How to Find the Right Wire Size for 100A Service 120V/240V Panel?
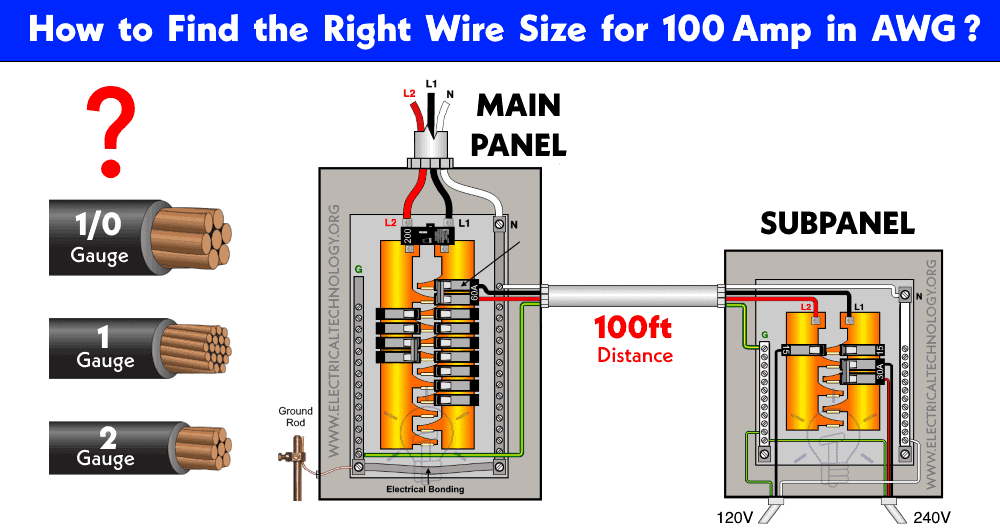
What Size Wire is Needed for a 100-Amp Subpanel Running 80 to 100 Feet to a 100-Amp Breaker?
The proper wire size for a 100-amp load circuit (e.g., a subpanel) depends on several factors, including the distance between the main panel and the load circuit (i.e., subpanel), as voltage drop over the length of the run is a significant consideration.
Other factors affecting wire size include voltage (120V or 240V), ambient temperature, the number of wires in a bundle, and the type of wiring used. Let’s go through the necessary electrical calculations to determine the correct wire size for a 100A circuit, considering both ideal and real-world scenarios.
In the US, a 25kVA, 7200V/240V distribution transformer provides electric power at 100 amps as follows:
- Power = 240V × 100A = 24,000 Watts
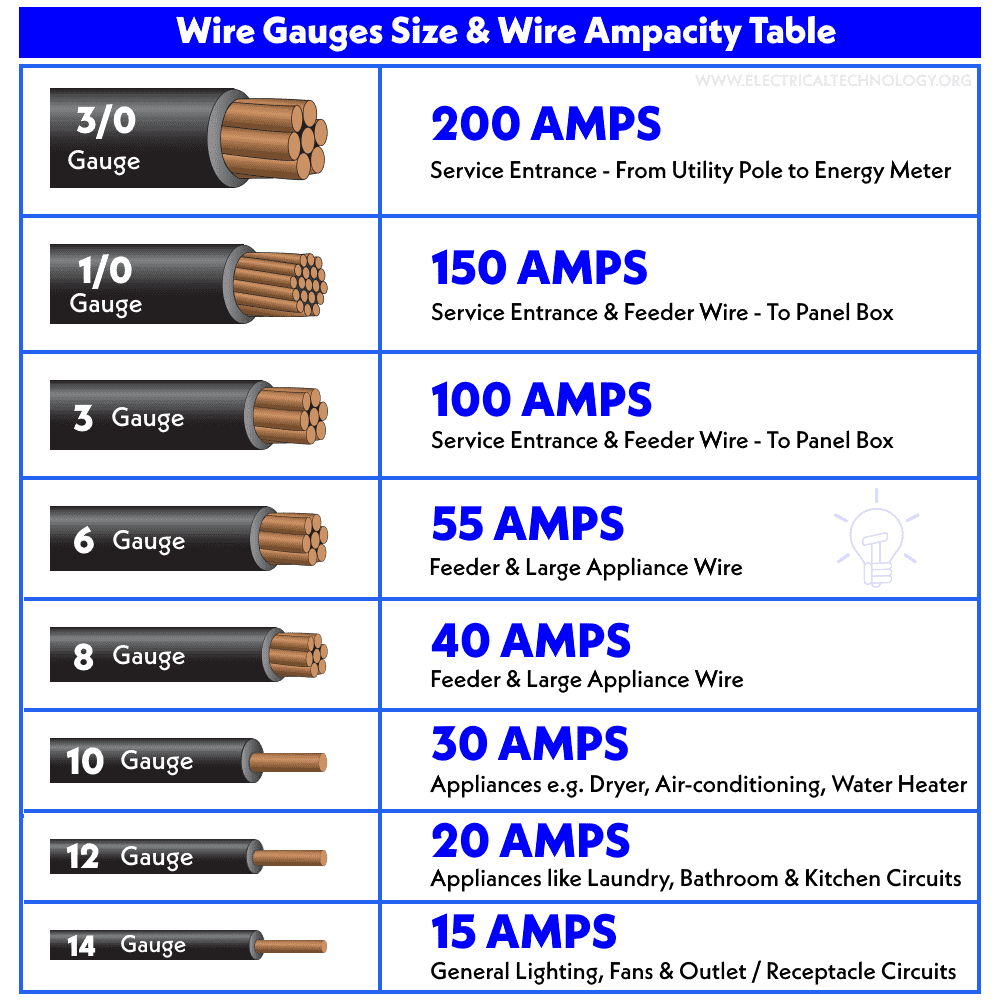
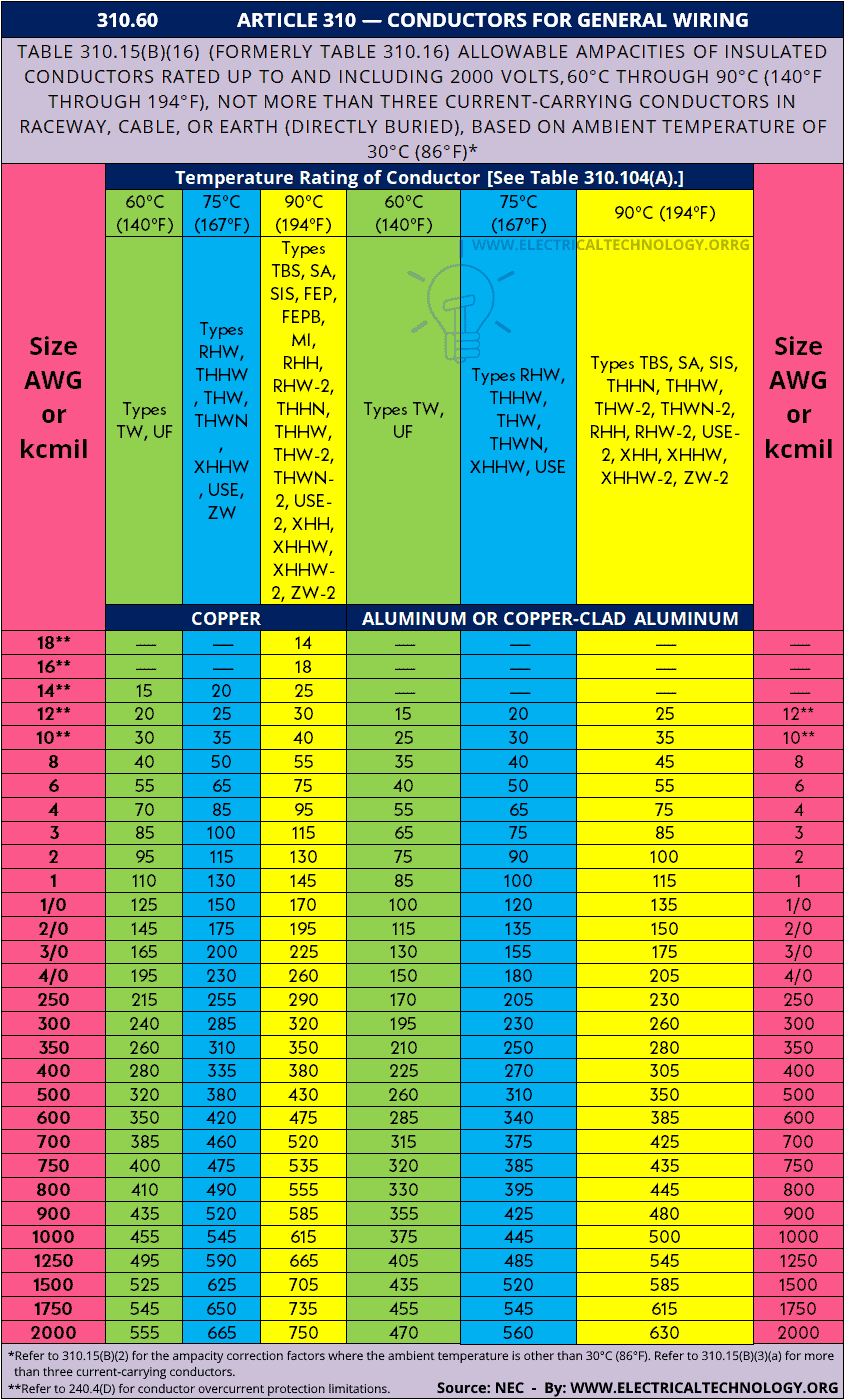
