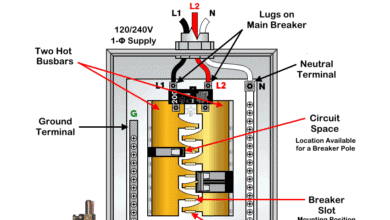
How to Wire a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
How to Install a 1-P, 15A – 120V GFCI Breaker for Branch Circuits
1-Pole GFCI Breaker
A single-pole GFCI (Ground-Fault Circuit Interrupter) breaker is a protective device designed to provide both overcurrent protection and ground-fault protection for 120V branch circuits. Unlike a standard single-pole breaker, a GFCI breaker continuously monitors the current balance between the hot (ungrounded) conductor and the neutral (grounded) conductor. If an imbalance exceeding 4–6 mA is detected, it indicates current leakage to ground, hence the GFCI breaker trips instantly to reduce the risk of electric shock and fire hazard.
1-pole GFCI breakers are commonly installed in 120/240V split-phase panels to protect circuits supplying receptacles or equipment in wet, damp, or hazardous locations such as bathrooms, kitchens, garages, outdoors, basements, laundry areas, and similar locations mandated by the National Electrical Code (NEC).
A GFCI breaker differs from a standard breaker. It protects one 120V hot conductor (supplied either from Hot 1 or Hot 2) and offer protection against ground faults and overcurrent.
A 1-P GFCI requires a neutral connection to the breaker, that’s why it includes a built-in white pigtail neutral wire which connects to the neutral busbar in the main panel. Similarly, the load side neutral is connected to the GFCI, not to the neutral busbar in the main panel. This way, a GFCI protects the entire branch circuit, not just individual receptacles. In short, a GFCI provides both overcurrent (like ordinary breaker) and ground-fault protection against electric shock hazards.
Characteristics:
- Number of Poles: 1-pole – connects to one line (either L1 or L2), i.e. one hot conductor (black or red).
- Voltage: Operates on and protects 120V branch circuits. (Line-to-Neutral).
- Amperage Rating: Commonly available in 15A, 20A, 25A and 30A.
- Wiring: The hot and neutral conductors from the GFCI breaker, along with Ground wire from the ground busbar, connect to the 120V branch-circuit load. The built-in white pigtail on the GFCI breaker always connects to the neutral busbar.
- Operation: Trips when it detects leakage current between Line to Neutral or there is an overload, short circuit, or fault on the single hot (or phase) wire.
- Application: As per NEC requirement – mostly used for standard lighting, outlets, receptacles, sockets and small appliances in outdoor and wet locations.
NEC Requirements for GFCI Protection:
NEC 210.8(A) requires GFCI protection for 125/250V, single-phase, 15 and 20-amp receptacles in specified locations including bathrooms, garages, outdoors, basements, kitchens, laundry areas, spas, hot tub and similar spaces.
As per 210.8(A), for dwelling and non-dwelling units, all 120/240V outlets and receptacles installed in the locations specified in 210.8(A)(1) through (A)(11) and supplied by single-phase branch circuits rated 150V or less to ground shall have GFCI protection.
GFCI protection is required for various applications in compliance with the following NEC Articles: 210.8, 406.3, 424.44, 426.28, 427.22, 511.12, 517.17, 517.20, 525.23, 530.44, 547.28, 555.35, 620.6, 625.54, 680.5, 680.21, 680.22, 680.23, 680.27, 680.32, 680.43, 680.44, 680.51 through 680.59, 680.62, and 680.71.
Wiring a Single-Pole GFCI Breaker in a 120/240V Panel
To replace or install a new 1-P GFCI breaker in a 120/240V main panel, follow the following step by step wiring guide.
- Turn Off Power: Switch OFF the main breaker supplying the panel. Confirm with a voltage tester that the bus bars are de-energized (except the service lugs prior to the main switch).
- Snap the new GFCI breaker firmly onto the panel bus bar (either on L1 or L2). If replacing with a standard breaker, use the exact slot used for the previous circuit breaker.
- Identify the following branch circuit conductors:
-
- Hot conductor (Black or Red)
- Neutral conductor (White)
- Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC) – Green/Bare conductor as Grounding wire
- GFCI breaker factory-attached pigtail (to be connected to the neutral busbar)
- Connect Load Side Conductors as follow:
-
- Insert the branch-circuit hot wire (black) into the breaker’s LOAD terminal.
- Insert the branch-circuit neutral (white) into the neutral terminal on the GFCI breaker.
