How to Wire a 50A – 250V, NEMA 6-50 Receptacle
How to Install NEMA 6-50 (50A – 250V) Industrial Grade Receptacles with 2-P GFCI and Standard Breakers for EVs and RVs?
A NEMA 6-50R is a heavy-duty electrical receptacle designed for high-power appliances. It is commonly used for welders, plasma cutters, electric ranges and ovens, heaters, generators, RVs, and some electric vehicle (EV) charging systems. It has two “hot” slots for 250V power and a round ground slot but no neutral wire. It means, 6-50R is incompatible with devices that require a 120V neutral connection.
The NEMA 6-50 is a 2P, 3W receptacle rated for 50 amps at 250V, single-phase power. For continuous loads operating for extended periods, an industrial-grade 50-amp outlet is recommended. These outlets are ideal for high-wattage residential equipment, industrial welding applications, Level 2 EV charging, and large machinery.
In this wiring guide, we will explain how to properly wire a NEMA 6-50 receptacle using both standard and GFCI breakers. We will also cover the correct breaker and wire sizes used with 50-amp receptacle for high-wattage applications and EV charging installations.
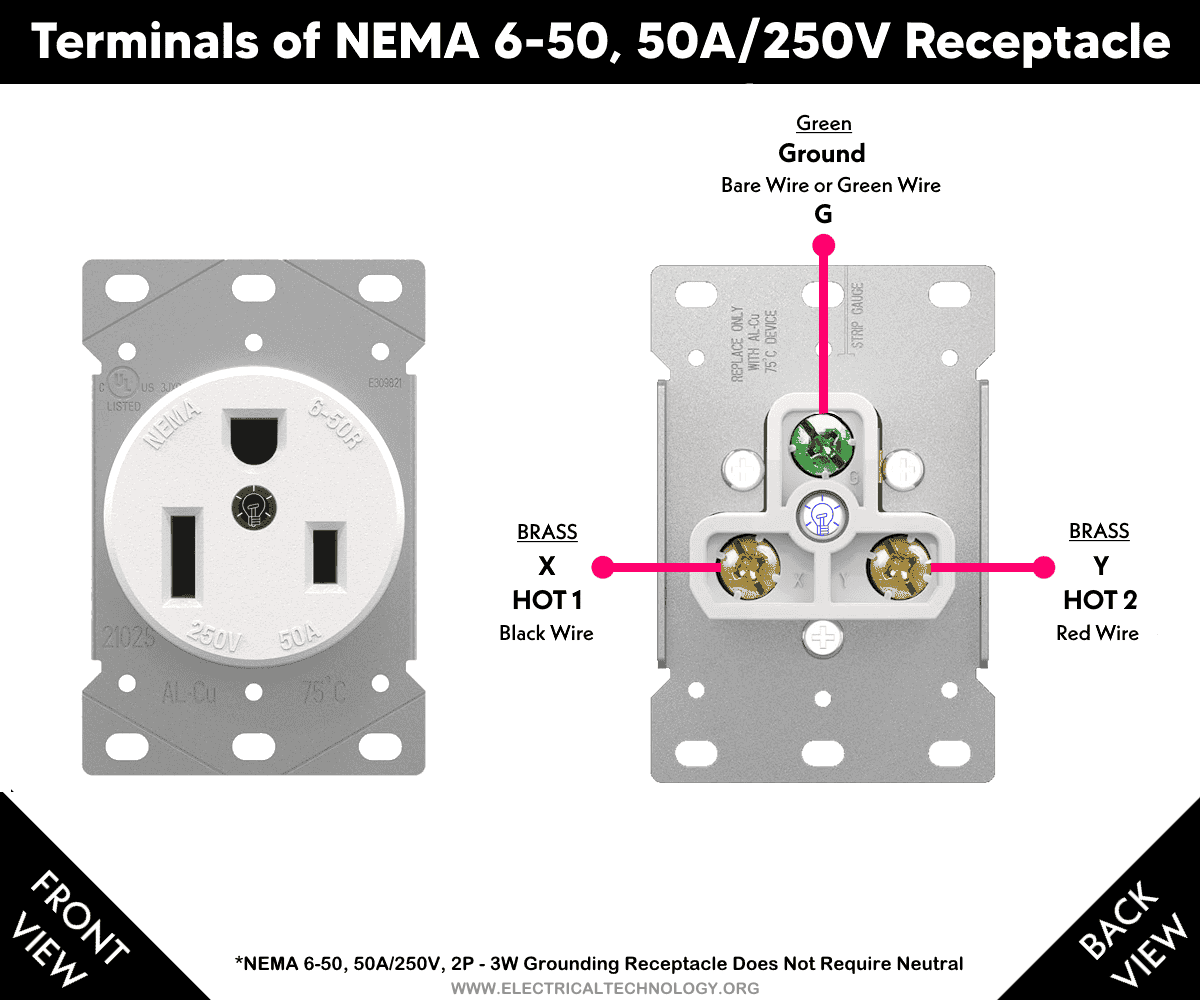
The NEMA 6-50 Receptacle
The NEMA 6-50R is a 50-amp, 250V receptacle with two hot wires and a grounding wire, designed to be used with a matching NEMA 6-50P plug. The “50” in 6-50R indicates the maximum current rating in amperes, while the “R” stands for “Receptacle” (outlet). Similarly, the “P” in NEMA 6-50P stands for “Plug,” with “50” indicating its maximum current rating.