Based on this, the ideal wire size for a 100-amp breaker is #1 AWG for copper and #1/0 AWG for aluminum, according to the AWG size chart and NEC Table 310-15B (formerly 310-16) Article 310.60 (below).
As it may applicable for 100A load circuits, however, this may not be suitable when considering distance and demand factor for main or subpanels, as it could lead to significant voltage drops. To address this, we will perform more detailed calculations based on NEC codes and related tables to determine the correct wire size for a 100-amp circuit over a distance of 100 feet.
Hence, the suggested wire size for a 100-amp service is #4 AWG for copper and #2 AWG for aluminum, according NEC Table 310-12(A).
Factors Affecting the 100A Wire Size
NEC (National Electric Code) guidelines for 100A wire size:
- 100-Amp Circuit Usage: NEC 210.19 for continuous load circuits states that a 100-amp circuit should operate at 80% of its rated load. This means using a 125% rated breaker for load current, a minimum 100-amp breaker, for an 80-amp continuous load circuit. Similarly, the demand factor involves when selecting the wire size for 100A main or subpanel.
- Voltage Drop: Add 20% additional ampacity for every 100 feet to counter voltage drop in long-distance runs (over 50 feet or 15.25 meters) – NEC 310-16.
- Demand Factor: Consider a 35% demand factor for general lighting in load centers and main panels (NEC 220.45).
- Temperature Rating: The ampacity (current-carrying capacity) of the wire depends on the temperature rating of the wire’s insulation.
- Wire Insulation Type: Different insulation types of cables include THHN/THWN, SE (Service Entrance) Cable, SER, XHHW-2, UF-B, MC (Metal Clad) Cable, RHH/RHW-2, Direct-Burial Cable are used with 100A circuit based on the requirements
Correct Wire Size for 100-Amp Subpanel at 100ft
The required wire size in AWG for a 100A breaker in a main panel or subpanel is generally smaller than for a dedicated 100A breaker used with a specific circuit. This is because of the demand factor in the NEC which states all the load points are not operational simultaneously.