- Terminate the breaker’s white pigtail to the neutral bus bar in the panel
- Terminate the bare or green grounding conductor to the grounding bus bar.
- Restore Power and Test/Reset the Breaker as follow:
- Replace the panel cover and Turn ON the main breaker as well as newly installed GFCI breaker.
- Press the TEST button on the breaker to verify proper operation. Reset the breaker after testing.
- Restore Power and Test/Reset the Breaker as follow:
- Replace the panel cover and Turn ON the main breaker as well as newly installed GFCI breaker.
- Press the TEST button on the breaker to verify proper operation. Reset the breaker after testing.
In the example wiring diagram, a 15A/120V, 1-P GFCI breaker is wired to protect a 15A – 125V receptacle (NEMA 5-15). As per NEC Table 310.16, the suitable size for a 15A circuit and the associated NEMA 5-15R outlet is #14 AWG. The same wire size i.e. #14AWG should be used for equipment ground conductor (EGC) per NEC Table 250.122.
Click image or open in a new tab to enlarge
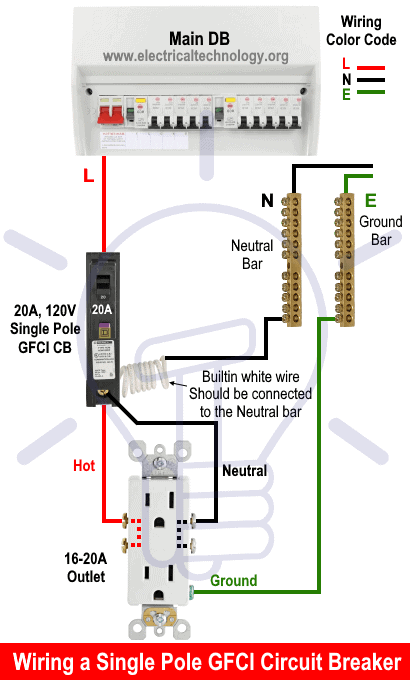
Similarly, the following wiring diagram shows a 20A/120V 1-Pole GFCI breaker wired with a 20A – 125V receptacle (NEMA 5-20) outlet.
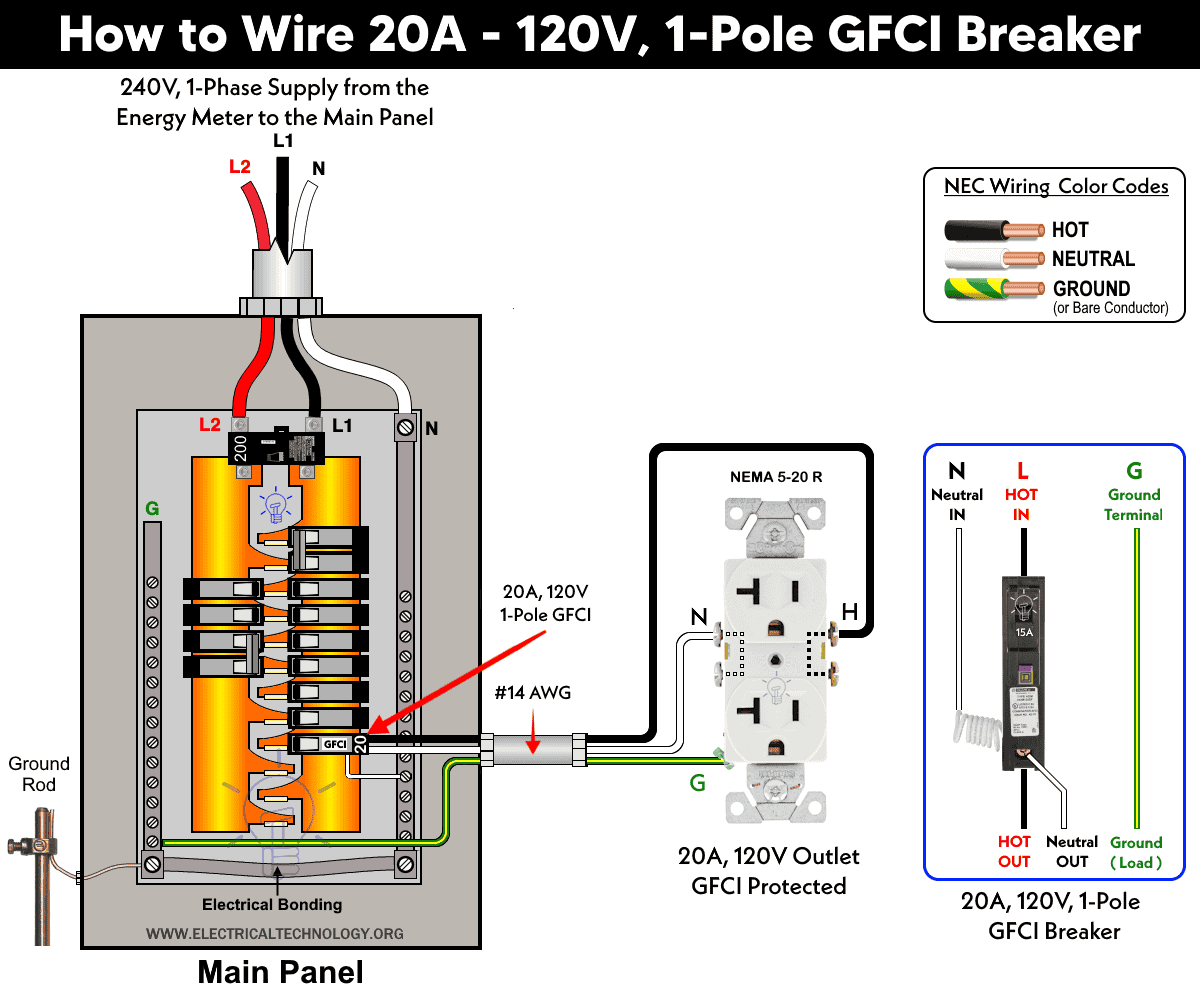
Expect the 15/20A outlets and receptacles, a single-pole GFCI breaker can be wired for different ratings and NEMA outlets used in 120V supply systems such as.
- Wiring a 1-pole GFCI breaker for 15A outlet
- Wiring a 1-pole GFCI breaker for 15A, 20A and 30A GFCI outlets
- Wiring a 1-pole GFCI breaker for 20A outlet
- Wiring a 1-pole GFCI breaker for 30A receptacle
- Wiring a 1-pole GFCI breaker for 30A TT-30 receptacle (Used with Travel Trailers & RVs)
Instructions, Precautions & Codes
- As per NEC Table – 310.16, Table – 210.24(1) and NEC 240.4(D)(4), the suitable wire size is 14 AWG copper (or #12 AWG aluminum) to use with a 15A outlet and protected by a 15/120V GFCI/Breaker.