The NEMA 6-50 has a 2-pole, 3-wire configuration, which means it does not require a neutral wire. It includes two hot slots (Hot 1 and Hot 2) and one grounding slot for the equipment grounding conductor (EGC).
Terminals
There are four terminals in a 6-50R receptacle:
- G Terminal (Green Screw): Connects to the Bare or Green Wire – Grounding Wire (EGC)
- X Terminal (Brass Screw): Connects to Black Wire – HOT 1 (Line 1)
- Y Terminal (Brass Screw): Connects to Red Wire – HOT 2 (Line 2)
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
Electrical Ratings & Specifications
- Poles: 2-Pole, 3-Wire – Grounding – No Neutral
- Voltage: 250V Single-Phase AC Supply – 60 Hz
- Breaker / GFCI: 50A
- Current: 40A – 50A
- Wattage: 12,000 W
- Wire Size: #6 AWG (Copper Only)
- Temp. Rating: -40°C to 75°C (-40°F to 167°F)
- Dielectric-strength: Withstand 2,000V Min.
- Grade & Material: Industrial Grade – Thermoplastic/Composite, Nylon & Galvanized Steel
- Mounting: Flush / Screw Mounting
- Outdoor Box: 2-gang outdoor box – NEMA 3R rainproof enclosure
- Wiring: Hardwired / Dedicated Circuit
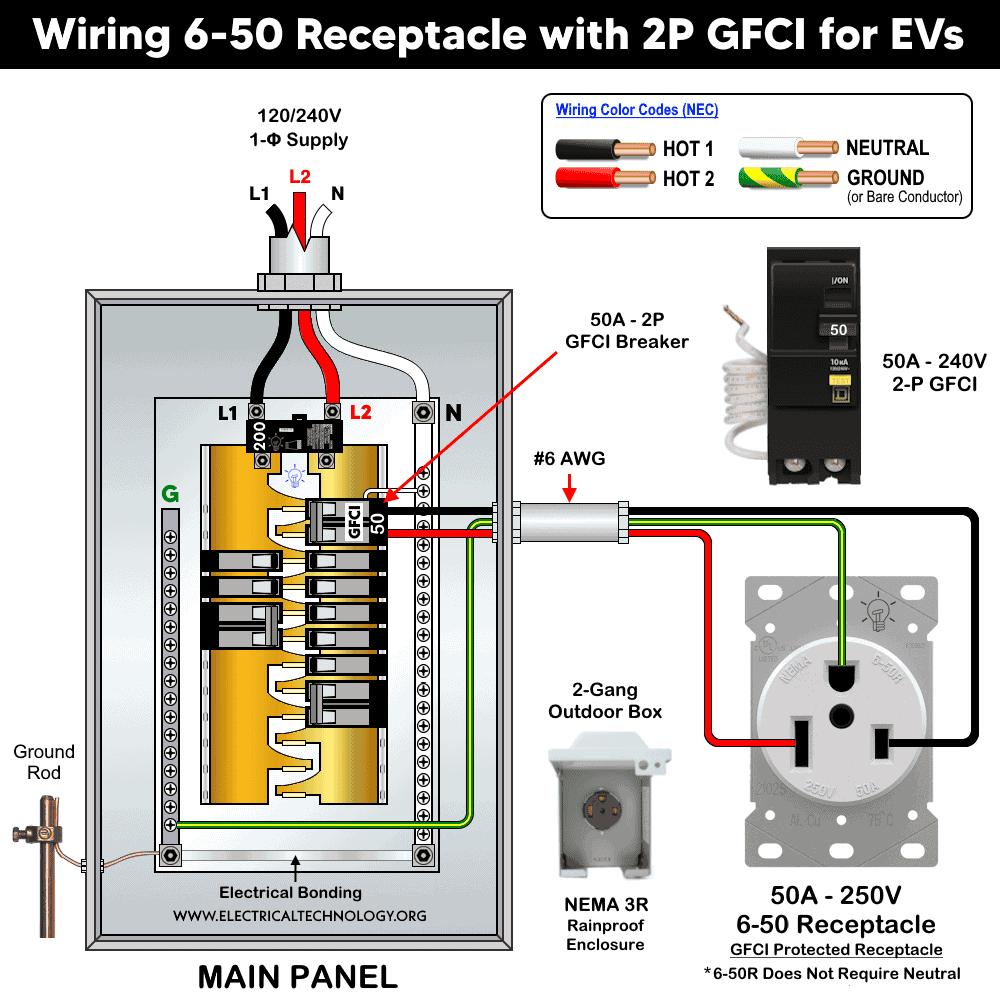
Wiring NEMA 6-50 Receptacle with a 2P GFCI
A NEMA 6-50 can be installed as either a plug-in or a hardwired connection for EV charging applications. If ground-fault protection is not already built into the EVSE (charger), the NEMA 6-50 must be protected by a 2-pole GFCI breaker to ensure safety.