For example, the air conditioner runs during the summer while the heater is off, and the opposite occurs in the winter. Similarly, appliances like electric irons, stoves, hair dryers, light bulbs, washing machines, and TVs are rarely used all at once. Hence, less current flows in the circuit. On the other hand, a dedicated circuit may operate at full rated amperes.
For this reason, demand factor mentioned in the NEC 220.42 and 220.45 should be consider while sizing a main panel or selecting the wire size for a subpanel.
NEC 220.14 allows the use of 220.55 and Table 220.55 for calculating branch circuit loads for ranges. Be sure to reference Note 3 in Table 220.55 as well.
For non-continuous loads like water heaters and ranges, calculate the demand for one unit in Column B of Table 220.55 as 80% of the nameplate rating. For example, use 8 kW for calculations if the required load is 10 kW (80% of 10 kW).
In residential applications, calculate general resistive and lighting load circuits using a demand factor of 100% for the first 3 kVA and 35% for the remaining continuous load (as specified in 220.42 and 220.45)
Example:
What is the correct wire size for a 100A main or subpanel service entrance breaker having a distance of 100 ft (30.50 meters)?
Solution:
A 100A circuit can handle up to 24,000 watts of load on a 240V circuit. Applying the continuous, non-continuous, and demand factors. According to NEC Table 220.42 and 220.45, the first 3 kVA of load is rated at 100%, while the remaining load can be rated at a demand factor of 35%, specifically for general lighting loads.
- The first 3 kVA at 100% = 3 kW
- Remaining 24 kVA (24 kVA – 3 kVA) at 35% = 7.35 kW
3kW (at 100% of 24kW) + 7.35kW (at 35% of (24kW – 3kW)) = 10.35 kW
To calculate the current, use Ohm’s Law: I = P ÷ V
Current = 10.35 kW ÷ 240 V = 43.125 A
If the main panel or subpanel is more than 50 ft (15.25 m) away, the NEC recommends adding 20% ampacity for every 100 ft (30.50 m) to account for voltage drop:
43.125 A × 20% = 51.75
To add the safety factor of 80% load on the rated current, i.e. the breaker should be rated at 125%. In other words, no more than 80% of load should be connected to the rated OCPD device. Multiply 1.25 to the calculated value as:
The breaker for this load should be rated at 125%:
× 1.25 = 64.68 A
According to NEC Table 310.16, the suitable wire size for a 100A breaker in the main panel or subpanel is #4 AWG copper or #2 AWG aluminum having a distance of 100 feet (30.5 meter). The suitable ground wire size for 100-Amp service with main or subpanel is #8 AWG copper or #6 AWG aluminum.
Wire Size for 100-Amp Subpanel Based on NEC – 83% Rule
NEC 310.12 states that the ampacity of the service or feeder should not less than the 83% of its rated capacity. Table 310.12(A) in Section 310.12 shows the recommended wire sizes for service and feeder in single-phase dwelling units. Keep in mind that this rule is only applicable for the first service entrance coming in to a dwelling or where the subpanel is supplying power up to 400A to the entire load of a dwelling unit.
Example:
What is the correct Wire size for 100A Service/Feeder for a Main panel or subpanel provided supply to the entire dwelling unit?
Solution:
According to 83% rule in NEC 310-12:
100A x 83% = 83 A
Based on the NEC Table 310.12, the correct wire size for 100A service is #4 AWG Copper or #2 AWG Aluminum.
Wire Size for a 100A Load Circuit
Keep in mind that a 100A breaker in the panel and a 100A dedicated load circuit are different things and require different wire sizes. The total lighting load for the dwelling unit is used to size the feeder circuit that supplies the branch circuits. The NEC mandates that the ampacity of the feeder circuit must be sufficient to carry the total load of all the branch circuits connected to it.
100A Continuous Load
If your total calculated load, for example, is a 100A continuous load circuit, the NEC requires you to rate the OCPD (overcurrent protection device, such as a breaker) at 125% of the minimum wire ampacity for the power circuit. This means you should connect only 80% of the load to the rated fuse or breaker.