- As per NEC Table 250.122, use the same #14 AWG copper for ground (EGC) wire size.
- The correct size of breaker is 1-pole, 15A circuit breaker or GFCI for a 15A-125V outlet – NEC 210.21(B)(2).
- For a 1-pole, 15A GFCI circuit, you may use NM-B (Romex) for indoor and dry locations, UF-B for outdoor or underground runs, and THHN/THWN conductors when installed in conduit.
- A single-pole 15A GFCI/breaker can be used for 12A continuous load (which lasts 3 or more hours) and maximum 15A non-continuous load – 210.19(A), 210.20(A), 215.2(A), 215.3, and 230.42(A).
- A 1-pole, 15-amp breaker/GFCI at 120 volt can handle non-continuous load of 1,800 watts (15A × 120V). For continuous use, limit the load to about 1,440 watts (80% of 1,800W).
- Do not use 20A outlet on 15A circuit breaker. If more than one receptacle on the same circuit, you may allowed to use 15A outlet on 20A circuit breaker. In other words, It is code to use 15A outlet on 20A breaker (NEC 210.21(B)(2)), but it is not allowed to use 20A outlet on 15A breaker.
Resources:
Standard Breakers & GFCI Breakers Wiring Installations
- How to Wire a 1-Pole GFCI … You are Here
- How to Wire a 2-Pole GFCI
- How to Wire a 3-Phase, 3-Pole GFCI
- How to Wire a 1-Pole Breaker
- How to Wire a 2-Pole Breaker
- How to Wire a 3-Pole Breaker
- How to Wire a Tandem Breaker
- How to Wire GFCI Circuit Breakers
- How to Wire an AFCI Breaker
Sizing Breakers, Wires, and Panels
- How to Size a Circuit Breaker?
- How to Size a Breaker and Wires in AWG with EGC for Load?
- How to Find the Proper Size of Wire & Cable In Metric & Imperial Systems
- How to Size a Load Center, Panelboards and Distribution Board?
- How to Determine the Right Size Capacity of a Subpanel?
- How to Find the Right Wire Size for 100A Service 120V/240V Panel?
- How to Size Service-Entrance Conductors and Feeder Cables?
