybrid Supercapacitors |
| Dielectric Medium | Uses materials like aluminum oxide, ceramic, or polymer films as dielectric between electrodes. | Uses activated carbon; the double electric layer formed acts like a dielectric. |
| Charge / Discharge Time | Very fast: typically in the range of 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁶ seconds. | Faster than batteries; charges in seconds or minutes and stores more energy per unit volume than electrolytic capacitors. |
| Charge / Discharge Efficiency | > 0.95 | 0.85 – 0.98 |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to 65°C (-4°F to 149°F) | -40°C to 65°C (-40°F to 149°F) |
| Energy Storage Capacity | Less than 0.1 Wh/kg | 1 – 10 Wh/kg |
| Energy Density | Low | Very High |
| Specific Power | Up to 100,000 W/kg | Up to 10,000 W/kg |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Advantages | – Prevents excessive current draw – Low cost – High integration density – Real/Reactive power control/filtering – Long operational life |
– High energy storage – Fast charging/discharging – High load current support – Long cycle life – Acts as backup power in electronics |
| Applications | – Power supply smoothing – Power factor correction – Signal coupling/decoupling – Filters (high/low pass) – Snubber circuits – Oscillators |
– Cordless tools – LED Flashlights in digital cameras – Laptop/handheld power stabilization – UPS systems – Memory backup (CMOS, RAM, microcontrollers) |
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Shunt Capacitors and Shunt Reactors
- Difference between Fuse and Circuit Breaker
- Difference between Contactor and Starter
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB & RCB, RCD or RCCB Circuit Breakers
- Difference between AC and DC Resistance & How to calculate it?
- Difference between Star and Delta Connections – Comparison Of Y/Δ
- Difference Between NEMA and IEC Motor Starters & Contactors
- Difference Between Direct-On-Line (DOL) and Star Delta Starter
- Difference between Circuit Breaker and Isolator / Disconnector
- Difference Between Squirrel Cage and Slip Ring (Wound) Rotor
- Difference Between ON Delay and OFF Delay Timer
- Difference Between EGC and GEC in Electrical Grounding
- Difference Between GND, 0VDC, Common and Virtual Ground
- Difference Between AC Ground and DC Ground?
- Difference Between Monocrystalline, Polycrystalline, and Thin-Film Solar Panels
- Difference Between Active Transducer and Passive Transducer
- Difference Between Voltage Stabilizer and Voltage Regulator (AVR)
- Difference Between 15-Amp and 20-Amp Outlet?






What is the Electrolyte used in Super capacitors ? Why it is not mentioned ? what is the life of Super capacitors ? Why there is limitation of voltage per capacitors (2.7Volts) ? Connecting in series reducing the value of capacitor,How we can achieve the higher rating ? Is it by series parallel combination ? What is the Maximum Capacity & Maximum operating Voltage Super capacitors available in Markets ? I need all these Answers in my E.mail,Thanks .
A next post “Supercapacitor, Types, Construction, Working Principle, Advantages & Disseminates and Applications” will be published very soon.
how much supercapacitor hold the current. and what rate it can be DISCHARGE for use. what will be ratio of price
Explain super capacitors
Difference between battery n capacitor
Including life cycle
You can see the previous post “Difference between Battery and Capacitor.
How can you tell the difference between an electrolytic capacitor and a super capacitor just by looking at them?
Capacitor and super capacitor are same in shape but in equipment there’s some difference
This series of articles is fantastic in their content, especially for the layman. Thanks