Therefore, the required breaker and wire size based on ampacity for a 100A dedicated continuous load circuit is as follows:
Wire Ampacity = 100 Amps × 1.25 = 125 Amps.
Required Wire Size: #1/0 AWG Copper (#3/0 AWG for Aluminum)
In other words, if your continuous load is 100A, you should select a 125A breaker for this dedicated circuit, with #1/0 AWG copper or #3/0 AWG aluminum wire.
100A Non-continuous Load
For a 100A non-continuous load circuit, you can use a 100A breaker, and the appropriate wire size would be #1 AWG copper or 1/0 AWG aluminum, both of which are sufficient for this application.
AWG Table and Chart:
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
Resources:
Wire Sizes for Standard Breakers, Outlet and Branch Circuits
- Wire Size for 15A Breaker and Outlet
- Wire Size for 20A Breaker and Outlet
- Wire Size for 25A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for a 30A Breaker and Outlet
- Wire Size for a 35A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for a 40A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 45A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 50A Breaker and Outlet
- Wire Size for 55A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 60A Breaker and Outlet
- Wire Size for 70A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 80A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 90A Breaker and Load
- Wire Size for 100A Breaker and Load
Sizing Wires for for General Wiring Installations
- What is the Right Wire Size for a 4.8kW, 240V Range: #10 or #12?
- How to Find the Proper Size of Wire & Cable In Metric & Imperial Systems
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker?
- How to Size a Breaker and Wires in AWG with EGC for Load?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Size Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection?
- How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection
- How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?
- How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?
- How to Size Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC)?
- How to Size Motor Starter & Contactor – NEMA & NEC
- How to Size Motor Branch Circuit Conductors and Cables
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panelboard?
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
- How to Size and Find the Numbers of Ceiling Fan in a Room?
- How to Size a Generator? Portable, Backup & Standby for Home & Commercial Applications
- How to Determine the Number of Lighting Branch Circuits?
- How to Determine the Number of Branch Circuits? – 3 Ways
- How to Size a Single Phase and Three Phase Transformer in kVA?
- How to Determine the Suitable Size of Inverter for Home Appliances?
- How to Calculate the Right Size of Solar Charge Controller?
- How to Calculate the Right Size Battery for PV System?
- How to Calculate the Number of Panels for a Load without Battery Backup?
- How to Size Panels, Batteries, Charge Controller and Inverter for PV System in Home
- How to Calculate the Number of Fluorescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Number of Incandescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Battery Charging Time & Battery Charging Current ?
- How to Calculate the Floor Area For General Lighting?
- How to Find the Number of Lights on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Size the Earth Conductor, Earthing Lead & Earth Electrodes?
- How to calculate the Cable size for LT & HT Motors?
- How To Locate Faults In Cables? Cable Faults, Types & Causes
- How To Calculate Your Electricity Bill?
Tools:
- Electrical Cable & Wire Size Calculator for Copper & Aluminum
- Wire & Cable Size in AWG Calculator for 1 and 3-Phase Load
- American Wire Gauge “AWG” Chart – Wire Size & Ampacity Table
- American Wire Gauge (AWG) Calculator – AWG Size Chart & Table
- Standard Wire Gauge “SWG” Calculator – SWG Size Chart & Table
- AWG/SWG to mm/mm2, inch/inch2 & kcmil Calculator & Conversion
General Wiring Installations:
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Wire Single-Phase, 230V Consumer Unit with RCD?
- How to Wire a Garage Consumer Unit?
- How to Connect a Portable Generator to the Home Supply – 4 Methods
- How to Connect Automatic UPS / Inverter to the Home Supply System?
- How to Wire an Outlet Receptacle? Socket Outlet Wiring Diagrams
- How To: Electrical & Electronics Tutorials
- Basic Electrical Wiring Installation Tutorials