- How to Size Feeder Conductors with Overcurrent Protection
- How to Size a Branch Circuit Conductors with Protection?
- How to Size Equipment Grounding Conductor (EGC)?
- How to Size Grounding Electrode Conductor (GEC)?
- How to Size Motors FLC, HP, Voltage, Breaker Size and Wire Size
- What is the Correct Wire Size for 100A Breaker and Load?
- What is the Right Wire Size for 15A Breaker and Outlet?
- What is the Suitable Wire Size for 20A Breaker and Outlet?
General Outlets and GFCI/AFCI Receptacles Wiring
- How to Wire an Outlet Receptacle? Socket Outlet Wiring Diagrams
- How to wire a GFCI Outlet?
- How to Wire GFCI Combo Switch and Outlet
- How to Wire an AFCI Combo Switch
- How to Wire an AFCI Outlet?
- How to a Wire 3-Way Combination Switch and Grounded Outlet?
- How to Wire Combo Switch and Outlet? – Switch/Outlet Combo Wiring Diagrams
- How to Wire a 15A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 120V Outlet – NEMA 5-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 15A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-15 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 20A – 240V Outlet – NEMA 6-20 Receptacle
- How to Wire a 50A – 125/250V Outlet – NEMA 14-50 Receptacle
Switches Wiring
- How to Wire Single Pole, Single Throw (SPST) as 2-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Single Pole, Double Throw (SPDT) as 3-Way Switch?
- How to Wire Double Pole, Single Throw Switch? Wiring DPST
- How to Wire Double Pole, Double Throw Switch? Wiring DPDT
- How to Wire Double Switch? 2-Gang, 1-Way Switch – IEC & NEC
- How to Wire 4-Way Switch (NEC) or Intermediate Switch as 3-Way (IEC)?
- How to Wire Auto & Manual Changeover & Transfer Switch – (1 & 3 Phase)
Finding the Number of Breakers/Outlets in a Circuit
- How to Determine the Number of Circuit Breakers in a Panelboard?
- How to Find the Number of Outlets on a Single Circuit Breaker?
- How to Find Voltage & Ampere Rating of Switch, Plug, Outlet & Receptacle
- How to Calculate the Number of Fluorescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Calculate the Number of Incandescent Lamps in a Final Sub Circuit?
- How to Determine the Number of Lighting Branch Circuits?
- How to Determine the Number of Branch Circuits? – 3 Ways
- How to Find the Number of Lights on a Single Circuit Breaker?
Main Panels Wiring Tutorials
- How to Wire 120V/240V Main Panel? Breaker Box Installation
- How to Wire 208V/120V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase Main Panel?
- How to Wire 240V, 208V & 120V, 1 & 3-Phase, High Leg Delta Main Panel?
- How to Wire 277V/480V, 1-Phase & 3-Phase Main Service Panel?
- How to Wire a Subpanel? Main Lug Installation for 120V/240V
- Single Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home according to NEC & IEC
- Three Phase Electrical Wiring Installation in Home – NEC & IEC
- How To Wire a Single Phase kWh Meter – 120V/240V
- How to Wire a Three-Phase Meter? 120/208/240/277/347/480/600V
General Wiring Installation Tutorials:
- How to Toggle Electric Water Heater Between 120V and 240V?
- How to Wire 120V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Simultaneous?
- How to Wire 240V Water Heater Thermostat – Non-Continuous?
- How to Wire 3-Phase Simultaneous Water Heater Thermostat?
- How to Wire Twin Timer for 120V/240V Circuits – ON/OFF Delay
- How to Wire ST01 Timer with Relay & Contactor for 120V/240V Motors?
- How to Wire Multifunction ON/OFF Delay Timer for 120V/240V Motors?
- Even More Residential Wiring Installation Tutorials
Related Posts:
- Difference Between Circuit Breaker and GFCI
- Difference Between 1-Pole and 2-Pole Breakers – NEC & IEC
- Should GFCI Protection Be in the Main Panel or Receptacle?
- How Does a Standard Breaker Respond to Electrical Fault?
- Why Doesn’t a Standard Breaker Protract Against Ground Faults?
- How Do GFCI and Standard Breakers Respond to Ground Faults?
- Can you use 15A Breaker on 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can I Use a 1-Phase Breaker on a 3-Phase Supply & Vice Versa?
- Can I Use a 240V Breaker on a 120V Circuit and Vice Versa?
- Can You use a 15A Outlet on a 20A Circuit and Vice Versa?