As shown in the wiring diagram, connect Hot 1 (black) and Hot 2 (red) from the 2-pole, 50A GFCI breaker to the X and Y terminals of the NEMA 6-50 receptacle. Then, connect the ground wire (bare copper or green/yellow) to the G terminal. For proper operation, make sure to connect the white pigtail wire from the GFCI to the neutral bus bar in the 120/240V or 208/240V main panel.
Although the NEMA 6-50 receptacle can accept wire sizes ranging from #12 AWG to #4 AWG, #6 AWG copper conductors are recommended for a 50A circuit and associated 6-50R outlet.
For outdoor installations, use a NEMA 3R weatherproof (rainproof) 2-gang enclosure to protect the receptacle from moisture and environmental exposure.
The wiring diagram below illustrates the proper installation of a NEMA 6-50R, 50-amp heavy-duty receptacle using a 2-pole, 50A GFCI breaker.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
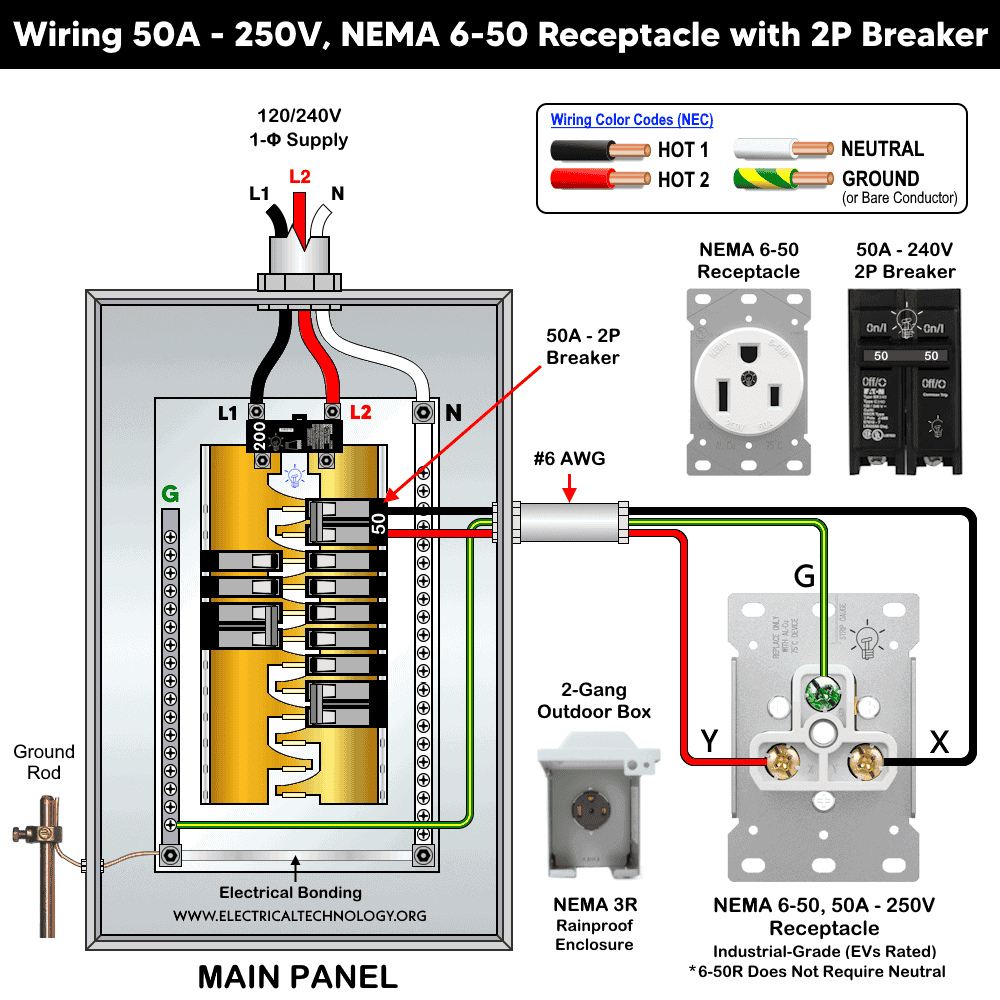
Wiring NEMA 6-50 Receptacle with a 2P Breaker
The wiring configuration for a NEMA 6-50 receptacle with a 50A, 2-pole standard breaker is identical to that used with a 2-pole GFCI breaker.
Using a standard breaker can help prevent nuisance tripping, particularly when the EV charger already includes built-in GFCI protection (as is the case with most modern EVSE units).
The wiring diagram below shows how to properly connect a NEMA 6-50, 50-amp receptacle using a 2-pole, 50A standard breaker for EV charging, RVs or other high-power appliances.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
FAQs:
Should I Use a GFCI or Standard Breaker with NEMA 6-50 Receptacle?
For most modern EV chargers (EVSE), a standard 2-pole, 50A breaker is recommended with a NEMA 6-50R receptacle (unless your local electrical code specifically mandates GFCI protection). Many EVSE units already include built-in GFCI protection, and adding a GFCI breaker in series can lead to nuisance tripping.
If GFCI protection is required (such as in garages or outdoor installations), use a 2-pole, 50A GFCI breaker.
As per code:
- NEC 210.8(A) and (B): Requires GFCI protection for all 125–250V receptacles rated up to 50A that are installed in garages, outdoors, and other specified locations.
- NEC 625.54: Requires ground-fault protection for personnel for all electric vehicle supply equipment (EVSE).
Options When Following NEC 2023 (instead of older versions):
- Install a GFCI breaker upstream of the NEMA 6-50 receptacle to safely use a mobile connector and plug-in adapters.
- Replace the receptacle with a disconnect switch and hardwire the EVSE, eliminating the need for a GFCI breaker if the EVSE has built-in protection.
In short:
- Use a GFCI breaker for plug-in EVSE where required by NEC or local code.
- Use a standard breaker for hardwired EVSE or when the charger has internal ground-fault circuit interrupter (GFCI) protection and local code allows.
How Many Amps Can 50A, 6-50 Receptacle Handle Safely?
A NEMA 6-50 receptacle is rated for a maximum of 50 amps. For continuous loads (defined by the NEC as 3 hours or more, such as EV charging), the circuit must be derated to 80% of the breaker rating. This requirement, commonly called the 125% rule, is specified in NEC 210.19(A)(1) and 210.20(A).
- Continuous Load: 50A × 80% = 40A maximum continuous load
- Non-Continuous Load: Full 50A rating
An industrial-grade 50-amp receptacle, however, is specifically designed to safely handle a full 50A continuous load for extended periods without overheating or premature failure.
These ratings comply with:
- NEC 210.19(A)(1), 215.2, and 230.42(A) – Conductor and circuit sizing for continuous and non-continuous loads
- NEC 110.14(C) – Considerations for conductor temperature rating and termination.
How Many Watts Can a 50A, 6-50 Receptacle Hold?
At 240V, a 50A outlet can supply:
- Maximum: 50A × 240V = 12,000 watts
- Continuous load (80% rule): 40A × 240V = 9,600 Watts
Which Breaker Size is Suitable for 6-50 Receptacle?
For continuous loads, the 80% rule applies (meaning only 80% of the breaker rating should be used for loads) running 3 hours or more. In addition, the overcurrent protection device (OCPD), such as a fuse or circuit breaker, must be sized to handle 125% of the continuous load.
- Continuous Load: 40A × 125% = 50A breaker required
- Non-Continuous Load: Up to the full 50A rating is permitted
According to NEC 210.19(A)(1), 210.20(A), Table 210.21(B)(3), and 210.23(D), the appropriate breaker size for a 50A outlet (NEMA 6-50) is a 2-pole, 50A breaker or GFCI breaker rated for 240V single-phase circuits.
What is the Correct Wire Size and Cable Type to Use with NEMA 6-50R?
As mentioned earlier, a 50-amp outlet can be used for 40A continuous loads and up to 50A for non-continuous loads. An industrial-grade receptacle can safely handle a full 50A continuous load for extended periods.
For this ampacity, #6 AWG copper conductors are recommended. According to NEC Table 310.16 and CEC Table 2, #6 AWG copper can carry:
- 55A at 60 °C (140 °F)
- 65A at 75 °C (167 °F)
- 75A at 90 °C (194 °F)
This makes #6 AWG copper a suitable wire size for a NEMA 6-50 outlet – Based on NEC Table 310.16) and CEC Table 2.
Similarly, for a circuit protected by a 50A overcurrent protection device (OCPD), the equipment grounding conductor (EGC) can be #10 AWG copper, in accordance with NEC Table 250.122.
Cable Type:
- Indoor, fixed branch circuit (most homes): use #6/3 with ground NM-B (6-3-1)
- Conduit or long runs / outdoor / exposed: run individual THHN/THWN conductors or MC / SER
- Direct-burial / underground: UF-B or THHN
- EGC (Ground Wire): Min #10 AWG
Can You Install NEMA 6-50R in 120V AC Circuit?
No! you cannot install a NEMA 6-50R receptacle on a 120 V circuit.
The NEMA 6 series (6-15, 6-20, 6-30, 6-50, etc.) is specifically designed for 250 V loads. The two hot blades deliver 250 V phase-to-phase with no neutral connection, and the U-shaped pin is ground.
A 120 V circuit needs one hot, one neutral, and a ground. The 6-50R does not have a neutral slot as it is a 3-wire device (Hot-Hot-Ground). If you wired it to a single hot and neutral for 120 V (as technically possible), it would be unsafe and a code violation of NEC 406.4(A) & 406.4(A). Moreover, plugging a 250V appliance into a receptacle wired for 120V will result in malfunction, overheating, or equipment damage.
If you need a 120V outlet with a similar current capacity, use the correct NEMA configuration i.e. NEMA 5-50R (50A, 120V – rare, but available).
Instructions, Precautions & Codes
- If the primary purpose of the 6-50R outlet is EV charging, install an industrial-grade, EV-rated receptacle.
- Hardwiring is generally recommended over a plug-in 50A receptacle for EV charging. This minimizes heat buildup at the receptacle and ensures a more secure connection.
- The 6-50R should not be installed in a single-gang wall box. Instead, use a 2-gang outdoor-rated box with a NEMA 3R weatherproof (rainproof) enclosure for outdoor applications.
- According to NEC Table – 310.16 and 210.24(1), the correct breaker and wire size for a 50A, 240V 6-50R outlet is 2-pole, 50A breaker / GFCI With #6 AWG copper conductors for branch circuit. For runs longer than 50 ft (15.25 m), consider upsizing to a larger wire gauge to reduce voltage drop.
- A standard 50A receptacle can supply 40A continuous load and up to 50A for non-continuous loads, per NEC 210.19(A), 215.2, and 230.42(A). However, industrial-grade 6-50R devices are designed to safely handle a 50A continuous load for extended periods.
- It is a code violation to connect a 50A receptacle to a 40A breaker.
- It is a code violation to use undersized wire (e.g., #10 or #12 AWG) on a 50A breaker.
- For long runs (100 ft / 30.5 m or more), NEC recommends adjusting for voltage drop. Add 20% additional ampacity for every 100 ft, and consider ambient temperature corrections per NEC 110.14(C), 310.15(B)(2), and 310.16.
- For EV charging, a 50A, 240V outlet must be installed on a dedicated circuit per NEC 625.41.
Resources:
Related Wiring Tutorials
NEMA Family Outlets/Receptacle Wiring
NEMA 5 -Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 120V NEMA 5-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 120V – NEMA 5-50 Receptacle
NEMA 6-Series
- How to Wire a 15A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 240V – NEMA 6-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 240V – NEMA 6-50 Receptacle … (You are Here)
NEMA 10-Series
- How to Replace a 20A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-20R?
- How to Replace a 30A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-30R?
- How to Replace a 50A – 120/240V Outlet – NEMA 10-50R?
NEMA 14-Series
- How to Wire a 20A – 125/250V NEMA 14-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125/250V NEMA 14-30 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 125/250V NEMA 14-50 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 60A – 125/250V – NEMA 14-60 Receptacle
NEMA General Outlets/Receptacle
- How to Replace a 15A – 125V Outlet – NEMA 1-15 Receptacle
- How to Replace a 20A – 250V Outlet – NEMA 2-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 30A – 125V, NEMA TT-30 Receptacle for RVs
General Wiring Installations:
- How to Size a Breaker and Wires in AWG with EGC for Load?
- How to Wire an Outlet Receptacle? Socket Outlet Wiring Diagrams
- How to a Wire 3-Way Combination Switch and Grounded Outlet?
- How to Wire Combo Switch and Outlet? – Switch/Outlet Combo Wiring Diagrams
- How to Wire 120V & 240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- How to Wire 277V & 480V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase, Commercial Main Service Panel?
- How to Wire 240V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Continuous?
- How to Wire 3-Phase Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
- How to Wire ST01 Timer with Relay & Contactor for 120V/240V Motors?
- How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
Switches Wiring
- How to Wire Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) as 2-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) as 3-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Double Pole, Single Throw Switch? Wiring DPST
- How to Wire Double Pole, Double Throw Switch? Wiring DPDT
- How to Wire Double Switch? 2-Gang, 1-Way Switch – IEC & NEC
- How to Wire 4-Way Switch (NEC) or Intermediate Switch as 3-Way (IEC)?
GFCI/AFCI Breaker/Outlet Wiring
- How to Wire a GFCI Circuit Breaker?
- How to wire a GFCI Outlet?
- How to Wire GFCI Combo Switch and Outlet – GFCI Switch/Outlet
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker?
- How to Wire an AFCI Outlet?
Related Posts:
- What is the Right Wire Size for 50A Breaker and Outlet?
- What is the Difference Between 15-Amp and 20-Amp Outlet?
- Difference Between Socket, Outlet and Receptacle
- Difference Between NEMA 14-50 Standard Vs EV Receptacle
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- Can you use 15A Breaker on 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You use a 15A Outlet on a 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Ground Terminal Up or Down: Which Way Should Outlets Face?
- What Do the Green Dot or Orange Triangle Outlets Mean?
- What Do the Different Colors of Electrical Outlets Indicate?
- Why are Outlets and Receptacles in Hospitals Upside Down?
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panelboard?
- How to Find the Proper Size of Circuit Breaker? Breaker Size Calculator & Examples
- How to Find The Suitable Size of Cable & Wire for Electrical Wiring Installation?
- Why is the Neutral Prong or Slot Wider on a Plug or Outlet?
- What Will Happen If You Connect a Male-to-Male Plug Between Outlets